Hawking Radiation | 12 Jun 2024
Recently, scientists proposed that small, hot "morsel" black holes, ejected during larger black hole mergers, could emit detectable high-energy photons. These morsel black holes would emit Hawking radiation (named after Stephen Hawking) at an increasing rate as they lose mass, leading to their explosive demise.
- Smaller black holes are hotter and emit Hawking radiation faster than larger ones.
- Gravitational waves could detect black hole mergers, followed by gamma-ray telescopes spotting high-energy photons from morsel black holes as they emit Hawking Radiation.
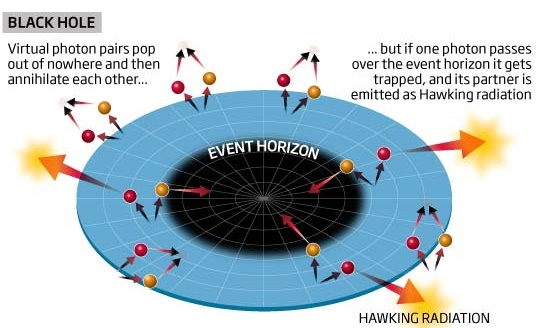
- It is predicted that the gravitational field of a black hole should cause the creation of particles, mostly photons directly from the vacuum of space.
- Hawking's Radiation:
- It is the idea that black holes leak thermal radiation, gradually evaporating and ending their existence with a final explosion.
- When one particle goes past the event horizon, it can't join back with its partner. The particles outside are known as Hawking radiation.
- The event horizon is a region of space beyond the black hole or "point of no return.