Gupteswar Forest as Biodiversity Heritage Site | 20 Feb 2024
For Prelims: Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS), ‘Biological Diversity Act, 2002
For Mains: Biodiversity-Heritage Site (BHS), Environmental pollution and degradation.
Why in News?
The pristine Gupteswar Forest, adjacent to Gupteswar Shiva temple in Odisha’s Koraput district has been declared as the 4th Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS) of the state.
What are the Key Points Related to Gupteshwar Forest?
- Area and Importance:
- The forest covers 350 hectares of demarcated area and holds immense cultural significance with its sacred groves, traditionally revered by the local community.
- Flora and Fauna Diversity:
- It harbours a remarkable diversity of flora and fauna. The forest is home to at least 608 faunal species, including 28 species of mammals.
- Significant Species:
- Notable faunal species documented in the forest include the mugger crocodile, kanger valley rock gecko, sacred Grove Bush Frog, and various avifauna such as black baza, Jerdon’s baza, Malaber trogon, common hill myna, white-bellied woodpecker, and banded bay cuckoo.
- The limestone caves within the forest are home to eight species of bats, two of which are under the near-threatened category.
- Hipposideros galeritus and Rhinolophus rouxii are under the near-threatened category of the IUCN.
- Floral Diversity:
- The forest also boasts a rich floral diversity. It includes threatened medicinal plants like the Indian trumpet tree and Indian snakeroot.
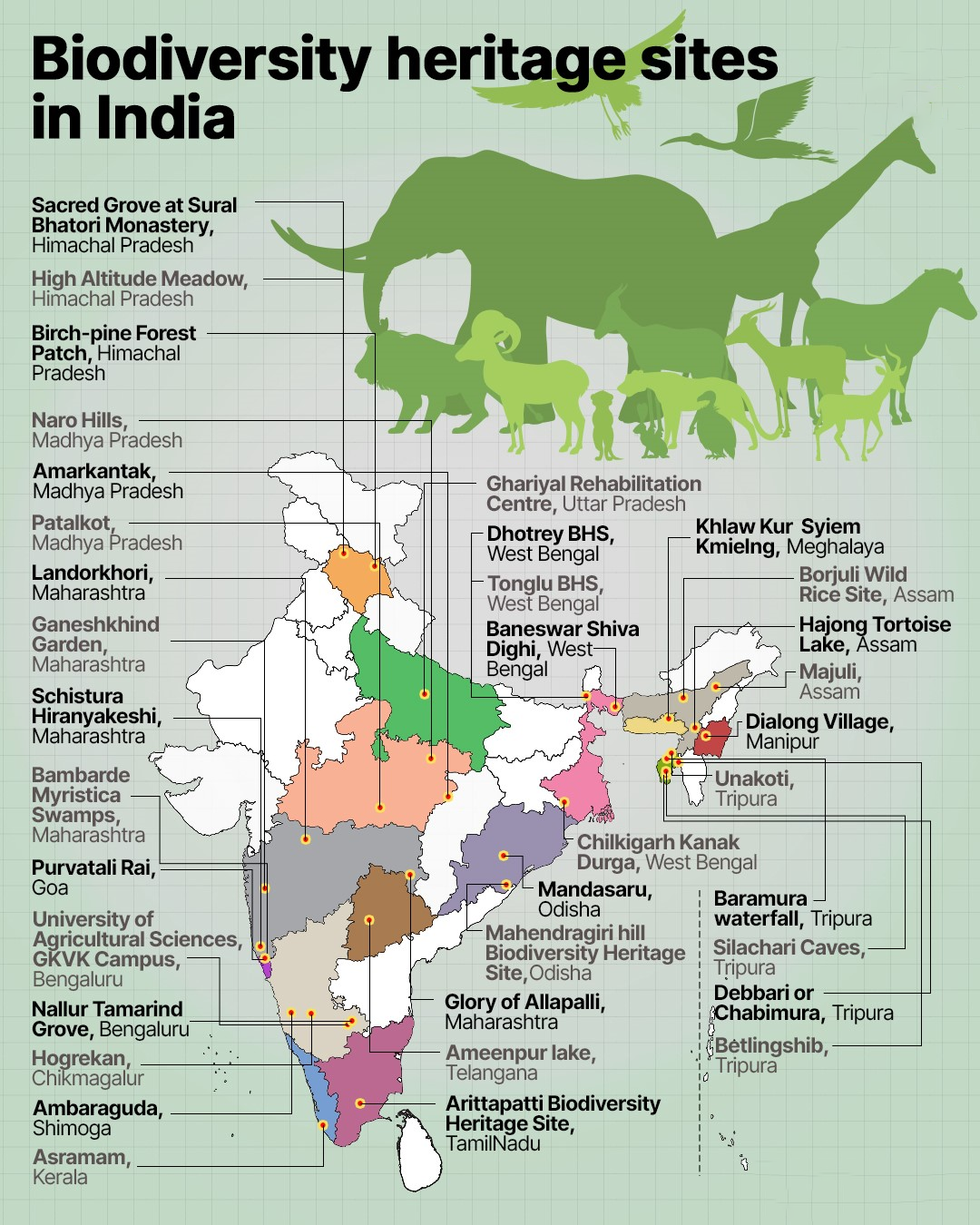
What is a Biodiversity Heritage Site?
- About:
- Biodiversity Heritage sites (BHS) are well-defined areas that are unique, ecologically fragile ecosystems with a high diversity of wild and domesticated species, the presence of rare and threatened species, and keystone species.
- Legal Provision:
- As per provision under Section 37(1) of ‘The Biological Diversity Act, 2002’ State Governments are empowered to notify in the official gazette, in consultation with ‘local bodies’, areas of biodiversity importance as Biodiversity Heritage Sites.
- Restrictions:
- Creation of BHS may not put any restriction on the prevailing practices and usages of the local communities, other than those voluntarily decided by them. The purpose is to enhance the quality of life of the local communities through conservation measures.
- First BHS of India:
- Nallur Tamarind Grove in Bengaluru, Karnataka was the first Biodiversity Heritage Site of India, declared in 2007.
- According to the National Biodiversity Authority, India has a total of 45 Biodiversity Heritage Sites as of February 2024.
- Last Five Additions to BHS:
- Haldir Char Island West Bengal (May 2023)
- Birampur-Baguran Jalpai West Bengal (May 2023)
- Tungkyong Dho Sikkim (June 2023)
- Gandhamardan Hill Odisha (March 2023)
- Gupteswar Forest Odisha (Feb 2024)
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. Two important rivers – one with its source in Jharkhand (and known by a different name in Odisha), and another, with its source in Odisha – merge at a place only a short distance from the coast of Bay of Bengal before flowing into the sea. This is an important site of wildlife and biodiversity and a protected area. Which one of the following could be this? (2011)
(a) Bhitarkanika
(b) Chandipur-on-sea
(c) Gopalpur-on-sea
(d) Simlipal
Ans: (a)
Q2. With reference to India’s biodiversity, Ceylon frogmouth, Coppersmith barbet, Gray-chinned minivet and White-throated redstart are (2020)
(a) Birds
(b) Primates
(c) Reptiles
(d) Amphibians
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. How does biodiversity vary in India? How is the Biological Diversity Act, 2002 helpful in the conservation of flora and fauna? (2018)