India's Ageing Workforce | 26 Aug 2023
For Prelims: India's Ageing Workforce, CMIE's (Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy), Stable employment opportunities, Informal Sector.
For Mains: Concerns over India's Ageing Workforce.
Why in News?
Despite having the largest youth population globally, India's workforce is ageing rapidly according to an analysis of India's workforce using data from CMIE's (Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy)’s Economic Outlook, which is a concerning trend.
- An ageing workforce basically means that if one looks at all the employed people in India, the share of young people is going down while the share of those closer to 60 years of age is going up.
What are the Key Highlights of the Analysis?
- Age Groups and Workforce Composition:
- The analysis categorizes the workforce into three distinct age groups to better understand the ageing workforce trend,
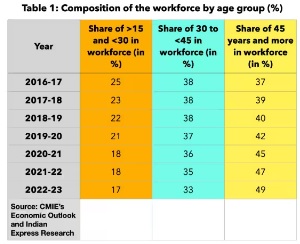
- Aged 15-29 years: The share of this age group in the total workforce has decreased from 25% in 2016-17 to 17% in the financial year 2022-23.
- Aged 30-44 years: The share of individuals in this age group has also declined from 38% to 33% over the same period.
- Aged 45 years and older: This age category's share has grown significantly, increasing from 37% to 49%.
- The analysis categorizes the workforce into three distinct age groups to better understand the ageing workforce trend,
- Falling Employment Rates Among Youth:
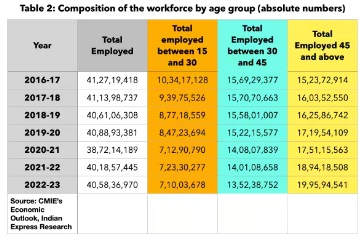
- While the youth population has grown by 2.64 crore (from 35.49 crore in 2016-17 to 38.13 crore in 2022-23), the number of employed individuals in this group has fallen by a staggering 3.24 crore.
- Consequently, the employment rate for this age group has plummeted from 29% to 19% over seven years.
- Varying Impact on Different Age Groups:
- While the decline in employment rates is most pronounced among the youth, the trend extends to other age groups as well, albeit to a lesser extent.
- Notably, the oldest age category (45 years and above) has experienced a relatively smaller decline in employment rates and has actually seen an increase in the absolute number of employed individuals.
What are the Factors Contributing to an Ageing Workforce?
- Lack of Adequate Job Opportunities:
- One of the primary reasons for the declining youth employment is the lack of sufficient job opportunities.
- The rapid growth of the youth population has not been matched with a proportional increase in available jobs, leading to intense competition for limited positions.
- Skill Mismatch:
- A mismatch between the skills possessed by the youth and the skills required by the job market can result in higher rates of unemployment.
- The education system may not be adequately preparing young individuals for the evolving job landscape, leading to underemployment or unemployment.
- Informal Sector Dominance:
- A significant portion of India's workforce is engaged in the informal sector, which often lacks stable employment opportunities and social security benefits.
- Youth entering the job market may find it challenging to secure stable and formal employment, leading to instability and underutilization of skills.
- Educational Attainment and Aspirations:
- While educational attainment is rising among the youth, there may be a disconnect between the skills acquired through education and the skills demanded by the job market.
- Aspirations for higher-level jobs might lead to a situation where youth are willing to wait for suitable positions, contributing to a decline in youth employment.
What are the Concerns and Implications of the Ageing Indian Workforce?
- Productivity:
- Older employees might experience reduced productivity due to health issues and declining physical abilities. This could impact overall economic output.
- There may be an increased demand for healthcare services, which could strain the healthcare system and affect both public and private spending.
- Innovation:
- Younger workers often bring fresh perspectives and technological savviness, which can drive innovation in industries.
- An ageing workforce lacks this dynamism.
- Younger workers often bring fresh perspectives and technological savviness, which can drive innovation in industries.
- Economic Growth:
- A declining workforce can impact economic growth potential, as a smaller working-age population contributes less to production and consumption.
- Sectors that rely heavily on manual labor, such as construction and manufacturing, might face labor shortages if younger workers are not available to replace older ones.
- Skill Shortages:
- An aging workforce can create skill shortages, particularly in industries that require specialized knowledge.
- This can hinder technological progress and innovation.
- Consumption Patterns:
- Older individuals often have different consumption patterns, focusing more on savings and essential goods, which can impact consumer demand and industries geared toward luxury goods.
Way Forward
- Policies that discourage early retirement and incentivize older individuals to remain in the workforce can help extend their productive years.
- This could include flexible retirement age, reduced working hours, and financial incentives.
- Companies can adopt age-inclusive workplace policies that address the needs of older workers, such as ergonomic facilities, health support, and opportunities for upskilling
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. Performance of welfare schemes that are implemented for vulnerable sections is not so effective due to the absence of their awareness and active involvement at all stages of the policy process – Discuss. (2019)