International Relations
India-Russia Trade
- 25 Oct 2022
- 9 min read
Why in News?
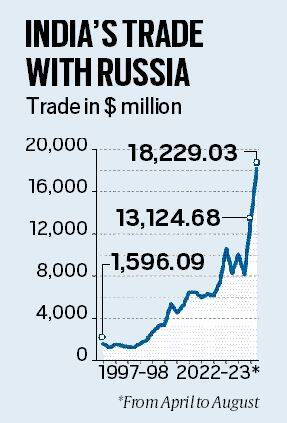
Recently, the Ministry of Commerce and Industry has released data showing that India’s bilateral trade with Russia has soared to an all-time high of USD 18,229.03 million in just five months (April-August) of FY 2022-23.
What are the Findings?
- Overview:
- The total annual bilateral trade between the two countries stood at USD 13,124.68 million in 2021-22, and USD 8,141.26 million in 2020-21.
- Pre-Covid, it was USD 10,110.68 million in 2019-20, USD 8,229.91 million in 2018-19, and USD 10,686.85 million in 2017-18.
- Russia has now become India’s seventh biggest trading partner — up from its 25th position last year.
- The US, China, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Iraq and Indonesia were the six countries which recorded higher volumes of trade with India during the first five months of 2022-23.
- Of the total USD 18,229.03, India’s imports from Russia accounted for USD 17,236.29 million, while India’s exports to Moscow were only worth USD 992.73 million, leaving a negative trade balance of USD 16,243.56 million.
- An analysis of the data shows that Russia’s share in India’s total trade has increased to 3.54%, up from 1.27% in 2021-22. While Russia’s share in India’s total trade was 2.1% in 1997-98, it has hovered below 2% for the last 25 years.
- The total annual bilateral trade between the two countries stood at USD 13,124.68 million in 2021-22, and USD 8,141.26 million in 2020-21.
- Drivers:
- It is mainly due to a sudden jump in imports from Russia, mainly oil and fertilisers, which began to surge earlier in 2022.
- There was an over 500% increase in three months – 561.1% in June, 577.63% in July and 642.68% in August – as compared to the same months of the previous year.
- Petroleum oil and other fuel items (mineral fuels, mineral oils and products of their distillation; bituminous substances; mineral waxes) accounted for 84% of India’s total imports from Russia.
- Fertilizers were second, fertilisers and fuel together account for over 91% of the total imports from Russia this year.
- It is mainly due to a sudden jump in imports from Russia, mainly oil and fertilisers, which began to surge earlier in 2022.
What are the Different Aspects of Indo-Russia Relations?
- Historical Background:
- During the Cold War, India and the Soviet Union had a strong strategic, military, economic and diplomatic relationship. After the Dissolution of the Soviet Union, Russia inherited its close relationship with India which resulted in both nations sharing a Special Strategic Relation.
- However, the relations have taken a steep downfall over the past few years, especially in the post-Covid scenario. One of the biggest causes for this is Russia’s close relations with China and Pakistan, which have caused many geopolitical issues in the past few years for India.
- Political Relations:
- In 2019, Russia signed the Executive Order on awarding PM Narendra Modi Russia’s highest state decoration – The order of St Andrew the Apostle. The order was presented to PM for his distinguished contribution to the development of a privileged strategic partnership between Russia and India and friendly ties between the Russian and Indian peoples
- Two Inter-Governmental Commissions – one on Trade, Economic, Scientific, Technological and Cultural Cooperation (IRIGC-TEC), and another on Military-Technical Cooperation (IRIGC- MTC), meet annually.
- Trade Relations:
- The two countries intend to increase bilateral investment to USD 50 billion and bilateral trade to USD 30 billion by 2025.
- Defence and Security Relations:
- Both countries regularly conduct the Tri-Services exercise ‘INDRA‘.
- The joint military programmes between India and Russia include:
- BrahMos cruise missile programme
- 5th generation fighter jet programme
- Sukhoi Su-30MKI programme
- Ilyushin/HAL Tactical Transport Aircraft
- KA-226T twin-engine utility helicopters
- some frigates
- The military hardware purchased/leased by India from Russia includes:
- S-400 Triumf
- Kamov Ka-226 200 to be made in India under the Make in India initiative
- T-90S Bhishma
- INS Vikramaditya aircraft carrier programme.
- Nuclear Relations:
- Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant (KKNPP) is being constructed within the scope of the Russia-India Inter-Governmental Agreement.
- Both India and Russia are implementing Rooppur Nuclear Power Project in Bangladesh.
What is the Significance of Russia for India?
- Balancing China:
- The Chinese aggression in the border areas of eastern Ladakh, brought India-China relations to an inflection point, but also demonstrated that Russia can contribute to defusing tensions with China.
- Russia organized a trilateral meeting among the foreign ministers of Russia, India, and China following deadly clashes in the Galwan Valley in the disputed territory of Ladakh.
- Emerging New Sectors of Economic Engagement:
- Apart from traditional areas of cooperation such as weapons, hydrocarbons, nuclear energy, and diamonds, new sectors of economic engagement are likely to emerge — mining, agro-industrial, and high technology, including robotics, nanotech, and biotech.
- India’s footprint in the Russian Far East and in the Arctic is set to expand. Connectivity projects may get a boost too.
- Combating Terrorism:
- India and Russia are working to close the gap on Afghanistan and are calling for early finalization of the Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism.
- Support At Multilateral Forums:
- Additionally, Russia supports India’s candidacy for permanent membership of a reformed United Nations Security Council and of the Nuclear Suppliers Group.
- Russia’s Military Exports:
- Russia has been one of the largest arms exporters to India. Even as Russia’s share in India’s arms imports fell by over 50% in the last five-year period compared to the previous five years (2011–2015).
- In the last 20 years, India imported arms and weapons worth USD 35 billion from Russia, according to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute which tracks global arms trade.
Way Forward
- Russia will remain a key defense partner for India for decades to come.
- On the other hand, Russia and China are currently in a quasi-alliance setup. Russia repeatedly reiterates that it does not see itself as anybody’s junior partner. That’s why Russia wants India to act as a balancer.
- The two countries have been discussing how they can cooperate in using India as a production base for exporting to third countries Russian-origin equipment and services.
- To address this, Russia has made legislative changes allowing its companies to set up joint ventures in India to address it following an Inter-Governmental Agreement signed in 2019.
- This agreement needs to be implemented in a time bound manner.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question:
Prelims
Q. Recently, India signed a deal known as ‘Action Plan for Prioritization and Implementation of Cooperation Areas in the Nuclear Field’ with which of the following countries? (2019)
(a) Japan
(b) Russia
(c) The United Kingdom
(d) The United States of America
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. What is the significance of Indo-US defence deals over Indo-Russian defence deals? Discuss with reference to stability in the Indo-Pacific region. (2020)