Great Nicobar Island Project Conundrum | 21 Jun 2024
For Prelims: Great Nicobar Island, National Green Tribunal (NGT), Shompen, Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG), Nicobar Megapode bird, leatherback turtles
For Mains: Significance and Concerns Related to Great Nicobar Island Project
Why in News?
Recently, the opposition party has described the proposed Rs 72,000-crore infrastructure upgrade at the Great Nicobar Island as a "grave threat" to the island's indigenous inhabitants and fragile ecosystem, and demanded immediate suspension of all clearances and a thorough, impartial review of the proposed project, including by the concerned Parliamentary committees.
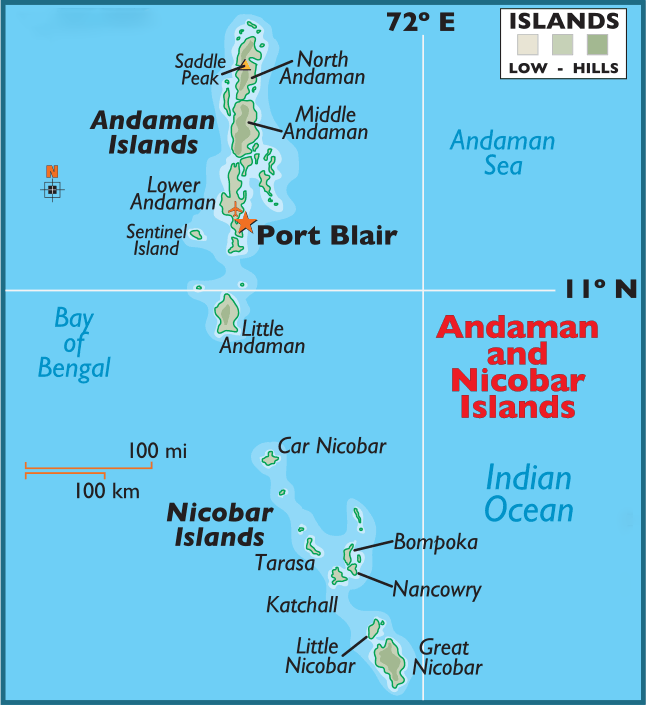
Great Nicobar Island
- Great Nicobar is the southernmost and largest of the Nicobar Islands, a sparsely inhabited 910-sq-km patch of mainly tropical rainforest in southeastern Bay of Bengal.
- Indira Point on the island, India’s southernmost point, is located 90 nautical miles (<170 km) from Sabang at the northern tip of Sumatra, the largest island of the Indonesian archipelago.
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands consist of 836 islands, divided into two groups known as the Andaman Islands located in the north and the Nicobar Islands situated in the south, separated by the 10° Channel which is 150 kilometres wide.
- Great Nicobar has two national parks, a biosphere reserve, small populations of the Shompen, Onge, Andamanese and Nicobarese tribal peoples, and a few thousand non-tribal settlers.
What is the Great Nicobar Island Project?
- About:
- The Great Nicobar Island (GNI) project, launched in 2021, is a mega project to be implemented at the southern end of the Andaman and Nicobar islands.
- It involves developing a trans-shipment port, an international airport, township development, and a 450 MVA gas and solar-based power plant on the island.
- The project was implemented after a report by NITI Aayog which identified the potential to utilise the advantageous position of the island, which is approximately equidistant from Colombo in Sri Lanka to the southwest and Port Klang (Malaysia) and Singapore to the southeast.
- The Great Nicobar Island (GNI) project, launched in 2021, is a mega project to be implemented at the southern end of the Andaman and Nicobar islands.
- Features:
- The mega infrastructure project is being implemented by the Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation (ANIIDCO) and is proposed to include an International Container Trans-shipment Terminal (ICTT), a greenfield international airport.
- It is close to the Malacca Strait, the main waterway that connects the Indian Ocean to the Pacific, and the ICTT is expected to allow Great Nicobar to participate in the regional and global maritime economy by becoming a major player in cargo transshipment’.
- The site for the proposed ICTT and power plant is Galathea Bay on the southeastern corner of Great Nicobar Island, where there is no human habitation.
- Strategic Importance:
- The upgrade is aimed at facilitating the deployment of additional military forces, larger and more warships, aircraft, missile batteries, and troops.
- Close surveillance of the entire area around the archipelago, and the building up of a strong military deterrence at Great Nicobar is of vital importance to India’s national security.
- The island is close to the Malacca Strait, the main waterway that connects the Indian Ocean to the Pacific, and the ICTT is expected to allow Great Nicobar to participate in the regional and global maritime economy by becoming a major player in cargo transshipment’.
- The Bay of Bengal and Indian Ocean regions are extremely important for India's strategic and security interests. This is because the Chinese military (the People's Liberation Army Navy) is trying to increase its presence and influence in this entire region.
- India is particularly concerned about the possibility of China building up its naval forces at important choke points in the Indo-Pacific area, such as the Malacca, Sunda, and Lombok Straits.
- Furthermore, China is attempting to expand its foothold in this region by building a military facility on the Coco Islands, which are located just 55 km north of India's Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
- This raises concerns for India, as the Andaman & Nicobar Islands are strategically very important for India's maritime security in the region.
- The upgrade is aimed at facilitating the deployment of additional military forces, larger and more warships, aircraft, missile batteries, and troops.
What are the Challenges Related to the Great Nicobar Island Project?
- Impact on Indigenous Tribes: The Shompen and Nicobarese are a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) of hunter-gatherers, with an estimated population of only a few hundred individuals. They live in a tribal reserve on the island.
- There are serious concerns that the proposed infrastructure upgrade could have a potentially devastating impact on the Shompen tribe and their way of life, which is closely tied to the island's natural environment.
- Also, the project violates the letter and spirit of the Forest Rights Act (2006), which holds the Shompen as the sole legally empowered authority to protect, preserve, regulate and manage the tribal reserve.
- Threat to Island Ecology: The project will impact the island’s ecology with the felling of nearly a million trees. It is feared that the port project will destroy coral reefs with spinoff effects on the local marine ecosystem, and pose a threat to the terrestrial Nicobar Megapode bird and leatherback turtles who nest in the Galathea Bay area.
- This area is about 15% of the GNI’s land mass and constitutes one of the country’s largest forest diversions in a nationally and globally unique rainforest ecosystem.
- Seismic Vulnerability: Proposed port is located in a seismically volatile zone, which experienced permanent subsidence of around 15 feet during the 2004 tsunami. This raises concerns about the safety and viability of constructing such a large-scale infrastructure project in a high-risk, disaster-prone area.
- Lack of Adequate Consultation: There is an accusation against the local administration of not consulting the Tribal Council of Great and Little Nicobar Islands adequately, as per legal requirements.
- In April 2023, National Green Tribunal (NGT) declined to interfere with the environmental and forest clearance granted to the project. The Tribunal, however, ordered that a high-power committee should be constituted to look into the clearances.
Way Forward
- Inclusion of Tribal Councils: Ensure that the Tribal Councils of Great and Little Nicobar Islands are integral to all decision-making processes, respecting their traditional knowledge and legal rights under the Forest Rights Act (2006).
- High-Power Committee: Following the NGT’s order, establish a high-power committee to oversee environmental and forest clearances, ensuring it includes representatives from environmental groups, tribal councils, and independent experts.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following have coral reefs? (2014)
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Gulf of Kachchh
- Gulf of Mannar
- Sunderbans
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (a)
Q. Which one of the following pairs of islands is separated from each other by the ‘Ten Degree Channel’? (2014)
(a) Andaman and Nicobar
(b) Nicobar and Sumatra
(c) Maldives and Lakshadweep
(d) Sumatra and Java
Ans: (a)
Q. In which one of the following places is the Shompen tribe found? (2009)
(a) Nilgiri Hills
(b) Nicobar Islands
(c) Spiti Valley
(d) Lakshadweep Islands
Ans: (b)