Important Facts For Prelims
India Ranks Fifth in National Contribution to Warming
- 31 Mar 2023
- 3 min read
Why in News?
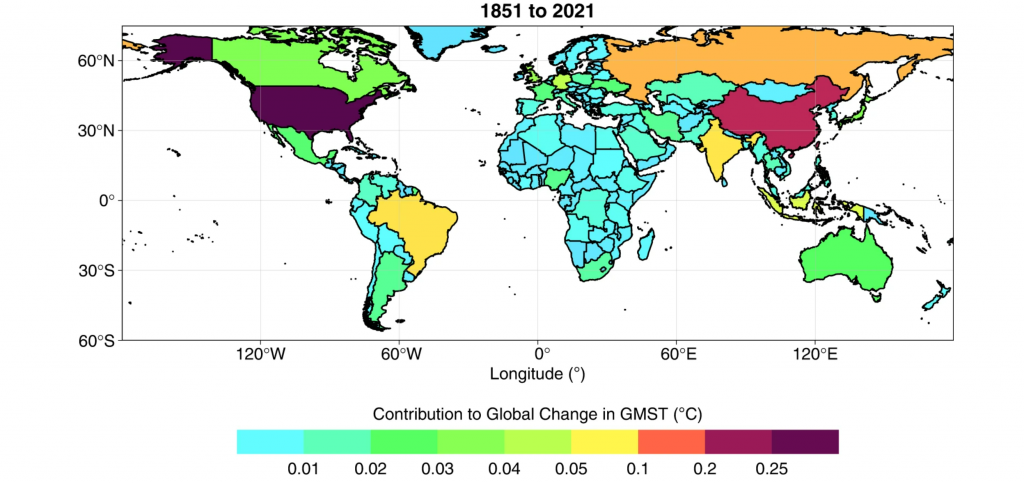
Recently, the research published in the journal “Scientific Data’ ranked India fifth among the top 10 contributors to global warming.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Top Contributor:
- The United States topped the list with its emissions causing 0.28°C (17.3%) of rise in temperature.
- China stood second and Russia took third place.
- India's Position:
- Since 2005, India climbed to the fifth spot from the 10th.
- India is responsible for 0.08 degrees Celsius of warming from the 1850s through 2021.
- India’s emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O) from 1851-2021 have resulted in 0.04°C, 0.03°C and 0.006°C of global warming over pre-industrial levels, respectively.
- Cause of Warming:
- The land-use and forestry sector is a significant contributor in half the countries.
- CO2 emissions from land use, land-use change and forestry (LULUCF) in Brazil led to 0.04°C of warming.
- Also, the LULUCF sector accounted for 38% of the total warming from CH4 emissions and 72% from N2O emissions between 1851-2021.
- The report highlighted emissions linked to historical deforestation and agricultural expansion.
- Fossil fuel remains the biggest contributor. Since 1992, the additional warming caused by global fossil fuel emissions has been over four times greater than the additional warming caused by land-use change.
What are Greenhouse Gases?
- A greenhouse gas (GHG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy at thermal infrared wavelengths, causing the greenhouse effect.
- The primary GHGs in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and ozone (O3).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. In the context of which of the following do some scientists suggest the use of cirrus cloud thinning technique and the injection of sulphate aerosol into stratosphere? (2019)
(a) Creating the artificial rains in some regions
(b) Reducing the frequency and intensity of tropical cyclones
(c) Reducing the adverse effects of solar wind on the Earth
(d) Reducing the global warming
Ans: (d)