Biodiversity & Environment
Impact of Disasters on Agriculture and Food Security: FAO
- 26 Oct 2023
- 7 min read
For Prelims: Impact of Disasters on Agriculture and Food Security, Food and Agriculture Organization, Extreme Disaster, Climate Change, Food Security, Rain-Fed agriculture.
For Mains: Impact of Disasters on Agriculture and Food Security, Poverty and developmental issues, Issues relating to poverty and hunger.
Why in News?
Recently, the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) has released a report titled 'The Impact of Disaster on Agriculture and Food Security' stating that the frequency of Extreme Disaster events has risen significantly over the past 50 years.
- The report estimated losses caused by disasters on agricultural production over the past three decades and delves into the diverse threats and impacts affecting the crops, livestock, forestry, and fisheries and aquaculture subsectors.
- It analyzed the complex interplay of underlying risks, such as Climate Change, Pandemics, Epidemics and Armed conflicts, and how they drive disaster risk in agriculture and Agrifood systems at large.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Magnitude of Agricultural Losses:
- Over the last 30 years, an estimated USD 3.8 trillion worth of crops and livestock production has been lost due to disaster events.
- This translates to an average annual loss of USD 123 billion, which is approximately 5% of the global agricultural Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- Agriculture is one of the most highly exposed and vulnerable sectors in the context of disaster risk, given its profound dependence on natural resources and climate conditions.
- Recurrent disasters have the potential to erode gains in food security and undermine the sustainability of agrifood systems.
- Impact on Different Countries:
- Disasters have the highest relative impact on lower and lower middle-income countries, where they can cause losses of up to 15 % of their total agricultural GDP.
- Small Island Developing States (SIDS) also experience significant losses, amounting to nearly 7% of their agricultural GDP.
- Losses by Product Groups:
- There are increasing trends in losses related to major agricultural products.
- Cereals are the most affected, followed by fruits and vegetables and sugar crops, with average losses of millions of tonnes each year.
- Meats, dairy products, and eggs also show substantial losses.
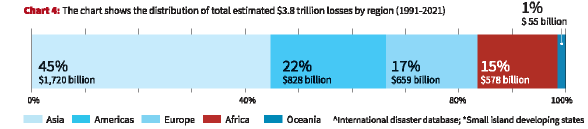
- Regional Differences:
- Asia experiences the largest share of total economic losses, followed by Africa, Europe, and the Americas.
- However, in Asia, these losses account for a smaller percentage of agricultural added value compared to Africa.
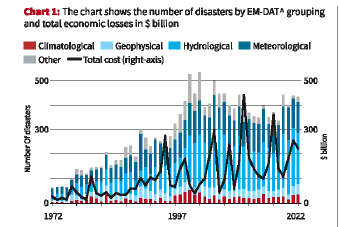
- Increasing Frequency of Disasters:
- Disaster events have been on the rise, increasing from 100 per year in the 1970s to around 400 events per year worldwide in the past two decades.
- These events are becoming more frequent, intense, and complex, with expected worsening impacts due to climate-induced disasters.
- Impact on Vulnerable Groups:
- Small-scale farmers, particularly those practicing Rain-Fed agriculture, are the most vulnerable to disaster impacts.
- Supporting the adoption of farm-level disaster risk reduction practices can help reduce losses and enhance resilience.
- Investment in farm-level disaster risk reduction good practices can perform on average 2.2 times better than previously applied practices.
What are the Recommendations?
- Proactive and timely interventions, such as anticipatory actions in response to forecasted hazards, can significantly reduce disaster risks in agriculture.
- For every USD 1 invested in anticipatory action, rural families can gain up to USD 7 in benefits and avoided agricultural losses.
- The report outlines three key priorities for addressing the impact of disasters on agriculture:
- Improving data and information on disaster impacts, developing multi-sectoral and multi-hazard disaster risk reduction approaches, and enhancing investments in resilience to reduce disaster risk in agriculture and improve livelihoods.
What is the Food and Agriculture Organization?
- About:
- FAO is a specialised agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger.
- World Food Day is celebrated every year around the world on 16th October. The day is celebrated to mark the anniversary of the founding of the FAO in 1945.
- It is one of the UN food aid organisations based in Rome (Italy). Its sister bodies are the World Food Programme and the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD).
- FAO is a specialised agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger.
- Initiatives Taken:
- Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS).
- Monitors the Desert Locust situation throughout the world.
- The Codex Alimentarius Commission or CAC is the body responsible for all matters regarding the implementation of the Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme.
- The International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture was adopted by the Thirty-First Session of the Conference of the FAO in 2001.
- Flagship Publications:
- The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture (SOFIA).
- The State of the World's Forests (SOFO).
- The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World (SOFI).
- The State of Food and Agriculture (SOFA).
- The State of Agricultural Commodity Markets (SOCO).
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. The FAO accords the status of ‘Globally Important Agricultural Heritage System (GIAHS)’ to traditional agricultural systems. What is the overall goal of this initiative? (2016)
- To provide modern technology, training in modern farming methods and financial support to local communities of identified GIAHS so as to greatly enhance their agricultural productivity.
- To identify and safeguard eco-friendly traditional farm practices and their associated landscapes, agricultural biodiversity and knowledge systems of the local communities.
- To provide Geographical Indication status to all the varieties of agricultural produce in such identified GIAHS.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)