World History
Holocaust and World War II
- 20 Jun 2024
- 13 min read
For Prelims: World War I, World War II, Decolonisation, Artificial Intelligence
For Mains: Causes and Effects of World War II, Rise of Global Powers, Rise of United Nations, Ethical Usage of AI, Types and Concerns on AI.
Why in News?
- Recently, the United Nations (UN) report has warned that Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology is being used to spread misinformation and hate-driven stories about World War II atrocities.
- It also warns that AI can also unintentionally create untrue or deceptive content related to the Holocaust, which can pose a significant risk of fueling the spread of anti-Semitism (hatred, prejudice for Jewish people).
What was Holocaust Incident?
- About:
- The word ‘holocaust’ comes from the Greek “holokauston”, meaning “an offering consumed by fire”.
- It refers to the systematic state-sponsored persecution and murder of around 6 million European Jews by Adolf Hitler’s Nazi regime.
- It took place between 1941 and 1945, with the planning and early persecution phases beginning as early as 1933 when Adolf Hitler came to power in Germany.
- Reason:
- The Nazis, motivated by antisemitism and a commitment to racial purity, saw Jews as a danger to the Aryan race. They also singled out other groups due to their racial, ideological, and political convictions.
- Historical Context:
- The defeat of Germany in World War I (1914-18) and the subsequent global economic depression of the 1930s created a tumultuous environment in the country which led to the rise of Nazi Party, led by Adolf Hitler.
- Hitler was appointed as the German Chancellor in 1933, and he immediately set out to consolidate his control over the government and the country.
- Once in power, Hitler moved swiftly to suppress all political opposition, curb press freedom, and begin the systematic persecution of various groups deemed undesirable by the Nazi regime.
- The groups targeted for persecution by the Nazis included homosexuals, Romani people, individuals with disabilities, and most notably, the Jewish population.
- Persecution of Jews:
- Jewish constituted less than 1% of Germany’s population but the community was perceived as economically privileged.
- Hitler's ideology blamed Jewish people for Germany’s World War I defeat and the economic hardships of the 1930s.
- A series of laws were enacted to strip Jews of their civil and political rights, and Nazi paramilitaries terrorised Jewish communities.
- The situation escalated dramatically with events like Kristallnacht (the Night of Broken Glass) in 1938, during which Nazi mobs destroyed Jewish-owned businesses, synagogues, and homes, and assaulted and killed numerous Jews.
- As persecution intensified, the outbreak of World War II in 1939 following Germany’s invasion of Poland exacerbated the plight of the Jewish population.
- This invasion marked the beginning of Hitler’s aggressive expansionism aimed at securing “lebensraum” (living space) for the German people.
- The Final Solution:
- The "Final Solution to the Jewish Question” was a systematic and organised effort by Nazis for genocide of millions of Jews to eradicate the Jewish population.
- The Nazis believed that killing the Jews would be more "efficient" than forcing them to migrate.
- The plan began with the increasing ghettoization (isolation) of Jewish people, followed by forced deportations to concentration camps.
- Millions of Jews were sent to concentration camps, where they were forced to do labour and kept in appalling conditions.
- Some of the concentration camps were equipped with sophisticated gas chambers, which were used for the collective murder of Jews and other "undesirable" population groups.
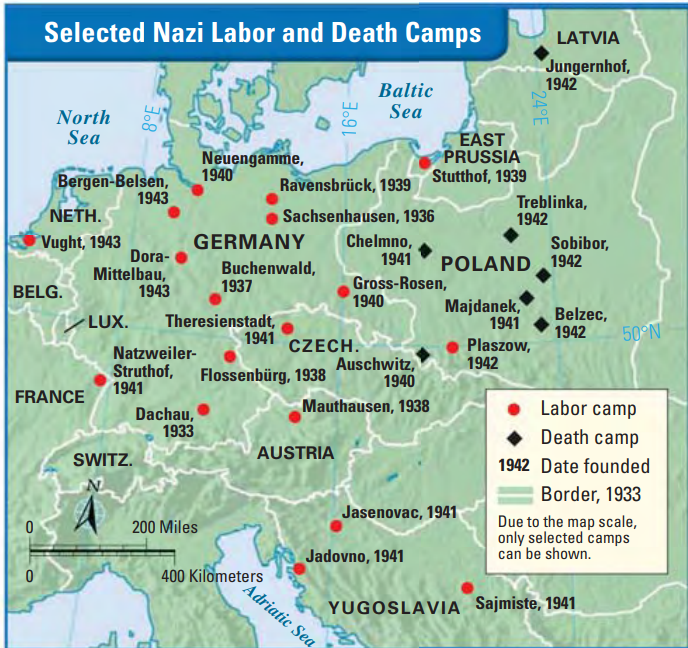
- Auschwitz and the Concentration Camps:
- Concentration camps were places of imprisonment to confine and persecute people deemed undesirable or a threat.
- Auschwitz (in Poland) was the largest Nazi concentration camp.
- It became a symbol of the Holocaust's brutality as over 1.1 million people, mostly Jews, perished there from torture, starvation, disease, and gas chambers.
- Liberated in 1945, the camp now serves as a memorial to the victims.
- International Holocaust Remembrance Day:
- Auschwitz became infamous for the cruelty and inhumane treatment inflicted upon its prisoners by the camp guards, who frequently subjected them to torture and abuse out of sheer malice and sadistic pleasure.
- The liberating of the camp by the Red Army (armed forces of the Soviet Union) on 27th January 1945 brought an end to its horrific operations, a date that is now observed globally as International Holocaust Remembrance Day to honour the memory of the victims.
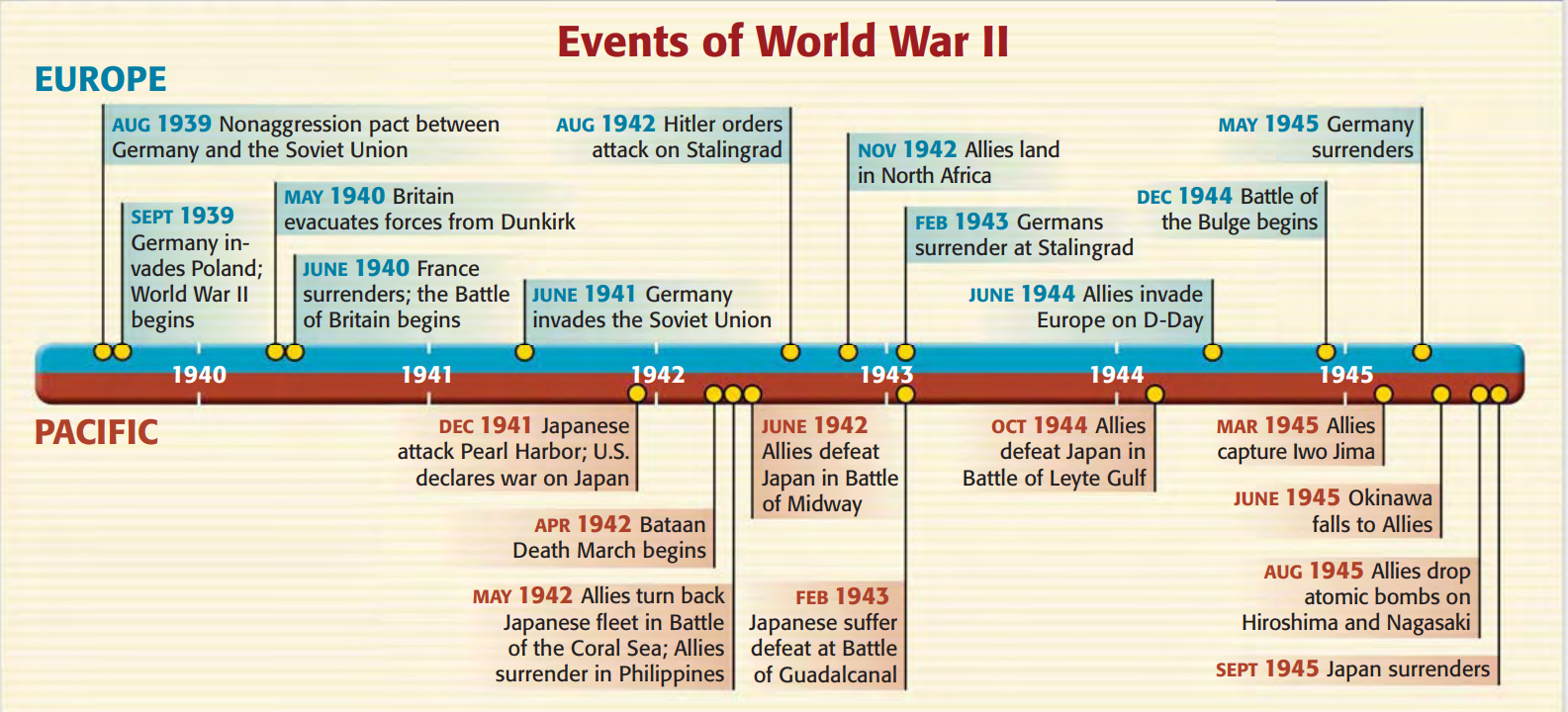
What was World War II?
- About:
- World War II (1939-1945) is one of the most significant and devastating conflicts in human history.
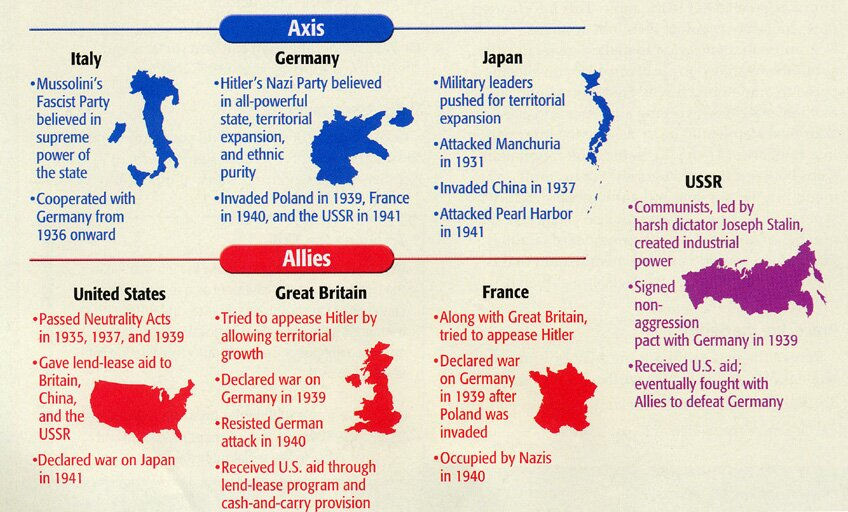
- It was fought between the Axis powers (Germany, Italy, and Japan) and Allied powers (France, Great Britain, the United States, the Soviet Union, and, to a lesser extent, China).
- Nearly some 100 million people had been militarised, and 50 million had been killed (around 3% of the world's population).
Note
- World War I (1914-18) was fought between Allied Power (France, Russia and Britain) and Axis (Central) Power (Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Bulgaria) in which Allied Powers won
- Causes of War:
- The Treaty of Versailles: After World War I, the victorious Allied Powers forced Germany to sign the Treaty of Versailles, which made Germany accept guilt for the war, pay reparations, lose territory, and prohibited them from having a large military.
- This humiliation paved the way for the spread of Ultra-Nationalism and Nazi regime under Adolf Hitler in Germany.
- Failure of League of Nations: The League of Nations, established in 1919 to maintain global peace, ultimately failed due to not all countries joining and lacking an army to prevent military aggression.
- Examples include League's inability to intervene in conflicts, such as the Italian invasion of Ethiopia and the Japanese invasion of Manchuria, undermining its credibility and effectiveness.
- The Great Depression: The global economic depression of the 1930s exacerbated political and social instability in many countries, contributing to the rise of extremist movements.
- The economic difficulties faced by countries like Germany and Japan led them to pursue aggressive expansionist policies to secure resources and markets.
- The Rise of Totalitarian Regimes: The establishment of authoritarian and totalitarian regimes, such as Nazi Germany, Fascist Italy, and Imperial Japan, with their expansionist and militaristic ideologies, was a major factor in the outbreak of the war.
- These regimes sought to expand their power and influence, often through the use of military force.
- The German Invasion of Poland (1939): The invasion was a violation of the Munich Agreement and was the immediate trigger for the outbreak of World War II.
- This invasion prompted declarations of war from France and the United Kingdom against Germany, marking the beginning of the war in Europe.
- The Japanese Expansion in Asia: The Empire of Japan's aggression in Asia, including the invasion of China and the attack on Pearl Harbor in 1941, brought the United States into the conflict.
- Japan's expansionist policies and desire to control resources and territories in the Pacific region contributed to the outbreak of the war in the Pacific.
- The Treaty of Versailles: After World War I, the victorious Allied Powers forced Germany to sign the Treaty of Versailles, which made Germany accept guilt for the war, pay reparations, lose territory, and prohibited them from having a large military.
- The End of the War and its Aftermath:
- End of War: The war in Europe ended with the surrender of Germany on 8th May 1945, following the capture of Berlin and the suicide of Adolf Hitler.
- The war in the Pacific concluded with the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, leading to Japan's surrender on 15th August 1945.
- New Superpowers: World War II brought about changes in the status of countries and continents. Britain and France lost their positions of preeminence as superpowers and yielded place to the USA and the USSR.
- Start of Decolonisation: After World War II, Britain and France faced significant domestic and international challenges that weakened their control over their vast colonial empires, which led to decolonisation in Africa and Asia and redrawing of boundaries to establish sovereign nation-states.
- End of War: The war in Europe ended with the surrender of Germany on 8th May 1945, following the capture of Berlin and the suicide of Adolf Hitler.
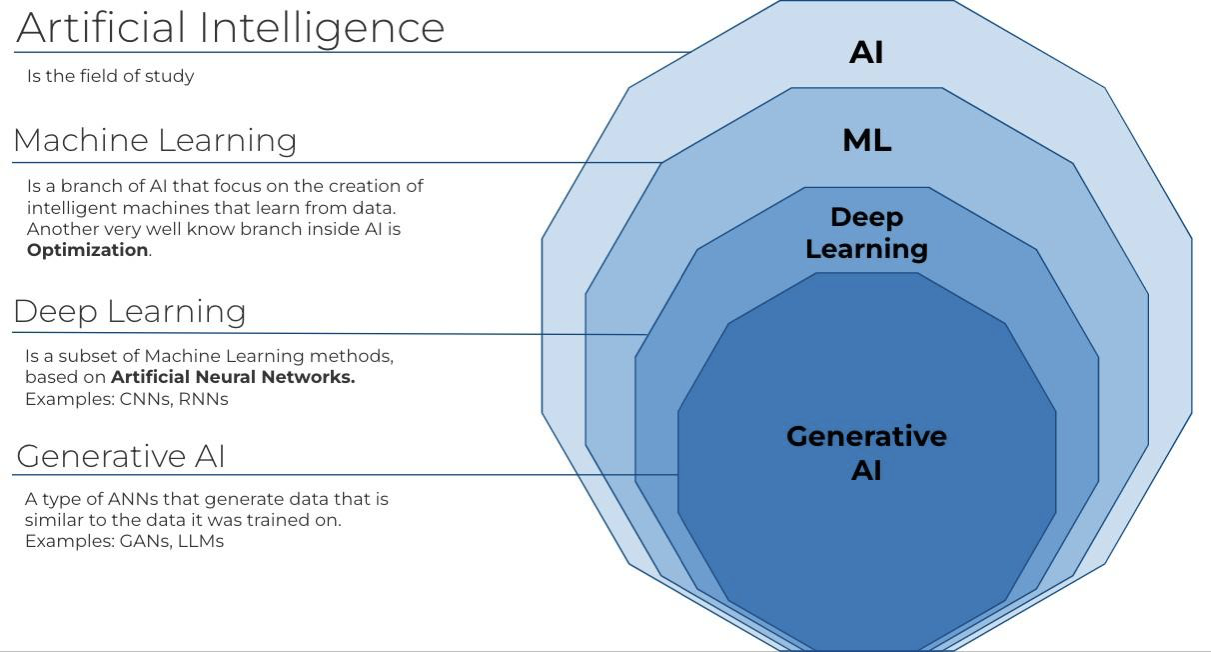
Artificial Intelligence
- Artificial intelligence, or AI, is technology that enables computers and machines to simulate human intelligence and problem-solving capabilities.
- It is the ability of a computer, or a robot controlled by a computer to do tasks that are usually done by humans because they require human intelligence and discernment.
- Characteristics & Components:
- The ideal characteristic of artificial intelligence is its ability to rationalize and take actions that have the best chance of achieving a specific goal. A subset of AI is Machine Learning (ML).
- Deep Learning (DL) techniques enable this automatic learning through the absorption of huge amounts of unstructured data such as text, images, or video.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q.1 Critically evaluate the role of the ideological factors, particularly the rise of fascism and Nazism, in leading to World War II. How did the failure of appeasement contribute to the outbreak of the war? Q.2 Analyze the differences between Nazism and Fascism. Q.4 To what extent can the policy of 'appeasement' be blamed for the outbreak of the Second World War? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)