India-Bangladesh Railway Links Restored | 08 Jun 2022
For Prelims: Mitali Express, Maitree Express, Maitri Setu Bridge, Sampriti Exercise, Exercise Bongosagar
For Mains: Different trends in Indo-Bangladesh relations, issue of connectivity in south Asia
Why in News?
Two years after train services were stopped due to the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic, passenger train services between India and Bangladesh resumed recently.
- The following trains have been flagged off after the resumption of train services:
- Bandhan Express from Kolkata to Khulna
- Maitree Express from Dhaka to Kolkata
- Mitali Express from New Jalpaiguri to Dhaka
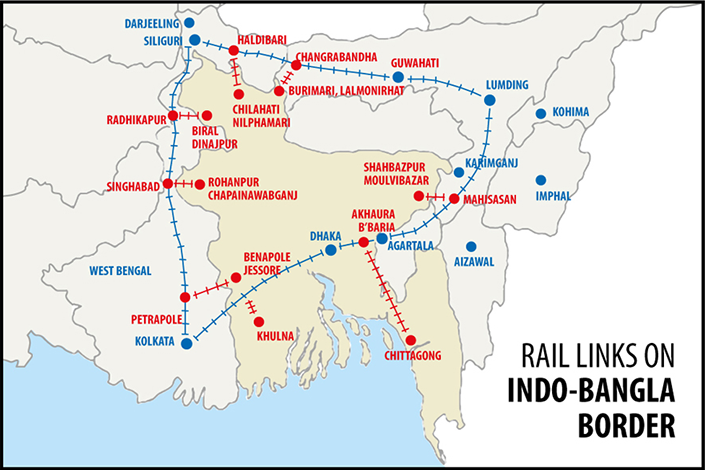
What are other Important Rail Links Between India and Bangladesh?
- Petrapole (India)-Benapole (Bangladesh),
- Gede (India)-Darshana (Bangladesh),
- Singhabad (India)-Rohanpur (Bangladesh),
- Radhikapur (India)-Birol (Bangladesh),
- Haldibari (India)-Chilahati (Bangladesh),
- Agartala (India)- Akahaura(Bangladesh),
Indo-Bangladesh ties
- Historical Ties:
- Fifty years ago, the Bangladesh Liberation War in 1971 had added the colours of victory for India as it led the charge towards the formation of the new nation of Bangladesh.
- Defence Cooperation:
- Joint exercises:
- SAMPRITI (Army)
- TABLE TOP (Air)
- IN-BN CORPAT (Navy)
- Exercise Bongosagar (Navy)
- SAMVEDNA (Multinational Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) Exercise with Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka and UAE).
- Border Management: India and Bangladesh share 4096.7 km. of border, which is the longest land boundary that India shares with any of its neighbours.
- Joint exercises:
- Economic Relations:
- Bangladesh is India’s largest trading partner in the sub-continent with the total bilateral trade between the two nations standing at USD 9.5 billion (2019-20), down compared to the previous fiscal (2018-19), having crossed USD10 billion.
- India’s exports to Bangladesh account for more than 85% of the total bilateral trade.
- In December 2020, to further boost the bilateral trade cooperation, an India-Bangladesh CEO’s Forum was launched.
- Bangladesh has appreciated the Duty-Free and Quota Free access given to Bangladeshi exports to India under South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA) since 2011.
- Cooperation in Connectivity:
- In March 2021, Maitri Setu–a 1.9 km bridge built over Feni River joining Sabroom in India and Ramgarh in Bangladesh was inaugurated.
- Protocol on Inland Water Transit and Trade (PIWTT).
- Bangladesh-Bhutan-India-Nepal (BBIN) Motor Vehicles Agreement is in pipeline.
- Partnership on Multilateral forums:
- Other Developments:
- Line of Credit:
- India has extended 3 Lines of Credits (LOC) to Bangladesh in the last 8 years amounting to USD 8 billion for development of infrastructure in sectors including roads, railways, shipping and ports.
- Covid-19 Support:
- Bangladesh is the biggest recipient of Made-in-India Covid-19 vaccine doses, accounting for 16% of the total supplies.
- India also offered collaboration in therapeutics and partnership in vaccine production.
- Line of Credit:
- Emerging Disputes:
- Bangladesh has already raised concerns over roll out of the National Register of Citizens (NRC) in Assam, an exercise carried out to identify genuine Indian citizens living in Assam and weed out illegal Bangladeshis.
- Currently, Bangladesh is an active partner of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) that Delhi has not signed up to.
- In the security sector, Bangladesh is also a major recipient of Chinese military inventory, including submarines.
Way Forward
- There should be efforts to resolve pending issues concerning sharing of waters, resolving continental shelf issues in the Bay of Bengal, bringing down border incidents to zero, and managing the media.
- Regular exchanges between younger entrepreneurs and civil society based on areas such as culture, music, sports, films, and sharing of best practices in sustainable development, human capital development, gender equitable growth, amongst others, needs to be pursued.
- Increasing tourist footfall at select border locations from both sides and facilitating a mechanism of exchange through the creation of a common entertainment zone at the border can help strengthen the camaraderie.
- There is a need to jointly work towards a new paradigm of security at the shared borders. A paradigm that enables borders to be not merely thick lines which demarcate national boundaries but act as “connector zones” for inclusive growth and prosperity.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Q. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- The value of Indo-Sri Lanka trade has consistently increased in the last decade.
- “Textile and textile articles” constitute an important item of trade between India and Bangladesh.
- In the last five years, Nepal has been the largest trading partner of India in South Asia.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- As per data from the Department of Commerce, Indo-Sri Lanka bilateral trade value for a decade (2007 to 2016) was 3.0, 3.4, 2.1, 3.8, 5.2, 4.5, 5.3, 7.0, 6.3, 4.8 (in billion USD). It reflects continuous fluctuation in the trend of trade value. There has been an overall increase but the same cannot be said as a consistent rise in trade value. Hence statement 1 is not correct.
- Bangladesh has been a major textile trading partner for India, with a share of more than 5% in exports and over 7% in imports. While annual textile exports to Bangladesh averages $2,000 million, imports are worth $400 (Year: 2016-17).
- The major items of exports are fibre and yarn of cotton, man-made staple fibres and man-made filaments while major import items include apparel and clothing, fabric and other made-up textile articles. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- According to the data, in 2016-17, Bangladesh isIndia’s largest trading partner in South Asia, followed by Nepal, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Bhutan, Afghanistan and Maldives. The level of Indian exports also follows the same order. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.