Indian Economy
India-Latin America Trade Relations
- 03 Jan 2025
- 17 min read
For Prelims: LAC Program, Countries with which India has signed Free Trade Agreements, Mercosur.
For Mains: Trade agreements with Mercosur, Latin American countries, Evolution of India's foreign policy towards Latin America, Challenges related to Latin America’s regional integration, Latin America's role in global issues like climate change, trade rules, and terrorism.
Why in News?
The Latin America and Caribbean (LAC) region has become a key focus of India's foreign policy, with sustained growth and diversified ties across all 33 nations. Despite progress, India still lags behind China, which has a far stronger presence in the region.
How is India's Relation with Latin America?
- Historical Background:
- Rich Ties: India-Latin America relations have a rich history, marked by significant contributions from figures like Pandurang Khankhoje (an agricultural scientist who played a key role in the advancement of agricultural practices in Mexico) and M.N. Roy (a political activist, founded both the Indian and Mexican Communist parties).
- India and Latin America shared a vibrant exchange of literary ideas through poet-diplomats and authors like Octavio Paz, Rabindranath Tagore, and Victoria Ocampo, shaping mutual perceptions.
- India’s poet-diplomat Abhay K, has authored books of poetry on the Latin American region, such as The Alphabets of Latin America and The Prophecy of Brasilia.
- Early Engagements: High-level engagement began with Prime Minister Nehru's visit to Mexico in 1961, followed by Indira Gandhi's tour of eight Latin American and Caribbean (LAC) nations in 1968.
- Recent Developments: The relationship gained momentum with PM Modi's participation in the BRICS Summit in Brazil in 2014.
- Economic Liberalization: Post-1990s economic liberalization led to strengthened trade, investments, and renewable energy cooperation.
- India signed trade agreements with seven LAC nations and launched the FOCUS LAC Program in 1997 to enhance exports and economic collaboration.
- Rich Ties: India-Latin America relations have a rich history, marked by significant contributions from figures like Pandurang Khankhoje (an agricultural scientist who played a key role in the advancement of agricultural practices in Mexico) and M.N. Roy (a political activist, founded both the Indian and Mexican Communist parties).
- Current Trade Landscape:
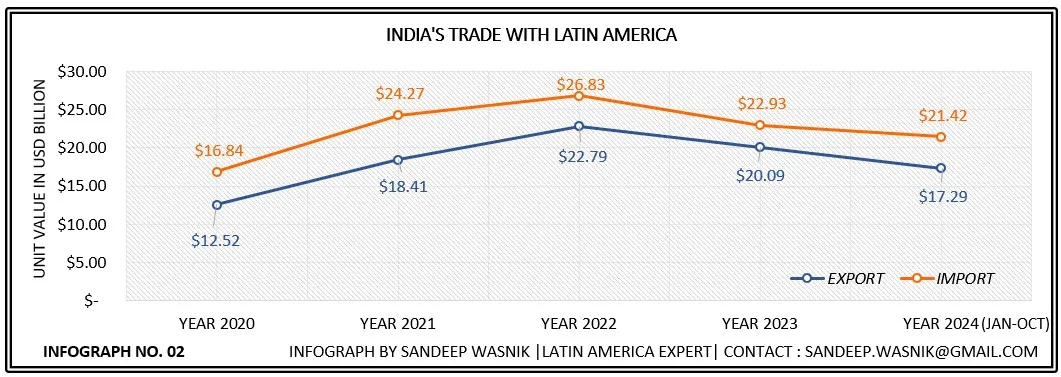
- Trade Figures: In 2023, India's imports from Latin America reached USD 22.93 billion, while exports stood at USD 20.09 billion, totaling a trade volume of USD 43.22 billion with a target of USD 100 billion by 2028.
- Key Trade Partners: Brazil, Mexico, and Colombia are India's primary trade partners in the region.
- Import Composition: Major imports include petroleum oils, gold (including gold plated with platinum), and soybean oil.
- Export Composition: Key exports consist of petroleum oils (excluding crude), motor cars, and other motor vehicles designed for transportation.
- Economic Positioning: Latin America is considered to be in the “goldilocks zone” for India—offering a balance between highly regulated markets like the US and Europe and less competitive markets in Africa.
- Political and Bilateral Cooperation:
- Foreign Policy Priority: Historically, Latin America has been a low priority in India's foreign policy due to its limited geopolitical influence. However, recent developments indicate a significant shift in this approach.
- Notably, External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar undertook a landmark visit to Guyana, Panama, Colombia, and the Dominican Republic in April 2023, marking the first time an Indian foreign minister has visited these countries.
- Enhanced Engagements: In 2022, G20 members Argentina, Brazil, and Mexico were placed under the purview of India’s foreign minister instead of a junior minister.
- Brazil's Leadership Role: Brazil is recognized as having the most political linkages with India due to its active participation in multilateral forums such as BRICS, IBSA (India, Brazil and South Africa), and the G20.
- Preferential Trade Agreements (PTAs): The signing of PTAs between India and Chile as well as India and Mercosur reflects Latin America's commitment to strengthening economic relations with India.
- MERCOSUR, a Latin American trading bloc established in 1991, comprises six members namely, Brazil, Argentina, Uruguay, and Paraguay, Venezuela, and Bolivia.
- Initially aimed at facilitating the free movement of goods, services, capital, and people, it became a customs union in 1995 and is now advancing towards a Common Market.
- Strategic Autonomy: Both regions have embraced a form of non-alignment termed ‘strategic autonomy’ by India and ‘Active Non-alignment’ (ANA) by Latin American countries, particularly evident in their shared positions regarding global issues like the war in Ukraine.
- Foreign Policy Priority: Historically, Latin America has been a low priority in India's foreign policy due to its limited geopolitical influence. However, recent developments indicate a significant shift in this approach.
- Cultural Ties:
- Literary Influences: Tagore's visit to Argentina in 1924 and his literary contributions have left a lasting impression on Latin American literature through translations by Mexican philosopher José Vasconcelos.
- Gandhi's Legacy: Mahatma Gandhi’s teachings on non-violence resonate strongly in Latin America, celebrated by organizations like Palas Athenas in Brazil.
- Trade Agreements/MoUs with LAC region:
What is the Importance of Latin America for India?
- Economic Opportunities: Latin America is rich in natural resources, including minerals like copper, lithium, and iron ore, which are vital for India’s growing industrial demands.
- The region's collective GDP exceeds USD 6 trillion, providing a substantial market for Indian exports and investments.
- Energy Security: With a rising demand for energy, Latin America has emerged as a key supplier of crude oil to India.
- In recent years, Crude oil imports from Venezuela, Mexico, and Brazil accounted for 30% of India’s total import from LAC.
- Strategic Partnerships: The geopolitical landscape has shifted, prompting India to enhance its engagement with Latin America to counterbalance China's growing influence in the region.
- Cultural and Educational Exchange: The cultural ties between India and Latin America have been bolstered through educational exchanges and collaborations in sectors like information technology and pharmaceuticals.
- Indian IT companies employ over 40,000 local professionals in the region, contributing to job creation and skill development.
- Food Security: Latin America's vast agricultural landscape offers opportunities for India to secure food supplies, particularly in pulses and oilseeds, which are essential for food security.
What are the Sectors in which India is Cooperating with Latin American Nations?
- Pharmaceuticals and Healthcare: India is recognized globally for its pharmaceutical industry, providing high-quality medicines at affordable prices.
- The top five destinations for these exports are the USA, Belgium, South Africa, the UK, and Brazil.
- Energy Cooperation: India is exploring and extracting lithium deposits in Bolivia. In 2023, India’s Altmin Private Limited signed a strategic partnership agreement with Bolivia's state-owned lithium company.
- Bolivia also joined the International Solar Alliance.
- Agriculture and Food Security: The LA region has vast agricultural resources that helps India in addressing its food security concerns.
- Collaborations in food processing and agricultural research are being explored to enhance productivity and sustainability in both regions.
- Infrastructure Development: Collaboration in developing modern infrastructure across LA nations, including railways, highways, and energy pathways.
- India values its development partnership with Bolivia under South-South Cooperation and has extended a USD 100 million Line of Credit to support development projects in sectors of Bolivia's choice.
Types of Trade Agreements
- Free Trade Agreement (FTA): An FTA is a comprehensive agreement between two or more countries aimed at reducing trade barriers, such as tariffs and quotas, on a wide range of goods and services.
- India has negotiated FTAs with several countries, including Sri Lanka and various trading blocs like ASEAN.
- Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA): A PTA is an agreement where partner countries provide preferential access to certain products by reducing tariffs on specific items. Some tariffs may even be eliminated entirely.
- Unlike FTAs, PTAs are generally less comprehensive and may only cover a limited number of goods. Some tariffs may even be reduced to zero for certain products.
- India has signed a PTA with Afghanistan.
- Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA): A CEPA is more extensive than an FTA, encompassing trade in services, investment, and broader economic cooperation. India has established CEPAs with South Korea and Japan.
- Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA): A CECA primarily focuses on trade tariffs and Tariff Rate Quotas (TRQs) but is less comprehensive than a CEPA. India has signed a CECA with Malaysia.
What are the Challenges in Deepening Engagement with Latin American Nations?
- Lack of Regional Mechanisms: India has yet to develop a framework to engage Latin America as a region or with sub-groups like Central American Integration System (SICA), Community of Latin American and Caribbean States (CELAC), Mercosur, and the Pacific Alliance.
- Regional integration within Latin America remains incomplete, making bilateral ties more feasible in the short term.
- Limited Trade Agreements: Existing Preferential Trade Agreements (PTAs) with Mercosur and Chile are narrow in scope compared to India’s FTAs with South Korea, Japan, or ASEAN.
- Despite growing exports, Latin America faces economic challenges such as inflation, political instability, and low investment in infrastructure, impacting trade.
- China's Dominance: India faces competition from China’s established trade presence, strategic investments, and free trade agreements (FTAs) with key Latin American countries.
- Geographical Barriers: Despite positive developments in trade sectors and cultural ties, geographical distance and language barriers pose challenges for social interactions, including high travel costs and visa difficulties for Indians traveling to Latin America.
- Many Indians still view Latin American countries through outdated stereotypes, such as "banana republics" characterized by instability and drug trafficking. Conversely, Latin Americans often see India as merely a land of spiritualism and gurus.
- Bilateral Synergies: The relationship is driven by bilateral cooperation on issues like climate change, trade, and security, though strategic sectors such as defense and space have seen limited engagement.
What Strategies can India Adopt to Increase its Relations with Latin America?
- Reactivating "Focus:LAC" Programme: This trade promotion programme can strengthen market access, improve institutional mechanisms, and develop economic infrastructure, creating a conducive environment for business.
- Increase selective trade where India have competitive advantage, like
- Bilateral Agreements and Investment Promotion: India must pursue Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) and preferential trade arrangements with Latin American countries, focusing on sectors like technology, agriculture, and clean energy.
- Promoting People-to-People (P2P) and Business-to-Business (B2B) Connections between India and Latin American countries will facilitate cultural exchanges and enhance economic collaboration.
- Diplomatic Engagement: Strengthening diplomatic ties through high-level visits, participation in regional trade summits, and fostering cultural exchange can pave the way for deeper economic collaboration.
- Enhanced Export Promotion: Indian exporters need financial support and targeted efforts to penetrate the Latin American market.
- Export promotion councils and industry associations can play a pivotal role in this regard.
- Advocating for Latin American Interests: India should actively raise its voice for Latin American nations such as Venezuela, Argentina, and Haiti in international forums.
- By doing so, India can strengthen its diplomatic ties and showcase solidarity with these nations, especially in addressing issues like economic instability and political challenges.
- Services Trade Enhancement: Create a comprehensive database of non-tariff barriers in services sectors across FTA partners.
- Establish mutual recognition agreements for professional qualifications on priority basis.
- Develop a digital platform for service providers to report market access issues.
- For example, implement a system similar to the EU's Trade Barriers Reporting mechanism.
- Set up dedicated service export promotion councils with market-specific strategies.
|
Drishti Mains Question Discuss the challenges and opportunities in India’s trade relations with Latin America. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20? (2020)
(a) Argentina, Mexico, South Africa and Turkey
(b) Australia, Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
(c) Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
(d) Indonesia, Japan, Singapore and South Korea
Ans: (a)
Q. Increase in absolute and per capita real GNP do not connote a higher level of economic development, if (2018)
(a) Industrial output fails to keep pace with agricultural output.
(b) Agricultural output fails to keep pace with industrial output.
(c) Poverty and unemployment increase.
(d) Imports grow faster than exports.
Ans: (c)
Q. Consider the following countries: (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
(a) 1, 2, 4 and 5
(b) 3, 4, 5 and 6
(c) 1, 3, 4 and 5
(d) 2, 3, 4 and 6
Ans: (c)