High Seas Treaty | 12 Jul 2024
For Prelims: Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) Agreement, High Seas Treaty, UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), 1958 Geneva Convention on the High Seas, Exclusive Economic Zone, climate change, El Nino, Ocean Acidification, Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA), Security and Growth for All in the Region (SAGAR), Sustainable Development Goals (SDG).
For Mains: Treaty on the High Seas, Significance for India and the World
Why in News?
Recently, India has decided to endorse and approve the Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) Agreement also called High Seas Treaty.
- This global agreement is designed to safeguard high seas marine biodiversity through collaboration at international level and it will operate within the framework of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
What are High Seas?
- About:
- According to the 1958 Geneva Convention on the High Seas, parts of the sea that are not included in the territorial waters or the internal waters of a country are known as the high seas.
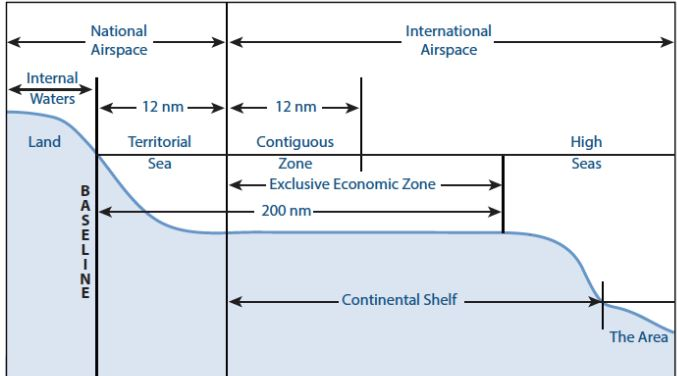
- It is the area beyond a country’s Exclusive Economic Zone (that extends up to 200 nautical miles from the coastline) and till where a nation has jurisdiction over living and non-living resources.
- No country is responsible for the management and protection of resources on the high seas.
- Significance:
- The high seas cover over 64% of the world's oceans and 50% of the Earth's surface, making them vital for marine life.
- They are home to around 270,000 known species, with many yet to be discovered.
- The high seas regulate climate, absorb carbon, store solar radiation, and distribute heat, crucial for planetary stability and mitigating climate change.
- They are essential for human survival, providing resources like seafood, raw materials, genetic and medicinal resources.
- Threats:
- They absorb heat from the atmosphere and are affected by phenomena like the El Nino, and ocean acidification which is endangering marine flora and fauna.
- Several thousand marine species are at risk of extinction by 2100 if current warming and acidification trends continue.
- Anthropogenic pressures on the high seas include seabed mining, noise pollution, chemical and oil spills and fires, disposal of untreated waste (including antibiotics), overfishing, introduction of invasive species, and coastal pollution.
- Despite these threats, only about 1% of the high seas are currently protected.
- They absorb heat from the atmosphere and are affected by phenomena like the El Nino, and ocean acidification which is endangering marine flora and fauna.
What is the High Seas Treaty?
- About:
- It is formally called the Agreement on Conservation and Sustainable Use of Marine Biological Diversity of Areas Beyond National Jurisdiction. In short, known as BBJN or High Seas Treaty.
- It is a new international legal framework under UNCLOS for maintaining the ecological health of the oceans.
- The treaty was negotiated in 2023 and is meant to reduce pollution, and promote the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity and other marine resources in ocean waters outside the national jurisdiction of any country.
- Key Objectives:
- Conservation and Protection of Marine Ecology: This includes the establishment of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) where activities would be regulated to conserve the marine ecosystem.
- Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits of Marine Resources: The treaty aims to ensure that the benefits from commercially valuable ocean organisms, either through scientific research or commercial exploitation, are shared equally among all countries.
- Mandatory Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA): The treaty makes it mandatory to conduct prior EIA for any activity that could potentially pollute or damage the marine ecosystem, even if the activity is within a country's national jurisdiction but the impact is expected in the high seas.
- Capacity Building and Transfer of Marine Technologies: This will help developing countries to fully utilise the benefits of the oceans while also contributing to their conservation.
- Signing and Ratification:
- Till June 2024, 91 countries have signed the treaty so far, with 8 of them having ratified it. It will become legally binding 120 days after 60 countries ratify it.
- Ratification is the process by which a country agrees to be legally bound to the provisions of an international law, while signing indicates agreement without legal obligation until ratification occurs. The process for ratification varies by country.
- Till June 2024, 91 countries have signed the treaty so far, with 8 of them having ratified it. It will become legally binding 120 days after 60 countries ratify it.
What is the Significance of the High Seas Treaty?
- Addressing the "Global Commons" Challenge:
- The high seas, covering 64% of the ocean, are a global commons, leading to resource overexploitation, biodiversity loss and environmental challenges.
- The UN estimates that approximately 17 million tonnes of plastics were dumped into the oceans in 2021, with this amount expected to increase in the coming years.
- This treaty has been compared to the 2015 Paris Agreement on climate change. It could lead to the protection of the vast ocean and the sustainable use of marine resources.
- The high seas, covering 64% of the ocean, are a global commons, leading to resource overexploitation, biodiversity loss and environmental challenges.
- Complementing UNCLOS:
- BBJN is in line with the principles of the UNCLOS, which forms the overarching legal framework for the oceans.
- UNCLOS sets general principles for equitable access, resource usage, and biodiversity protection in oceans but lacks specific implementation guidelines.
- The High Seas Treaty will address this gap, serving as an implementing agreement under UNCLOS once it comes into force.
- It will provide a legal mechanism to create and manage marine protected areas in the high seas.
- It will ensure the equitable and sustainable use of marine resources, balancing the interests of developed and developing countries.
- BBJN is in line with the principles of the UNCLOS, which forms the overarching legal framework for the oceans.
- Combating Emerging Threats:
- The treaty addresses emerging challenges such as deep-sea mining, ocean acidification, and plastic pollution, which pose grave threats to the health and resilience of the high seas ecosystems.
- Strengthening International Cooperation:
- By establishing a robust institutional framework and decision-making processes, the High Seas Treaty facilitates greater international cooperation and coordination in ocean governance.
- Contribution to Sustainable Development Goals (SDG):
- The successful implementation of this treaty will significantly contribute to the achievement of SDG 14 (Life Below Water).
- Significance for India:
- Global Leadership: India's commitment to ocean governance and marine resource sustainability such as establishing Marine Protected Areas (MPA) underscores its global leadership and makes it an environmental champion.
- Domestic Policy: The treaty's EIA mandate India to align its maritime policies, promoting responsible international cooperation.
- Economic Benefits: Provisions on benefit-sharing from marine genetic resources align with India's Blue Economy goals, offering potential economic gains.
- Strategic Considerations: Ratifying the treaty strengthens India's Indo-Pacific position, supporting a sustainable maritime environment through the SAGAR initiative.
United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)
- The UNCLOS is an international treaty adopted and signed in 1982, replacing the 4 Geneva Conventions of April 1958 related to territorial sea, contiguous zone, continental shelf, high seas, fishing, and conservation of living resources on the high seas.
- It divides oceans into 5 main zones:
What are the Other Conventions related to Seas?
- Convention on Continental Shelf, 1964: It defines and delimits the rights of States to explore and exploit the natural resources of the continental shelf.
-
Convention on Fishing and Conservation of Living Resources of the High Seas, 1966: It was designed to solve the problems involved in the conservation of living resources of the high seas, considering that because of the development of modern technology some of these resources are in danger of being overexploited.
-
London convention 1972: Its objective is to promote the effective control of all sources of marine pollution and to take all practicable steps to prevent pollution of the sea by dumping of wastes and other matters.
MARPOL Convention (1973): It covers pollution of the marine environment by ships from operational or accidental causes.
- It lists various forms of marine pollution caused by oil, noxious liquid substances, harmful substances in packaged form, sewage and garbage from ships, etc.
Way Forward
- National governments should adopt and ratify the agreement for the High Seas Treaty to take effect. Cooperation across all sectors globally is crucial to ensure the treaty's successful implementation and monitoring for the benefit of ocean life and human well-being.
- By adopting the High Seas Treaty, India and the world can mitigate the impact of shipping and fishing, fostering a sustainable blue economy that benefits both the economy and marine ecosystems.
- The treaty offers India a chance to showcase its commitment to ocean conservation and assume a leadership role in global high seas protection, strengthening its maritime reputation.
Conclusion
The High Seas Treaty represents a landmark agreement in global ocean governance. India's decision to ratify the treaty is a significant step that could have far-reaching implications for the conservation and sustainable use of marine resources worldwide.
|
Drishti Mains Question What is the High Seas Treaty and how this will help in better conservation and governance of the marine ecosystem and economy. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the ‘Trans-Pacific Partnership’, consider the following statements: (2016)
- It is an agreement among all the Pacific Rim countries except China and Russia.
- It is a strategic alliance for the purpose of maritime security only.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Q. With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC)’, consider the following statements: (2015)
- It was established very recently in response to incidents of piracy and accidents of oil spills.
- It is an alliance meant for maritime security only.
Which of the statements given above is/ are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. With respect to the South China sea, maritime territorial disputes and rising tension affirm the need for safeguarding maritime security to ensure freedom of navigation and overflight throughout the region. In this context, discuss the bilateral issues between India and China. (2014)