Impact of Early Smartphone Use on Adolescents | 29 Jan 2025
For Prelims: Anxiety, PRAGYATA guidelines, E-PG Pathshala, Metaverse, Virtual Reality, National Human Rights Commission, CHILDLINE 1098, Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing, National Educational Alliance for Technology
For Mains: Digital platforms and its impact on children, Cyber Security and Privacy, Technology and Society.
Why in News?
A study by Sapien Labs, titled “The Youth Mind: Rising Aggression and Anger”, highlights the troubling link between early smartphone use and deteriorating mental well-being in adolescents aged 13-17 in India and the US.
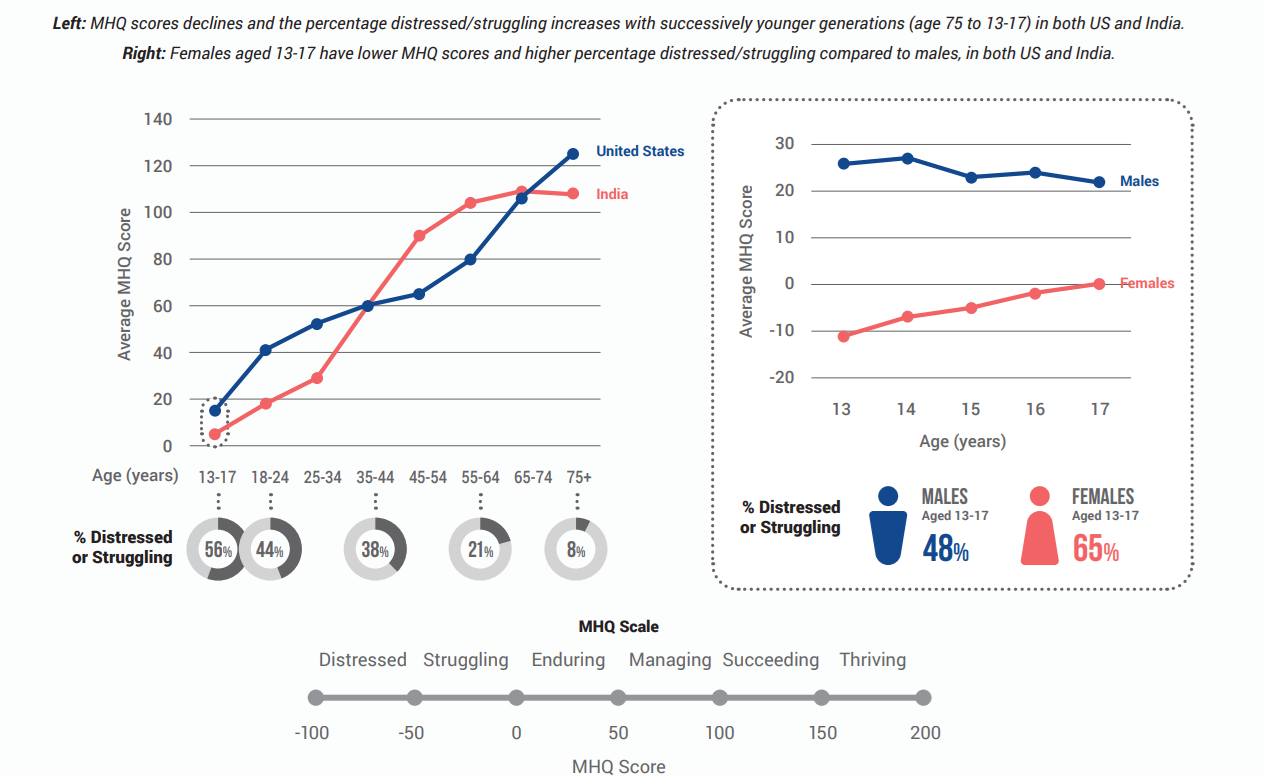
What are the Key Findings of the Study?
- Smartphone Use and Mental Health: The study based on Mind Health Quotient (MHQ) of adolescents reveals a significant correlation between the early initiation of smartphone use and the decline in mental health among adolescents, with symptoms such as aggression, anger, irritability, and hallucinations becoming more prevalent.
- Adolescents who start using smartphones at a younger age show more pronounced mental health issues.
- In addition to sadness and anxiety, new symptoms like intrusive thoughts and detachment from reality were observed, indicating a deeper mental health crisis.
- Online Exposure Risks: Early smartphone access exposes young people to inappropriate content, disrupts sleep, and reduces in-person interactions, which are vital for developing social skills and coping with conflict.
- Gender Differences: The study points out that females are particularly vulnerable, with rising aggression and anger being observed more frequently among girls.
- Notably, 65% of adolescent girls reported distress, significantly higher than boys.
- Cultural Differences: The decline in mental well-being is slower in India compared to the US.
- The decline in mental well-being is evident in both males and females in the US, but only females in India show a decline, with some aspects improving in males.
- Educational Technology as a Solution: The study suggests using educational technology and restricted access to smartphones with parental controls as potential solutions to mitigate the mental health impact.
Mind Health Quotient (MHQ)
- About: The MHQ is a comprehensive assessment of 47 aspects of mental function, measured across six dimensions (Mood and Outlook, Adaptability and Resilience, Social Self, Drive and Motivation, Cognition, and Mind-Body Connection).
- The aggregate MHQ score correlates with functional productivity, with higher scores linked to more productive days.
- Unlike "mental wellbeing," which focuses on emotional states, "mind health" encompasses both emotional and functional aspects, emphasizing the ability to navigate life's challenges and maintain productivity.
- MHQ Vs IQ and EQ: MHQ differs from Intelligence Quotient (IQ ) (measures cognitive abilities) and Emotional Quotient (EQ) (measures emotional intelligence (EI)).
- MHQ encompasses a broader range of mental functions, including mood, resilience, and mind-body connection.
What is the Impact of Early Digital Access to Children?
- The proliferation of the internet and social media has been a double-edged sword for children. While on one hand it has democratized learning for millions, on the other it has exposed children to harmful and toxic behaviours.
- Positive Impacts:
- Enhanced Learning Opportunities: Digital access offers a wealth of educational resources, and India’s initiatives like tablet sets pre-loaded with educational content, and PRAGYATA guidelines ensure that students focus on learning while limiting distractions.
- E-PG Pathshala provides access to online courses and collaborative learning, especially for students in remote areas.
- Personalised Learning: Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence -based platforms adapt to students' learning styles, providing customized educational experiences.
- Digital tools like games, simulations, and interactive platforms can make learning more engaging, helping children develop skills in various subjects, such as math, language, and science.
- Skills Development: Exposure to digital technology can help children develop important skills like problem-solving, coding, and digital literacy, which are vital in today’s technology-driven world.
- In recent years, "Kidfluencers" have driven a booming social media advertising industry, with children earning significant amounts through sponsored content.
- Social Connection: Helps reduce loneliness by keeping kids connected with family and friends.
- Access to Support: Provides easy access to mental health resources and coping strategies.
- Enhanced Learning Opportunities: Digital access offers a wealth of educational resources, and India’s initiatives like tablet sets pre-loaded with educational content, and PRAGYATA guidelines ensure that students focus on learning while limiting distractions.
- Negative Impacts:
- Physical Inactivity: Adolescence is crucial for developing emotional habits, with factors like sleep, physical activity, coping skills, and supportive relationships promoting well-being.
- However, early digital access to children leads to sedentary behavior, affecting both physical and mental health.
- Screen Addiction can cause anxiety, depression, and sleep problems and brain rot, leading to mental stagnation and reduced cognitive function.
- Privacy: Violations by tech companies, hackers, or advertisers can lead to identity theft, fraud, manipulation, and exposure to harmful content.
- Cyberbullying: Increases vulnerability to online harassment, impacting self-esteem.
- Children can fall victim to extortion or online exploitation by predators who manipulate or threaten them using personal information or explicit content.
- The internet exposes children to the risk of encountering pornography, as unfiltered content can lead to accidental exposure or targeted exploitation, raising serious legal, psychological, and safety concerns.
- In the realm of the Metaverse and Virtual Reality, virtual predators exploit children through scams, harassment, and discrimination, fostering an environment ripe for cyberbullying.
- FOMO: Social media often presents an idealised life, causing young people to feel like they're missing out (Fear of Missing Out (FOMO), leading to anxiety, stress, and inadequacy.
- Reduced Social Interaction: Excessive phone use can decrease face-to-face interactions, hindering social skills.
- Violence: Exposure to online violence, including violent games and graphic content, can desensitize children, normalize aggression, and lead to increased fear and emotional distress.
- Young internet users are vulnerable to recruitment by extremist and terrorist groups.
- Physical Inactivity: Adolescence is crucial for developing emotional habits, with factors like sleep, physical activity, coping skills, and supportive relationships promoting well-being.
Online Child Safety Statistics
- Mental Health: According to the World Health Organization (WHO) globally, 1 in 7 adolescents faces a mental disorder, contributing to 15% of the disease burden, with depression, anxiety, and behavioral disorders as leading causes, and early digital access being a key contributor.
- Neglecting adolescent mental health can lead to lasting physical and mental health issues, limiting opportunities for a fulfilling adult life.
- Cyberbullying: Over a third of young people in 30 countries report being cyberbullied, with 1 in 5 skipping school because of it.
- Online Sexual Exploitation: 80% of children in 25 countries report feeling in danger of online sexual abuse or exploitation.
- Children in India are at high risk of exposure to child sexual abuse material (CSAM) due to the rapid increase in internet usage and the availability of harmful content.
- According to the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC), India accounted for 5.6 million reports of CSAM out of 32 million globally in 2022, highlighting a significant problem.
What are India's initiatives to Protect Children Online and Productive Digital Access?
- Protect Children Online:
- POSCO Act (Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act), 2012: The POSCO Act has provisions to protect children from online sexual offences, including mandatory reporting and child-friendly procedures.
- CHILDLINE 1098: It is a National, 24 Hour, Emergency toll free phone service for children in need of care and protection. It is a project of The Ministry of Woman and Child Development.
- Digital Literacy Programs: The Ministry of Education and CBSE have incorporated cyber safety in school curricula to educate children on safe internet use.
- Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000: Section 67B of the IT Act, imposes stringent punishments for publishing or viewing CSAM online.
- Cyber Crime Prevention against Women and Children (CCPWC): The CCPWC is a Nirbhaya Fund project that raises awareness, strengthens law enforcement capacity, and enhances cyber forensic facilities.
- Productive Digital Access:
Way Forward
- Child Online Safety Toolkit: Install the Child Online Safety Toolkit on children's devices, this toolkit provides a hands-on, comprehensive approach to safeguarding young users online.
- It aligns with international frameworks like the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child (UNCRC), addressing key issues such as cyberbullying, emotional intelligence, and mental health.
- Delay Smartphone Ownership: Delaying smartphone ownership (until at least 8th grade) could help reduce aggression, anxiety, and suicide rates among adolescents, urging action from parents, schools, and governments.
- Stronger Regulations: Some countries, like Australia, have already taken steps to protect children by banning social media use for those under the age of 16.
- Implement the draft Data Protection Rules, 2025, through which India has introduced requirements for age verification and parental consent for children under 18 to access social media.
- Awareness: Promote digital literacy programs that teach children about the potential dangers of online spaces and equip them with skills to identify harmful content, cyberbullying, and online predators.
- Mental Health Support: Invest in accessible mental health resources like National Tele Mental Health Programme, Kiran Helpline, and MANAS Mobile App for children and adolescents, offering counseling and coping strategies for those impacted by excessive screen time and online exploitation.
|
Drishti Mains Question: How can early smartphone use impact the mental health of adolescents? Discuss the implications and possible measures to mitigate these effects. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Mains
Q. In order to enhance the prospects of social development, sound and adequate health care policies are needed particularly in the fields of geriatric and maternal health care.Discuss. (2020)
Q. What are the different elements of cyber security ? Keeping in view the challenges in cyber security, examine the extent to which India has successfully developed a comprehensive National Cyber Security Strategy. (2022)

.png)