International Relations
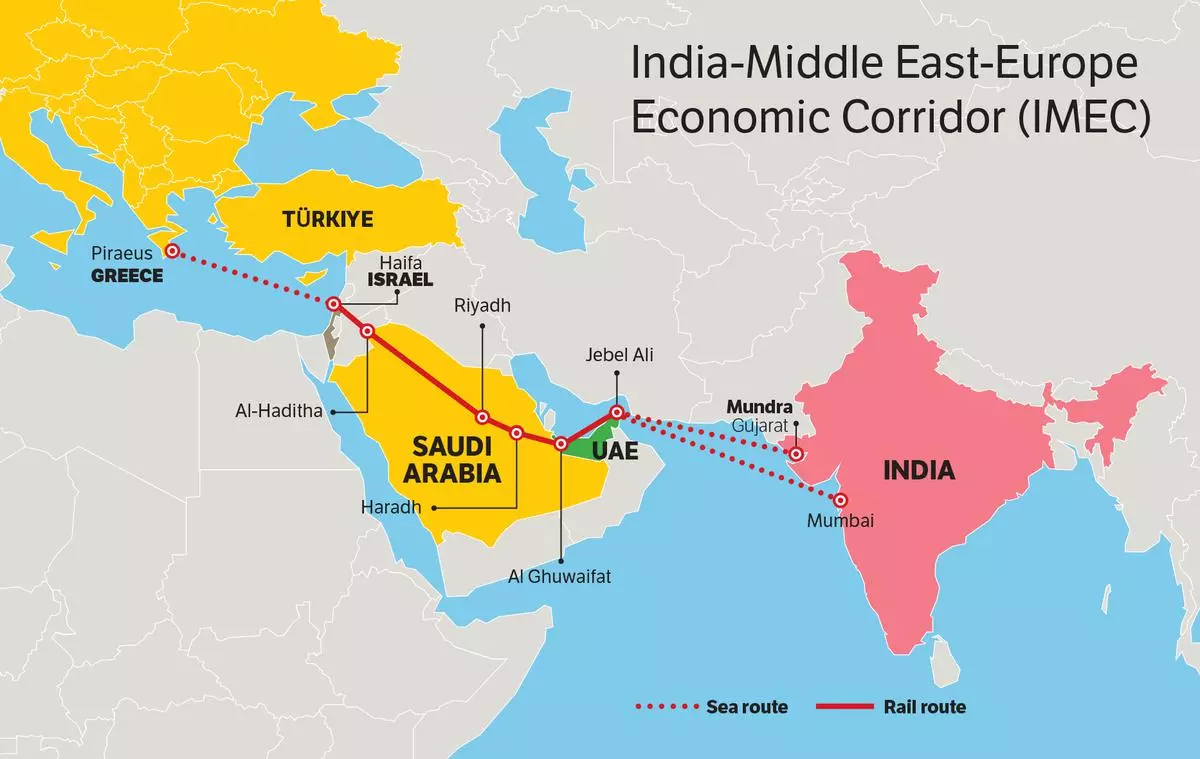
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor
- 17 Apr 2025
- 10 min read
For Prelims: India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor, G20, Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment, Belt and Road Initiative
For Mains: India’s infrastructure diplomacy, India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor, Role of geopolitics in economic development
Why in News?
The Union Minister of Commerce and Industry, at the High-Level Roundtable on Connectivity and Economic Growth in New Delhi, highlighted the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) as a transcontinental initiative poised to redefine global trade dynamics and strengthen international economic cooperation.
What is the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor?
- About: The IMEC is a strategic multi-modal connectivity initiative launched through a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) during the G20 Summit 2023 in New Delhi. Signatories include India, US, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, France, Germany, Italy and the European Union.
- The initiative is a part of the Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII), launched by the G7 in 2021.
- IMEC seeks to position itself as a viable alternative to China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) by promoting transparent, sustainable, and debt-free infrastructure without compromising national sovereignty.
- Corridor Segments: IMEC has two parts the Eastern Corridor (India to Gulf) and the Northern Corridor (Gulf to Europe).
- Objective: To develop an integrated network of ports, railways, roads, sea lines, energy pipelines, and digital infrastructure aimed at enhancing trade between India, the Middle East, and Europe.
- Importance for India: IMEC is set to reduce logistics costs by up to 30% and transportation time by 40%, compared to the Suez Canal Maritime route making Indian exports more competitive globally.
- India's One Sun One World One Grid (OSOWOG) initiative aligns with IMEC’s energy goals, enabling India to harness solar and green hydrogen power from the Middle East, a region rich in renewable energy potential.
- IMEC includes energy pipelines, clean energy infrastructure, and undersea cables to enhance trade and energy cooperation.
- It will attract Foreign Direct Investment into India, particularly in infrastructure, logistics, green energy, and digital technologies, helping India access low-cost renewable energy and transition to a low-carbon economy.
- Status of IMEC: The project faced a major setback due to the Israel-Hamas conflict in 2023. Geopolitical instability in the Middle East has temporarily slowed momentum.
- Despite this, diplomatic engagement continues India and the UAE signed an Intergovernmental Framework Agreement (IGFA) in 2024, it focuses on operational cooperation and building a joint logistics platform for IMEC.
What are the Challenges Hindering the Progress of IMEC?
- Geopolitical Instability: The Gaza Conflict is a major concern, disrupting diplomatic normalization in West Asia, a key premise for IMEC's success.
- Regional volatility, including the Saudi-Iran rivalry and instability in Iraq and Syria, poses major threats to infrastructure development and supply chain security under IMEC..
- Lack of Clear Financial Commitment: The IMEC aims to mobilize USD 600 billion by 2027 to bridge infrastructure gaps, but lacks a clear financial roadmap and cost-sharing plan among stakeholders.
- Infrastructure development of this scale needs long-term investments (anywhere between USD 3 billion to USD 8 billion), which remain uncertain amid global economic slowdown.
- Potential for Trade Disruption: Examples like the Suez Canal blockage (2021) and Black Sea shipping disruption (due to the Russia-Ukraine conflict) illustrate how fragile maritime trade can be.
- Similar incidents in the IMEC region could disrupt reliability, while increased militarization and naval presence by extra-regional powers like China in the Indian Ocean raise fears of maritime contestation.
- Limited Geographical Inclusion: Key regional players like Turkey, Iran, Qatar, and Egypt are currently not part of IMEC, limiting its geopolitical and economic reach.
- The long-term success of the IMEC hinges on consistent political cooperation, which is challenging due to the differing national interests and alliances of the involved countries.
- Competition from Established Routes: The Suez Canal route is well-established, and IMEC's cost-effectiveness in comparison is still debated.
- IMEC could be a costlier alternative with no guaranteed returns if regional challenges persist.
- Technological Challenges: IMEC’s digital infrastructure, including undersea data cables, faces integration issues due to differing tech standards among member nations.
- Ensuring seamless connectivity is complex, and the risk of cyberattacks like the Colonial Pipeline incident in the US underscores the vulnerability of global digital systems.
How Can India Steer IMEC Towards Effective Implementation?
- Strengthening Domestic Infrastructure for IMEC Readiness: India can use this period of slowed progress in West Asia to strengthen its ports (Mundra (Gujarat), Kandla (Gujarat), and Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust (Navi Mumbai)), develop economic zones along IMEC nodes, and upgrade domestic logistics for better integration into global value chains and positioning India as a reliable global supply chain alternative.
- Standardization of Trade Process: Efficient cross-border trade under IMEC requires all member countries to adopt frameworks like the India-UAE Virtual Trade Corridor to minimize paperwork and reduce delays.
- Towards Resilient Infrastructure: India can lead IMEC nations to adopt G20 Principles of Quality Infrastructure Investment (QII) principles to build sustainable, climate-resilient, and geopolitically adaptable projects.
- This approach can attract Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) and private capital via green bonds and sustainable finance, easing pressure on national budgets.
- Enhancing Regional Security Frameworks: India can push for stronger security ties via Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) and Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) to protect IMEC from terrorism, piracy, and cyber threats.
- Promoting Technological Integration: India can lead in digital connectivity by promoting Unified Payments Interface (UPI) based payment systems, undersea cables, 5G infrastructure, supporting e-commerce, fintech, and smart city initiatives while reducing the digital divide along IMEC.
India's Other Key Strategic Infrastructure Initiatives
- International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC): It was proposed in 2000 to connect Russia’s Baltic Sea coast to India’s western ports via Iran.
- Russia, India, and Iran signed preliminary agreements in 2002 to develop the 7,200-km-long INSTC.
- It currently includes 13 members: India, Iran, Russia, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkey, Ukraine, Belarus, Oman, and Syria, with Bulgaria as an Observer State.
- Chabahar Port Project: India, Iran, and Afghanistan signed a tripartite agreement to develop the Shahid Beheshti Terminal at Chabahar Port, marking India’s first foreign port project.
- The project aims to bypass Pakistan and provide India access to Afghanistan and Central Asia, enhancing transit trade between the three nations.
- India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway: The project aims to create a road link starting from Moreh in India’s Manipur state, passing through Myanmar, and ending at Mae Sot in Thailand.
- Kaladan Multimodal Transit Transport Project: The project aims to connect Kolkata’s eastern seaport with Myanmar's Sittwe port by sea, enhancing trade and connectivity with Southeast Asia.
Conclusion
IMEC with India's leadership, promises to reshape global trade by enhancing connectivity and fostering regional cooperation. Establishing an IMEC Secretariat will be crucial in streamlining operations and ensuring the smooth execution of the project. Its implementation will drive sustainable economic growth and a new era of global prosperity.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the strategic significance of the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor in reshaping regional geopolitics and trade dynamics. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. ‘Belt and Road Initiative’ is sometimes mentioned in the news in the context of the affairs of (2016)
(a) African Union
(b) Brazil
(c) European Union
(d) China
Ans: (d)