Important Facts For Prelims
Hirakud Dam Canal System Renovation
- 07 Oct 2024
- 4 min read
Why in News?
The six-decade-old canal system connected to Odisha's Hirakud Dam is set for a major renovation.
- This initiative aims to modernise irrigation infrastructure, reduce water wastage, and enhance agricultural productivity, providing much-needed support to farmers in the region.
What are the Key Objectives of the Renovation?
- Need for Renovation: Many canal infrastructures, including the Bargarh and Sasan main canals, are in disrepair.
- Existing earthen canals cause significant water loss, reducing irrigation efficiency.
- Water seepage makes some farmland unsuitable for farming, complicating challenges for local farmers.
- Key Features of the Renovation: Conversion of all earthen water courses to concrete paths for improved water distribution and management.
- The project will enhance water availability in tail-end areas for better farmer access.
- Impact on Local Farmers: Aims to reduce the gap between irrigation potential and actual usage. Enhanced irrigation capabilities will benefit farmers and increase crop yields.
What are the Key Facts About the Hirakud Dam?
- About: It is a multipurpose scheme conceived by Er. M. Visveswaraya in 1937, after a recurrence of devastating floods in the Mahanadi River.
- Built around 1952-53, the Hirakud Dam is one of India’s first major multipurpose river valley projects post-independence.
- It holds the title for the longest major earthen dam globally, stretching 25.8 km across the Mahanadi River.
- It was inaugurated by the then Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru in 1957.
- Hirakud Dam forms the Hirakud Reservoir, also known as Hirakud Lake, is one of the largest artificial lakes in Asia. Hirakud Reservoir was declared a Ramsar site in 2021.
- Purpose and Benefits: The dam has an installed capacity of 359.8 MW for hydroelectric power generation, contributing to the region's energy supply.
- The reservoir irrigates 436,000 hectares of land, benefiting farmers in the region.
- Cattle Island: It is located in one of the extreme points of Hirakud Reservoir. It is inhabited by a large herd of wild cattle.
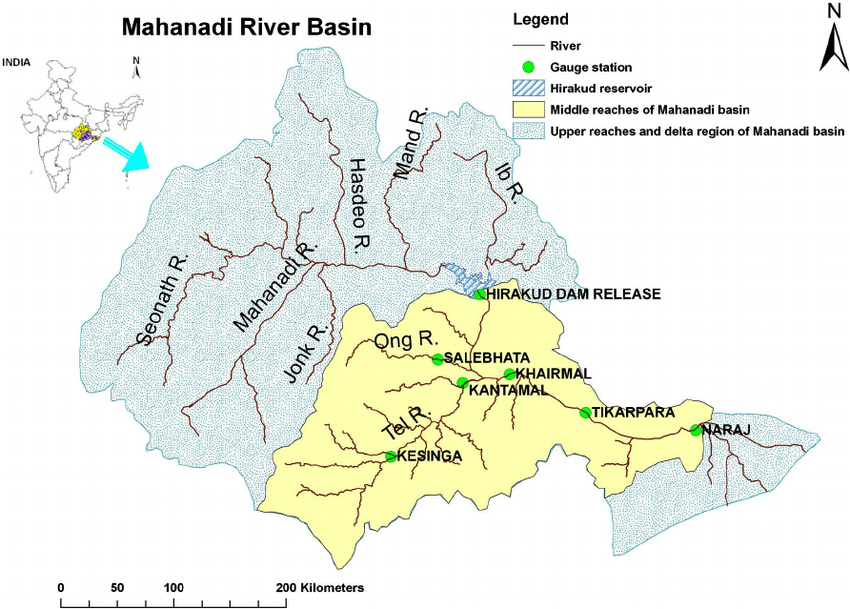
Mahanadi River
- Origin: The river originates from Sihawa range of hills in the Dhamtari district of Chhattisgarh.
- Mouth: It flows into the Bay of Bengal at False Point, Jagatsinghpur in Odisha.
- Tributaries:
- Left Bank: Seonath, Mand, Ib, Hasdeo, and Kelo.
- Right Bank: Ong, Parry, Jonk, and Telen.
- Basin and Geography: The Mahanadi basin extends over states of Chhattisgarh and Odisha and comparatively smaller portions of Jharkhand, Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh.
- It is bounded by the Central India hills on the north, by the Eastern Ghats on the south and east and by the Maikala range on the west.
- The Mahanadi is one of the major rivers of the country and among the peninsular rivers, in water potential and flood producing capacity, it ranks second to the Godavari.