Biodiversity & Environment
Green Protection to Aravalli
- 23 Jul 2022
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Physical Geography of Aravali Range, Punjab Land Preservation Act, Forest Conservation Act 1980
For Mains: Significance of Aravali Range, Forest Conservation, Supreme Court Judgements
Why in News?
Recently, the Supreme Court of India extended Green Protection to forest land in Aravalli ranges.
- The court’s ruling will mean around 30,000 hectares across the Aravallis and Shivaliks in Haryana will be considered forest land.
What is the Supreme Court Ruling?
- The Supreme Court held that all land covered by the special orders issued under Section 4 of the Punjab Land Preservation Act (PLPA) in Haryana will be treated as forests and be entitled to protection under the 1980 Forest Conservation Act.
- Such land covered under Section 4 can see no commercial activity or non-forest use without the consent of the central government.
- It also stated that land covered by the special orders issued under Section 4 of PLPA have all the trappings of forest lands within the meaning of Section 2 of the Forest Act.
- The court directed the state government to clear any non-forest activity from such land in three months and report compliance.
- The bench considered a September 2018 judgment which held all land under PLPA could be treated as forest.
- The recent verdict clarified that the previous judgment failed to closely examine the scheme of Section 4 of PLPA and its legal effect in relation to Section 2 of the Forest Act.
What are Section 4 of PLPA & Section 2 of Forest Act?
- Section 4 of the Punjab Land Preservation Act (PLPA):
- Special orders under Section 4 of PLPA are the restrictive provisions issued by the state government to prevent deforestation of a specified area that could lead to soil erosion.
- When the state government is satisfied that deforestation of a forest area forming part of a larger area is likely to lead to erosion of soil, the power under Section 4 can be exercised.
- Therefore, the specific land which a special order under Section 4 of PLPA has been issued will have all the trappings of a forest governed by the Forest Act.
- While the land notified under the special orders of Section 4 of PLPA shall be forest lands, not all land under PLPA will ipso facto become forest lands within the meaning of the Forest Act.
- Section 2 of the Forest Act:
- Section 2 of the Forest Act imposes prohibitions on the de-reservation of forests or use of forest land for non-forest purposes without prior approval of the central government.
- Once a land is covered under Section 2 of the Forest Act, whether the special orders under Section 4 continue to be in force or not, it shall continue to remain forest land.
- Section 2 of the Forest Act imposes prohibitions on the de-reservation of forests or use of forest land for non-forest purposes without prior approval of the central government.
What do we need to know about Aravalli Range?
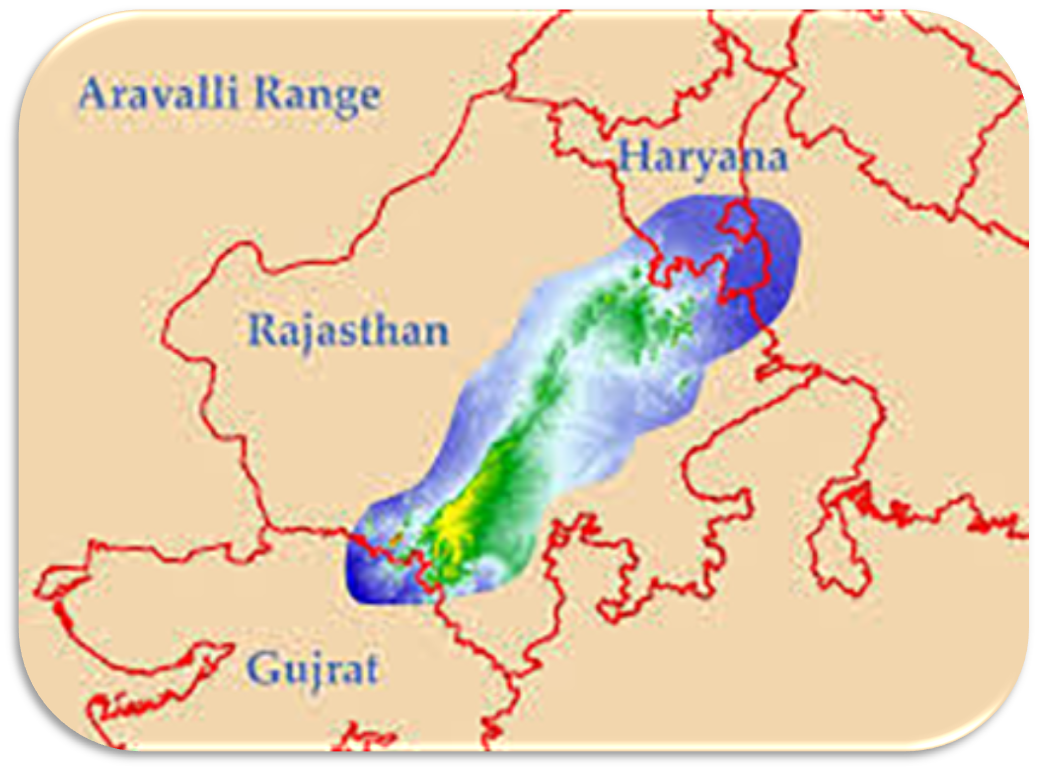
- About the Aravalli Range:
- Location:
- They stretch for a distance of about 720 km from Himmatnagar in Gujarat to Delhi, spanning Haryana and Rajasthan.
- Formation:
- The Aravallis date back to millions of years when a pre-Indian subcontinent collided with the mainland Eurasian Plate.
- Age:
- Carbon dating has shown that copper and other metals mined in the ranges date back to at least the 5th century BC.
- Characteristics:
- The Aravallis of Northwestern India, one of the oldest fold mountains of the world, now form residual mountains with an elevation of 300m to 900m.
- Guru Shikhar Peak on Mount Abu is the highest peak in the Aravalli Range (1,722 m).
- It has been formed primarily of folded crust, when two convergent plates move towards each other by the process called orogenic movement.
- Extension:
- The mountains are divided into two main ranges – the Sambhar Sirohi Range and the Sambhar Khetri Range in Rajasthan, where their extension is about 560 km.
- The hidden limb of the Aravallis that extends from Delhi to Haridwar creates a divide between the drainage of rivers of the Ganga and the Indus.
- Location:
- Their Significance:
- Checks Desertification:
- The Aravallis act as a barrier between the fertile plains in the east and the sandy desert in the west.
- Historically, it is said that the Aravalli range checked the spread of the Thar desert towards the Indo-Gangetic plains, serving as a catchment of rivers and plains.
- Rich in Biodiversity:
- Provides habitat to 300 native plant species, 120 bird species and many exclusive animals like the jackal and mongoose.
- Impacts Climate:
- Aravallis have an impact upon the climate of northwest India and beyond.
- During monsoons, it provides a barrier and monsoon clouds move eastwards towards Shimla and Nainital, thus helping nurture the sub-Himalayan rivers and feeding the north Indian plains.
- In the winter months, it protects the fertile alluvial river valleys from the cold westerly winds from Central Asia.
- Checks Desertification:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2015)
Place of Pilgrimage Location
- Srisailam : Nallamala Hills
- Omkareshwar : Satmala Hills
- Pushkar : Mahadeo Hills
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- Srisailam is situated on top of Nallamala Hills. It is on the right side of the river Krishna in Kurnool district of Andhra Pradesh. It has been a popular centre of Shaivite pilgrimage for centuries. Hence, pair 1 is correctly matched.
- Omkareshwar is situated in the Khandwa district of Madhya Pradesh. It is one of the 12 Jyotirlingas of Lord Shiva. It is on an island called Mandhata or Shivapuri in the Narmada River. The shape of the island is said to be like the Hindu ‘Om’ symbol. On the other hand, Satmala hills run across Nashik district in Maharashtra. They are an integral part of the Sahyadris range within Nashik. Hence, pair 2 is not correctly matched.
- Pushkar is a town in the Ajmer district of Rajasthan. It is a religious pilgrimage site for Hindus and Sikhs. Pushkar is in the centre-east part of Rajasthan, on the western side of Aravalli mountains, whereas the Mahadeo hills are a range of hills in Madhya Pradesh State of central India. The hills are situated in the northern section of the Satpura Range. Hence, pair 3 is not correctly matched.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.