International Relations
India China Partnership for Global Harmony
- 08 Nov 2023
- 11 min read
For Prelims: A Global Community of Shared Future: China’s Proposals and Actions, Protectionism, G20 summit, BRICS, Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, New Development Bank, Conference on Disarmament, Sustainable Development Goals, Line of Actual Control, China's Belt and Road Initiative.
For Mains: Role of India and China in Building a Global Community of a Shared Future, Challenges and Obstacles in India-China Collaboration.
Why in News?
Recently, China released a white paper “A Global Community of Shared Future: China’s Proposals and Actions”, to address the common challenges and opportunities faced by humanity in the 21st century.
- Amidst global turmoil, with Russia- Ukraine crisis and issues in West Asia, attention turns to the historically linked civilizations of India and China. Their shared visions for the future could provide hope for global harmony.
What are the Key Vision Points for the Global Community of Shared Future?
- Economic Globalization and Inclusivity: Uphold the correct path of economic globalization. Jointly build an open world economy that represents the interests of developing nations, rejecting unilateralism, protectionism, and zero-sum games.
- Peace, Cooperation, and Development: Embrace peace, development, cooperation, and win-win results, steering clear of colonialism and hegemony, fostering joint efforts for global peace and contribution.
- Global Community of Shared Destiny: Construct a global community of shared destiny to evade conflict between emerging and established powers, emphasizing mutual respect, equity, and beneficial cooperation for deeper global partnerships.
- Genuine Multilateralism and Fair International System: Rejecting bloc politics and unilateral thinking, advocating for a fair, UN-centered international system. Upholding international law as the basis for global norms and order and promoting true multilateralism.
- Promotion of Common Human Values: Promoting equity, justice, democracy, and freedom without imposing a singular model of democracy.
- Embrace harmony amidst diversity, respecting each nation's right to choose its social systems and development paths.
How can India and China Cooperate in Building a Global Community of a Shared Future?
- About:
- As two ancient Asian civilizations that have been living side by side for thousands of years, China and India share common thoughts on the future and destiny of mankind.
- They have the responsibility, the ability and the opportunity to set an example for the rest of the world with their Oriental wisdom and civilizational heritage.
- The Chinese people have cherished the vision of “a world of fairness and justice for the common good” since ancient times.
- Ancient Indian literature also records the motto of “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam”, which means “the world is one family” in Sanskrit.
- It was also used as the theme of the G20 summit held in New Delhi in September 2023.
- Ancient Indian literature also records the motto of “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam”, which means “the world is one family” in Sanskrit.
- Also, in the 1950s, India and China jointly established the Five Principles of Peaceful Co-existence:
- Mutual respect for each other’s territorial integrity and sovereignty
- Mutual non-aggression
- Mutual non-interference
- Equality and mutual benefit
- Peaceful co-existence
- Areas and Platforms of Cooperation between India and China:
- Economic Cooperation: India and China are both members of the BRICS, the SCO, the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB), the New Development Bank (NDB).
- They can enhance their economic cooperation through these mechanisms and promote an open, inclusive, and balanced world economy that reflects the demands and interests of the developing countries.
- They can also expand their bilateral trade and investment, and explore new areas of cooperation such as digital economy, green economy, and innovation.
- Security Cooperation: Both India and China are members of the United Nations Conference on Disarmament (CD).
- They can cooperate in combating terrorism, extremism, and separatism, and maintain regional peace and stability.
- Cultural Cooperation: India and China are both ancient civilizations with rich and diverse cultures.
- They can enhance their cultural cooperation and mutual learning through increased people-to-people contact.
- They can also increase their exchanges and interactions in the fields of education, tourism, sports, youth, and media, and foster mutual understanding and friendship between the two peoples.
- Environmental Cooperation: India and China are both parties to the Paris Agreement on Climate change and the Convention on Biological Diversity.
- They can enhance their environmental cooperation and coordination on issues such as emission reduction, renewable energy, biodiversity conservation, and disaster management.
- They can also support each other in implementing Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Economic Cooperation: India and China are both members of the BRICS, the SCO, the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB), the New Development Bank (NDB).
- Benefits of India and China Cooperation
- Economic Growth and Trade Opportunities:
- Market Expansion: Both India and China possess massive consumer markets. Collaboration between the two could lead to greater trade opportunities, expanding markets for goods and services.
- Complementary Economies: China's manufacturing strength and infrastructure, coupled with India's services sector and skilled workforce, can create a symbiotic economic relationship.
- This collaboration can fill gaps and leverage the strengths of each other's economies.
- Technological Advancements and Innovation: Collaborative efforts in technology, research, and innovation can lead to breakthroughs in various sectors such as renewable energy, healthcare, and artificial intelligence.
- Pooling resources and expertise could accelerate advancements in areas like space exploration, cybersecurity, and climate change mitigation.
- Global Governance and Diplomacy: By aligning in global issues, both countries can act as a counterbalance to unilateral actions by other global powers, promoting a more multipolar world order.
- Together, India and China could influence international forums, speaking with a collective voice on global issues such as trade, security, and climate change.
- Working in tandem could strengthen their diplomatic outreach, potentially leading to more effective resolutions.
- Economic Growth and Trade Opportunities:
What are the Challenges and Obstacles in India-China Collaboration?
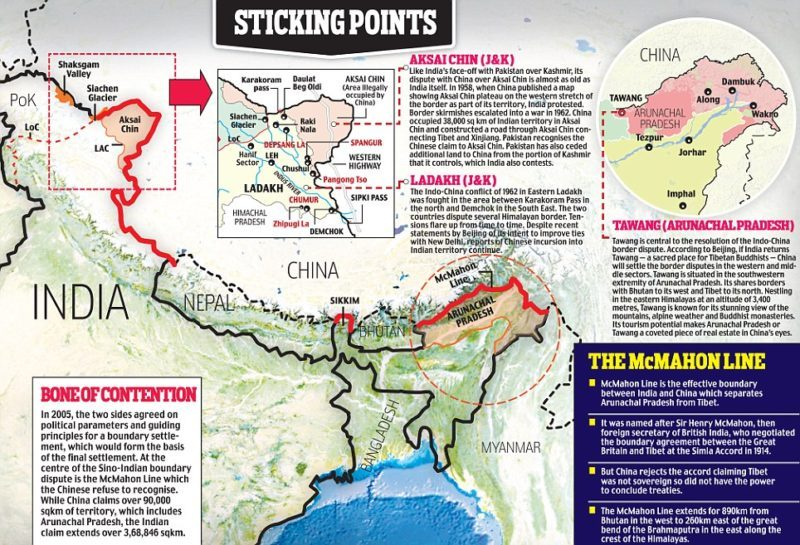
- Border Disputes: The long-standing border disputes, especially along the Line of Actual Control (LAC), have resulted in occasional military standoffs, creating mistrust and a potential for escalation.
- Also, India has criticized China's recent assertion regarding Arunachal Pradesh.
- Historical Conflicts and Layer of Suspicion: Historical conflicts and the 1962 Sino-Indian war have left deep-seated mistrust. Both nations view the other's intentions suspiciously, hindering efforts towards cooperation.
- Alongside China's use of its veto power against India in the UNSC and its close ties with Pakistan, India's abstention from China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) further contributes to the complexity of relations, adding layers of geopolitical tension and mutual suspicion.
- Strategic Competition and External Pressure: The strategic competition between China and India is a reality that cannot be ignored, as both countries have their own national interests and aspirations.
- The strategic competition is also influenced by external pressure, especially from the United States and its allies, who seek to contain China’s rise.
- Divergent Strategic Interests: Their strategic interests sometimes clash, especially in regions such as South Asia, where both countries seek influence.
- China's investments in countries surrounding India can be seen as encroaching on India's sphere of influence.
Way Forward
- Conflict Resolution Mechanisms: Establish robust conflict resolution mechanisms specifically tailored to address border disputes and other contentious issues, fostering a peaceful resolution through negotiations and mutual compromises.
- Implement confidence-building measures to reduce mistrust and promote transparency in military activities and intentions.
- Economic Collaboration: Encourage bilateral economic ties and cooperation by identifying sectors where both countries can mutually benefit. Focus on trade, investment, and joint ventures that promote shared prosperity.
- Respect for Sovereignty and Territorial Integrity: Affirm mutual respect for each other's sovereignty and territorial integrity, thereby maintaining stability and security in the region.
- Diplomatic Discretion and Sensitivity: Conduct diplomacy with a sense of discretion and sensitivity, acknowledging historical and geopolitical complexities without exacerbating existing tensions.
- Long-Term Vision: Strive for a long-term vision that prioritizes peace, stability, and mutual prosperity, setting aside short-term differences for the greater good of both nations and the region.
- Building trust, fostering understanding, and promoting common interests over differences is key to charting a positive path forward for India and China.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. “China is using its economic relations and positive trade surplus as tools to develop potential military power status in Asia”. In the light of this statement, discuss its impact on India as her neighbour. (2017)