GQ-RCP Platform for HIV Detection | 23 Nov 2024
Why in News?
Recently, researchers at the Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR), an autonomous institute under the Department of Science and Technology, have developed a new technology for early and accurate detection of HIV.
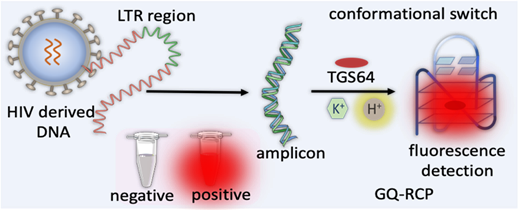
- The newly developed GQ Topology-Targeted Reliable Conformational Polymorphism (GQ-RCP) platform, adapted from SARS-CoV-2 diagnostics, highlights the innovative capabilities of Indian research institutions.
What are the Key Features of GQ-RCP Platform?
- GQ-RCP Platform: The G-Quadruplex (GQ) structure is a unique four-stranded DNA conformation that plays a crucial role in various biological processes, including gene regulation and genome stability.
- Functionality: This platform enables targeted detection of HIV-derived DNA structures using a fluorometric test, enhancing diagnostic reliability and significantly reducing false positives associated with HIV detection.
- The GQ-RCP platform promises to enhance early detection capabilities and reduce reliance on less specific general DNA sensing probes that contribute to diagnostic inaccuracies.
- Detection Process: The detection process involves reverse transcription and amplification of a genomic segment, transitioning double-stranded DNA into its GQ conformation through a pH-mediated process.
What is HIV?
- About:
- HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus, which is a virus that attacks the immune system in the human body.
- It primarily targets and damages CD4 immune cells (a type of White Blood Cell), which are essential for the body's ability to fight infections and diseases.
- Over time, HIV weakens the immune system, leaving the body vulnerable to opportunistic infections and cancers.
- Transmission:
- HIV is primarily spread through the exchange of certain bodily fluids such as blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and breast milk.
- Severity:
- If left untreated, the virus destroys a person’s immune system and they are said to be in the Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome stage (AIDS) where they get several opportunistic infections that may result in death.
- Cure:
- Although there are no cures for the infection at present, the disease can be managed using antiretroviral therapy.
- These medicines suppress the replication of the virus within the body, allowing the number of CD4 immune cells to bounce back.
What is the State of HIV Infection in India?
- Current Prevalence:
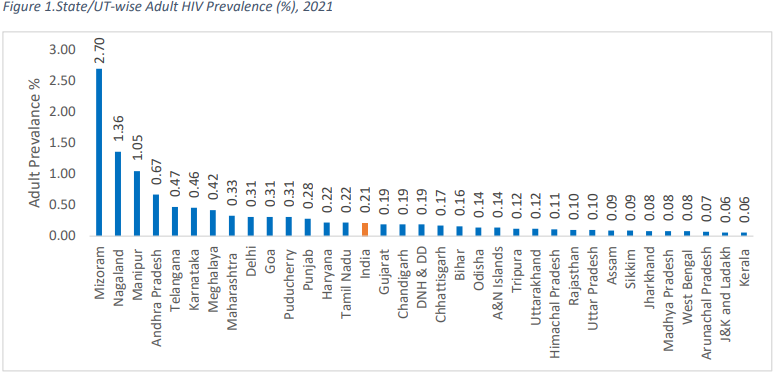
- According to the National AIDS Control Organization (NACO), as of 2021, approximately 2.4 million people are living with HIV in India, with an adult prevalence rate of 0.22%.
- The India HIV Estimates 2021 report indicated that there were about 2.3 million people living with HIV, showing a downward trend in new infections
- Demographic Distribution: The epidemic is concentrated among high-risk populations, including female sex workers (2.61%) and injecting drug users ( 5.91%),
- Children under 15 years account for about 3.5% of all infections, while women represent approximately 39% of the total HIV-positive population.
- High-Prevalence States: The northeast region States have the highest adult HIV prevalence (2.70% in Mizoram, 1.36% in Nagaland and 1.05% in Manipur), followed by southern States (0.67% in Andhra Pradesh, 0.47% in Telangana and 0.46% in Karnataka).
- The number of People Living with HIV (PLHIV) is estimated at around 24 lakhs. Southern States have the largest number of PLHIV viz. Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka are the top three.
What are the Government Initiatives Related to HIV?
- National AIDS Control Program (NACP):
- Launch and Evolution: Established shortly after the first AIDS case was reported in India in 1986, the NACP has evolved through multiple phases since its inception in 1992. The program focuses on prevention, treatment, and care for people living with HIV/AIDS.
- Phases of NACP:
- Phase I (1992-1999): Focused on awareness generation, blood safety, and establishing surveillance systems.
- Phase II (1999-2006): Expanded targeted interventions for high-risk populations and involved NGOs in implementation.
- Phase III (2007-2012): Dramatically scaled up targeted interventions and strengthened surveillance.
- It emphasised partnerships with civil society organizations to enhance community involvement.
- Phase IV (2012-2021): Aimed to consolidate gains and further integrate HIV services into the public health system. Focused on comprehensive care, support, and treatment for people living with HIV.
- Phase V (2021-2026): It aims to reduce new HIV infections and AIDS-related deaths by 80% by 2025-26 compared to 2010 levels.
- Legislative Framework: The HIV/AIDS Prevention and Control Act (2017) provides a legal framework to protect the rights of people living with HIV/AIDS, ensuring access to treatment without stigma or discrimination.
- International Support: India receives technical assistance and funding from various international partners such as UNAIDS, WHO, the World Bank, and private foundations like the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following diseases can be transmitted from one person to another through tattooing? (2013)
- Chikungunya
- Hepatitis B
- HIV-AIDS
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)