Social Issues
Global Report on Hypertension
- 22 Sep 2023
- 6 min read
For Prelims: World Health Organization (WHO), Hypertension, India Hypertension Control Initiative Program (IHCI)
For Mains: Hypertension and its implications on public health, Universal Health Coverage.
Why in News?
Recently, during the United Nations General Assembly’s (UNGA) 78th session, the World Health Organization (WHO) released a report titled "Global report on hypertension: The race against a silent killer."
- It is the first-ever report by the WHO on the worldwide implications of hypertension, commonly referred to as high blood pressure.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- A Global Epidemic:
- One in three adults across the world suffers from hypertension.
- The number of hypertension cases has doubled from 650 million to a staggering 1.3 billion between 1990 and 2019.
- Hypertension affects approximately 33% of adults aged 30-79 worldwide.
- Approximately four out of every five people with hypertension are not adequately treated.
- India's Hypertension Burden:
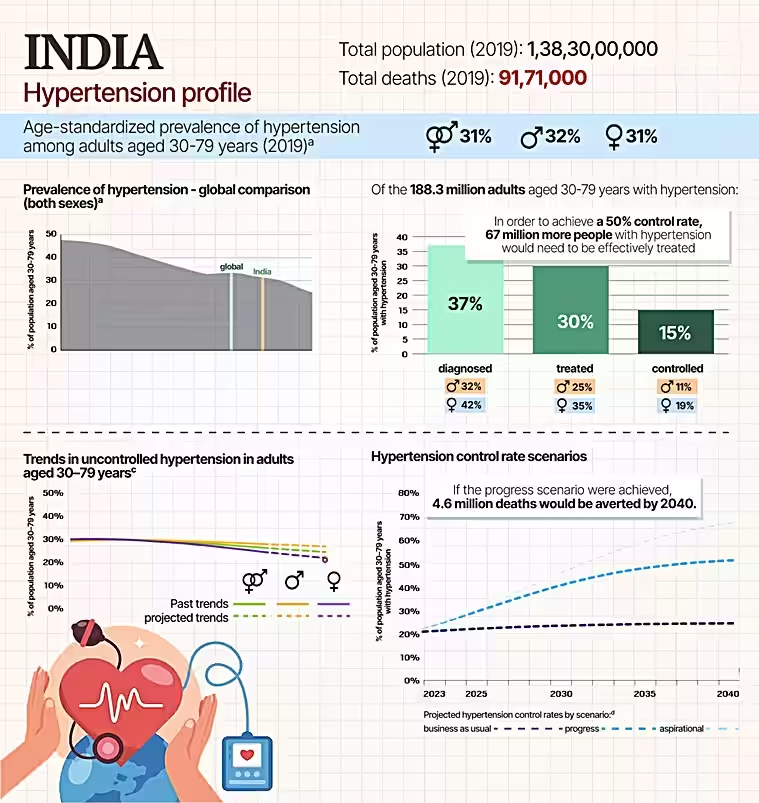
- India alone has an estimated 188.3 million adults aged 30–79 years grappling with hypertension.
- The prevalence of high blood pressure in India is slightly lower than the global average of 31%.
- To reach a 50% control rate, India needs to ensure that an additional 67 million people with hypertension receive effective treatment.
- If the progress scenario were achieved, 4.6 million deaths due to high blood pressure would be averted by 2040.
- Inadequate Treatment:
- About 80% of individuals with hypertension do not receive adequate treatment.
- Effective hypertension treatment has the potential to prevent 76 million deaths, 120 million strokes, 79 million heart attacks, and 17 million cases of heart failure by 2050.
- About 80% of individuals with hypertension do not receive adequate treatment.
- Disparities in Treatment Coverage:
- Treatment coverage for hypertension exhibits significant disparities among countries, with high-income nations having a more favourable coverage rate.
- The WHO region of the US leads with a 60% coverage rate, while the African region lags behind at 27%.
- More than three-quarters of adults with hypertension live in low- and middle-income countries.
- Treatment coverage for hypertension exhibits significant disparities among countries, with high-income nations having a more favourable coverage rate.
- The Urgency of Timely Treatment:
- Nearly 30% of individuals with uncontrolled hypertension exhibit blood pressure measurements above the threshold warranting urgent treatment.
- Globally, the percentage of adults aged 30–70 taking medication for hypertension has doubled from 22% in 1990 to 42% in 2019.
- Effective treatment coverage has quadrupled during the same period, reaching 21%.
- Nearly 30% of individuals with uncontrolled hypertension exhibit blood pressure measurements above the threshold warranting urgent treatment.
- The WHO's Call to Action:
- The WHO calls for prioritising the prevention, early detection, and effective management of hypertension as part of national health benefit packages.
- Recommendations:
- There is a need to strengthen hypertension control programs that remain under-prioritized and acutely underfunded.
- Strengthening hypertension control must become an integral part of every country's journey toward universal health coverage.
What is Hypertension?
- About:
- Hypertension (high blood pressure) is when the pressure in your blood vessels is too high (140/90 mmHg or higher). It is common but can be serious if not treated.
- Blood pressure is written as two numbers.
- The first (systolic) number represents the pressure in blood vessels when the heart contracts or beats.
- The second (diastolic) number represents the pressure in the vessels when the heart rests between beats.
- Blood pressure is written as two numbers.
- World Hypertension Day is celebrated on May 17 every year to promote awareness about hypertension and encourage people to prevent and control this silent killer.
- Hypertension (high blood pressure) is when the pressure in your blood vessels is too high (140/90 mmHg or higher). It is common but can be serious if not treated.
- Risk Factors:
- High-salt diets, lack of physical activity, and excessive alcohol consumption are significant contributors to hypertension, and genetics are believed to play a role in high blood pressure as well.
- Symptoms:
- Most people with hypertension don’t feel any symptoms. Very high blood pressure can cause headaches, blurred vision, chest pain and other symptoms.
- Complications of Uncontrolled Hypertension:
- Severe heart issues, including chest pain, heart attacks, heart failure, and irregular heartbeats, as well as increase the risk of stroke by affecting blood flow to the brain.
- Treatment:
- Lifestyle changes like adopting a low-salt diet, weight loss, physical activity, and quitting tobacco etc. and medications.
- Initiatives:
- Global:
- To achieve the global target to reduce the prevalence of hypertension by 25% by 2025, WHO and the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention launched the Global Hearts Initiative in 2016.
- The United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 3 (SDG 3) aims to ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all.
- India:
- India Hypertension Control Initiative Program (IHCI):
- Through programmes such as IHCI and the government’s push towards non-communicable disease screening and treatment at the primary healthcare level, India aims to put 75 million patients with hypertension or diabetes on standard care by 2025.
- India Hypertension Control Initiative Program (IHCI):
- Global: