International Relations
India-Oman Bilateral Meet
- 19 Dec 2023
- 10 min read
For Prelims: India-Oman Bilateral Meet, Indian Council of Cultural Relations (ICCR), India Oman Joint Vision Partnership For the Future, Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA).
For Mains: India-Oman Bilateral Meet, Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Why in News?
Recently, India and Oman have adopted the India Oman Joint Vision Partnership For the Future, setting the stage for bilateral cooperation and charting pathways for future collaboration between the two countries.
- This Vision Document focuses on building partnerships in broadly 8 to 10 areas. These include maritime cooperation and connectivity, energy security, space, digital payments, health, tourism, hospitality, agriculture and food security.
What are the Key Highlights of the Bilateral Meet?
- Bilateral Agreements:
- Both countries have signed agreements on cooperation in the field of information technology, combating financial crimes, culture, and the establishment of a Hindi chair of the Indian Council of Cultural Relations (ICCR) in Oman.
- Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA):
- Both nations are engaged in discussions to finalize a CEPA. Substantial progress has been made, and leaders from both sides emphasized concluding this agreement at the earliest to boost economic ties.
- Oman-India investment Fund:
- The two sides announced the third tranche of Oman-India investment fund worth USD 300 million that would be used for channelising investment into the fastest growing sectors of the Indian economy.
- The fund was started as a 50:50 joint venture between the SBI and the Oman investment authority, with the first tranche of USD 100 million followed by USD 200 million.
- Digital Payments and Trade:
- Discussions revolved around the possibility of using India's digital payment system, UPI (Unified Payments Interface), in collaboration with an Omani platform.
- Additionally, exploring the potential of conducting trade in Rupees was considered, although it's still in the exploratory stage.
- Regional and International Issues:
- Leaders exchanged perspectives on regional and global matters, including the ongoing conflict between Hamas and Israel.
- They discussed the challenge of terrorism and advocated for a two-state solution to address the Palestine issue.
How have Been India-Oman Relationships so Far?
- Background:
- The two countries across the Arabian Sea are linked by geography, history and culture and enjoy warm and cordial relations, which are attributed to historical maritime trade linkages.
- The Sultanate of Oman is a strategic partner of India in the Gulf and an important interlocutor at the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), Arab League and Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) fora.
- Gandhi Peace Prize 2019 was conferred on Late HM Sultan Qaboos in recognition of his leadership in strengthening the ties between India & Oman and his efforts to promote peace in the Gulf region.
- Defense Relations:
- Joint Military Cooperation Committee (JMCC):
- The JMCC is the highest forum of engagement between India and Oman in the field of defence.
- The JMCC is expected to meet annually, but could not be organised since 2018 when the meeting of the 9th JMCC was held in Oman.
- Military Exercises:
- Army exercise: Al Najah
- Air Force exercise: Eastern Bridge
- Naval Exercise: Naseem Al Bahr
- Joint Military Cooperation Committee (JMCC):
- Economic & Commercial Relations:
- Institutional mechanisms like Joint Commission Meeting (JCM) and Joint Business Council (JBC) oversee economic cooperation between India and Oman.
- India is among Oman’s top trading partners.
- India is the 2nd largest market for Oman’s crude oil exports for the year 2022 after China.
- India is also the 4th largest market for Oman’s non-oil exports for the year 2022 after UAE, US and Saudi Arabia and 2nd largest source of its import after UAE.
- Indian companies have invested in Oman in sectors like iron and steel, cement, fertilisers, textile etc.
- India-Oman Joint Investment Fund (OIJIF), a JV between State Bank of India and State General Reserve Fund (SGRF) of Oman, a special purpose vehicle to invest in India, has been operational.
- Indian Community in Oman:
- There are about 6.2 lakh Indians in Oman, of which about 4.8 lakh are workers and professionals. There are Indian families living in Oman for more than 150-200 years.
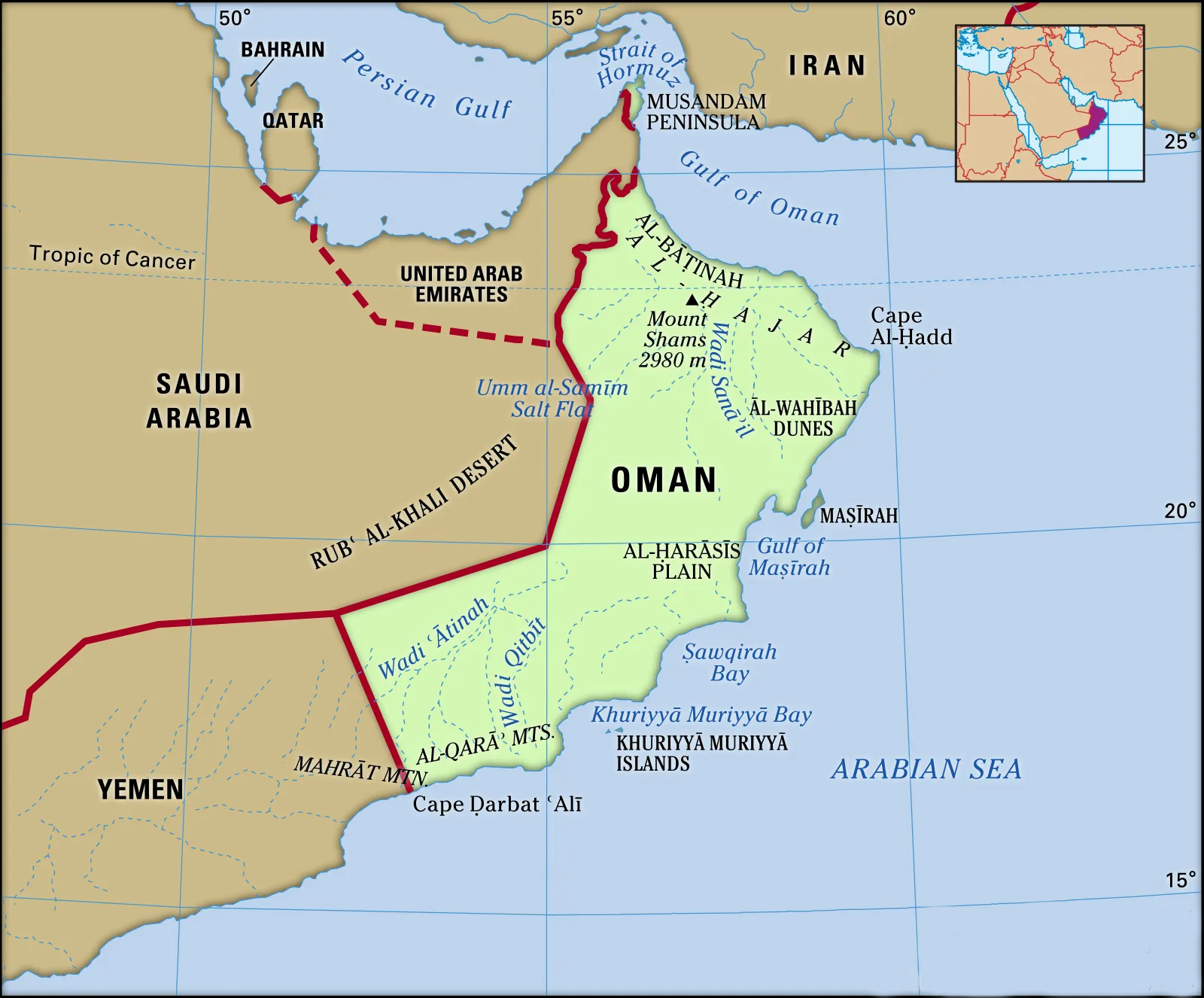
What is Oman’s Strategic Significance for India?
- Oman is at the gateway of Strait of Hormuz through which India imports one-fifth of its oil imports.
- Defence cooperation has emerged as a key pillar for the robust India-Oman strategic partnership. Defence exchanges are guided by a Framework MOU which was recently renewed in 2021.
- Oman is the only country in the Gulf region with which all three services of the Indian armed forces conduct regular bilateral exercises and staff talks, enabling close cooperation and trust at the professional level.
- Oman also actively participates in the Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS).
- In a strategic move to expand its footprint in the Indian Ocean region, India has secured access to the key Port of Duqm in Oman for military use and logistical support. This is part of India’s maritime strategy to counter Chinese influence and activities in the region.
- The Port of Duqm is situated on the southeastern seaboard of Oman, overlooking the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean.
- It is strategically located, in close proximity to the Chabahar port in Iran. With the Assumption Island being developed in Seychelles and Agalega in Mauritius, Duqm fits into India’s proactive maritime security roadmap.
Key Facts About Oman
- Border Countries:
- United Arab Emirates (UAE) to the northwest.
- Saudi Arabia to the west and southwest.
- Yemen to the southwest.
- Deserts:
- The largest desert in Oman is the Rub' al Khali or the "Empty Quarter," one of the largest continuous sand deserts in the world.
- River:
- Oman doesn’t have perennial rivers; however, during seasonal rains, wadis (seasonal riverbeds) flow with water.
- The most notable is Wadi Bani Khalid, known for its natural pools and stunning scenery.
- Highest Mountain:
- Jebel Shams, situated within the Al Hajar mountain range, is the highest mountain in Oman.
- Geography:
- Oman is located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, bordering the Arabian Sea, the Gulf of Oman, and the Persian Gulf.
Way Forward
- India does not have enough energy resources to serve its current or future energy requirements. The rapidly growing energy demand has contributed to the need for long term energy partnerships with countries like Oman.
- Oman’s Duqm Port is situated in the middle of international shipping lanes connecting East with West Asia.
- India needs to engage with Oman and take initiatives to utilise opportunities arising out of the Duqm Port industrial city.
- India should also work closely with Oman to enhance strategic depth in the region and add heft to its Indo-Pacific vision in the Western and Southern Part of Indian Ocean.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following is not a member of ‘Gulf Cooperation Council’? (2016)
(a) Iran
(b) Saudi Arabia
(c) Oman
(d) Kuwait
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) is an alliance of 6 countries in the Arabian Peninsula – Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates. Iran is not a member of the GCC.
- It was established in 1981 to promote economic, security, cultural and social cooperation between the members and holds a summit every year to discuss cooperation and regional affairs.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. A number of outside powers have entrenched themselves in Central Asia, which is a zone of interest to India. Discuss the implications, in this context, of India’s joining the Ashgabat Agreement, 2018. (2018)
Q. The question of India’s Energy Security constitutes the most important part of India’s economic progress. Analyse India’s energy policy cooperation with West Asian countries. (2017)