Rapid Fire
Human Interaction Threat to Lion-Tailed Macaques
- 26 Dec 2024
- 1 min read
The endangered lion-tailed macaque (LTM) faces threats from increasing human interactions, driven by habitat encroachment and food provisioning.
- Human-provided food causes malnutrition, disease, dependency, and increases risks of road accidents and human aggression.
- LTM is highly adaptable to human-altered environments and frequently interacts with humans.
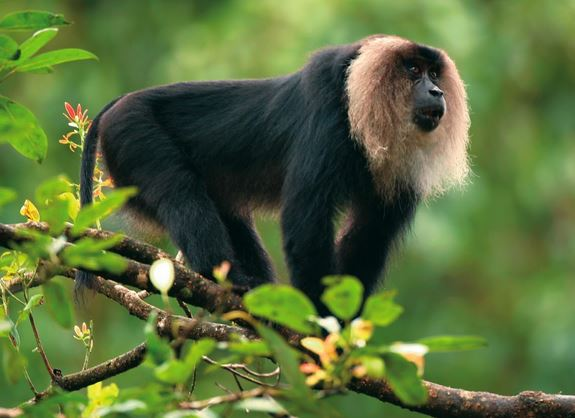
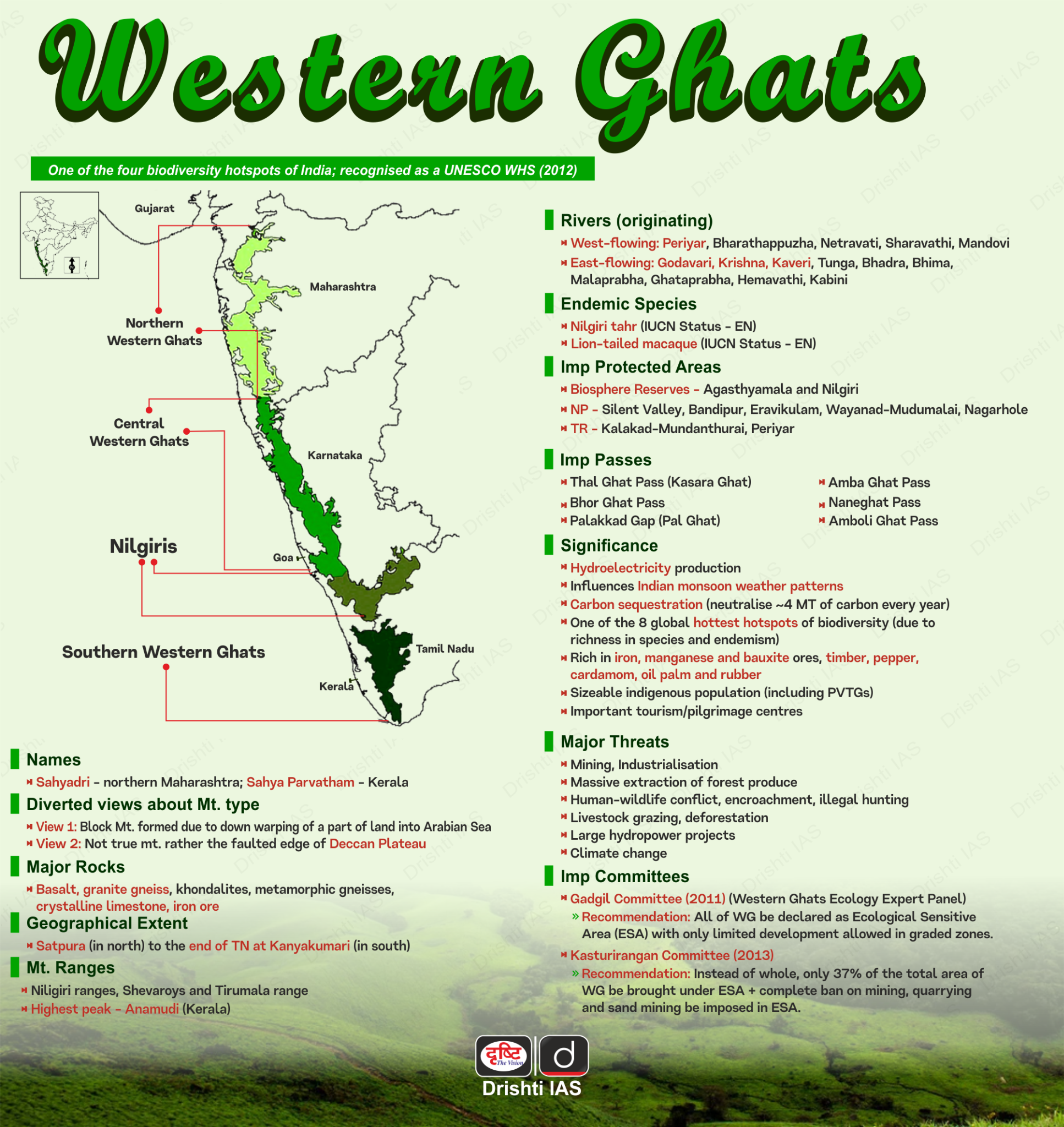
- About Lion-tailed Macaque:
- They are old world monkeys endemic to the Western Ghats of India.
- Their key habitats include the Anamalai Hills, Nelliyampathy, Nilambur Ghats, Sholayar, Gavi, Sabarimala, Vallimalai Hills and Agumbe of the Western Ghats.
- The lion-tailed macaque's black fur and light mane around its head and chin give it the nickname "beard ape."
- Dominant males of the group emit loud, human-like ‘whoops’ to alert outsiders entering their territory.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
- They are old world monkeys endemic to the Western Ghats of India.
Read More: Lion-Tailed Macaques