Global Hepatitis Report 2024 | 10 Apr 2024
For Prelims: World Health Organisation, Hepatitis, National Viral Hepatitis Control Program, India's Universal Immunization Programme
For Mains: Prevalence of Hepatitis at Global and Indian level, Challenges in tackling Hepatitis and how to achieve the global target
Why in News?
The recently released Global Hepatitis Report 2024 by the World Health Organisation (WHO) has highlighted India as one of the nations facing a significant burden of viral hepatitis, particularly Hepatitis B and C infections.
What are the Key Findings of the Report?
- India's Hepatitis Burden:
- Prevalence in India:
- India is one of the countries with the highest burden of viral hepatitis.
- India has an estimated 2.9 crore people living with Hepatitis B infection and 0.55 crore living with Hepatitis C infection.
- There were over 50,000 new Hepatitis B cases and 1.4 lakh new Hepatitis C cases reported in India in 2022.
- These viral hepatitis infections killed 1.23 lakh people in India in 2022.
- Drivers of Hepatitis Infections in India:
- Both Hepatitis B and C infections are transmitted through various means, including mother-to-child transmission, unsafe blood transfusions, contact with infected blood, and needle-sharing among drug users.
- Despite advancements in blood safety protocols, mother-to-child transmission remains a primary mode of infection for Hepatitis B in India.
- Both Hepatitis B and C infections are transmitted through various means, including mother-to-child transmission, unsafe blood transfusions, contact with infected blood, and needle-sharing among drug users.
- Diagnosis and Treatment Coverage:
- In India, only 2.4% of Hepatitis B cases and 28% of Hepatitis C cases are diagnosed.
- Treatment coverage is even lower, at 0% for Hepatitis B and 21% for Hepatitis C, despite the availability of affordable generic medicines.
- Barriers to Improving Hepatitis Outcomes:
- Limited reach and utilisation of the National Viral Hepatitis Control Program.
- Need to expand access to affordable diagnostics and treatment services under the program.
- Requirement to treat all diagnosed individuals, regardless of disease stage, to reduce health consequences and transmission.
- Prevalence in India:
- Global:
- Mortality Trends:
- Viral hepatitis caused an estimated 1.3 million deaths globally in 2022, on par with tuberculosis.
- Hepatitis B accounted for 83% of these deaths, while hepatitis C accounted for 17%.
- The rise in mortality suggests an increase in hepatitis-related liver cancer cases and deaths.
- The number of new viral hepatitis infections declined from 2.5 million in 2019 to 2.2 million in 2022.
- Viral hepatitis caused an estimated 1.3 million deaths globally in 2022, on par with tuberculosis.
- Prevalence:
- Globally, an estimated 304 million people were living with hepatitis B and C in 2022.
- WHO estimates indicate that 254 million people lived with hepatitis B and 50 million with hepatitis C in 2022.
- 12% of the burden is among children, particularly for hepatitis B.
- Globally, an estimated 304 million people were living with hepatitis B and C in 2022.
- Barriers to Scaling Up Testing and Treatment:
- Lack of funding and limited decentralisation have restricted the scaling up of testing services.
- Many countries are still not procuring hepatitis medicines at the available generic prices, leading to high costs.
- Patent-related barriers remain an obstacle to accessing affordable hepatitis C medicines in some countries.
- Mortality Trends:
What are the Key Facts About Hepatitis?
- About:
- Hepatitis is caused by infectious viruses (viral hepatitis), and noninfectious agents, leading to a range of health problems, some of which can be fatal.
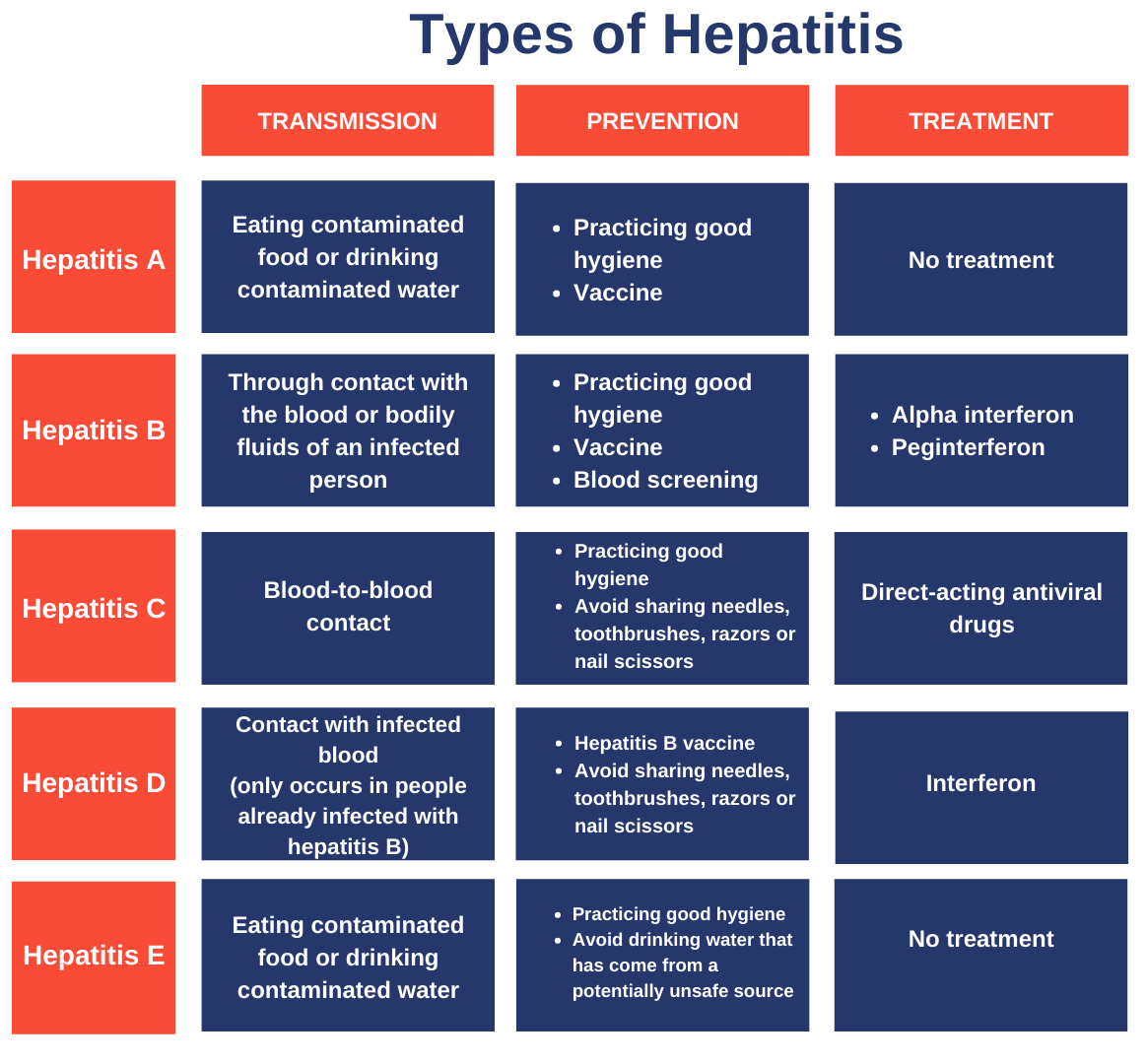
- There are five main strains of the hepatitis virus: A, B, C, D, and E, each with different modes of transmission, severity, geographical distribution, and prevention methods.
- Types B and C are the most common cause of liver cirrhosis (a condition in which the liver is scarred and permanently damaged), liver cancer, and viral hepatitis-related deaths.
- Some types of hepatitis are preventable through vaccination, and an estimated 4.5 million premature deaths could be prevented by 2030 through vaccination, diagnostic tests, medicines, and education campaigns.
- WHO's global hepatitis strategy aims to reduce new hepatitis infections by 90% and deaths by 65% between 2016 and 2030.
- Symptoms and Severity:
- Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E can exhibit mild or no symptoms.
- Symptoms of hepatitis A, B, and C include fever, malaise, loss of appetite, diarrhoea, nausea, abdominal discomfort, dark-coloured urine, and jaundice.
- Chronic liver infection, cirrhosis, and liver cancer can result from hepatitis A, B, and C.
- Hepatitis D is found in people already infected with hepatitis B and can cause a more serious infection and accelerated progression to cirrhosis. Chronic hepatitis D is rare.
- Hepatitis E symptoms include mild fever, reduced appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, itching, skin rash, joint pain, jaundice, dark urine, pale stools, and hepatomegaly or acute liver failure.
Way Forward
- Treating an estimated 40 million people with hepatitis B and curing 30 million people with hepatitis C by 2026 is crucial to regain the trajectory towards elimination.
- Targeted efforts are required to reach specific high-risk populations affected by viral hepatitis.
- Integrate hepatitis services into primary healthcare settings to improve access for individuals across all socioeconomic backgrounds.
- Expand and improve the National Viral Hepatitis Control Program by increasing funding, broadening its scope, and enhancing coordination among stakeholders. Prioritise early diagnosis and treatment initiation through the program.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q.Examine the barriers hindering the scaling up of testing and treatment services for viral hepatitis in India. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. Which one of the following statements is not correct? (2019)
(a) Hepatitis B virus is transmitted much like HIV.
(b) Hepatitis B unlike Hepatitis C, does not have a vaccine.
(c) Globally, the number of people infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses arc several times more than those infected with HIV.
(d) Some of those infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses do not show the symptoms for many years.
Ans: (b)
Q. Which of the following diseases can be transmitted from one person to another through tattooing? (2013)
- Chikungunya
- Hepatitis B
- HIV-AIDS
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)