Global Dependence on Oil and Natural Gas | 10 Jun 2023
For Prelims: UNFCCC COPs, Oil and Gas Production and Consumption
For Mains: India’s dependence on oil and natural gas, Challenges and Measures related to restricting oil and gas production
Why in News?
According to a new report from Climate Action Tracker (CAT), a non-profit organisation, the world’s largest fossil fuel-producing countries have neither made a commitment to end oil and gas production nor have they set a global target for renewable energy.
- The upcoming UNFCCC COP 28 shall focus on putting an end to oil and gas production.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Lack of Global Consensus:
- New oil and gas investments should have ended by now; there exists a globally accepted consensus on phasing out coal but there’s no such agreement on oil and gas.
- Though India called for a phasedown of all fossil fuels at COP27 in Egypt, a concrete decision regarding the same could not be finalized.
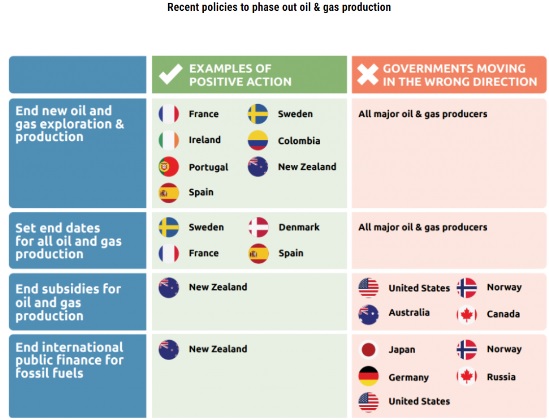
- Performance of Developed Countries:
- As of now, only Sweden, Denmark, France and Spain have set an end date while France, Sweden, Colombia, Ireland, Portugal, New Zealand and Spain have halted new oil and gas exploration and production.
- On the contrary, the US - world’s largest oil and gas producer, has more than doubled oil production since 2010.
- Australia - world's largest LNG exporter, projects an 11% increase in its LNG production between 2020 and 2030.
- CSS as an Alternative and its Challenges:
- The UAE - world’s 7th largest oil producer and 15th largest fossil gas producer has been pushing for the use of Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) in the energy sector instead of phasing out oil and gas.
- CCS involves capturing CO2 from power plants and other industrial processes, instead of emitting them into the atmosphere.
- Currently, CCS captures less than 0.1% of global carbon emissions accounting to technological, economic, institutional, ecological, environmental and socio-cultural barriers.
- CCS is expensive and could end up becoming a stranded asset; investments in CCS could rob funds from renewable energy projects.
- Other countries already investing in CSS techniques include the US, Australia and Canada. Saudi Arabia is looking to deploy CCS to reach its net zero climate targets.
- The UAE - world’s 7th largest oil producer and 15th largest fossil gas producer has been pushing for the use of Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) in the energy sector instead of phasing out oil and gas.
What is the Scenario of Oil and Gas Production/Consumption?
- Global Scenario:
- According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global production, transportation and processing of oil and gas emitted the equivalent of 5.1 billion tonnes of CO2 in 2022 - almost 15% of total energy-related greenhouse gas emissions.
- Oil and gas production is one of the largest emitters of methane, a potent greenhouse gas and a significant contributor of air pollution emissions.
- Under the IEA’s Net Zero by 2050 (NZE) scenario, the emissions intensity of oil and gas activities needs to be roughly halved by the end of this decade, leading to a 60% overall reduction in total emissions from oil and gas operations.
- According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global production, transportation and processing of oil and gas emitted the equivalent of 5.1 billion tonnes of CO2 in 2022 - almost 15% of total energy-related greenhouse gas emissions.
- Major Producers and Consumers:
- The top oil-producing nations in 2022 were the United States, Saudi Arabia, Russia, Canada, and China, with OPEC remaining a powerful cartel of oil producers.
- The US became the top petroleum liquids producer in the world accounting for 20% of the world’s production in 2022.
- The top oil consuming countries of 2022 were the US < China < India < Russia < Japan < Saudi Arabia < Brazil < South Korea < Canada < Germany.
- The top oil-producing nations in 2022 were the United States, Saudi Arabia, Russia, Canada, and China, with OPEC remaining a powerful cartel of oil producers.
- India’s Scenario:
- India is still highly exposed to the industrial activities related to fossil fuels - it is the world's 3rd largest oil consumer at around 5 million barrels a day with an annual growth rate of oil demand at 3-4%.
- India’s import dependency in oil and natural gas has also increased - in the case of natural gas, the net import dependency rose from just over 30% (2012-13) to nearly 48% (2021-22).
- Crude oil has also seen a similar increase in imports.
Why are the Countries not Restricting Oil and Gas Production?
- Economic Considerations: Oil and natural gas production often play a significant role in a country's economy, contributing to government revenues, employment, and overall economic growth.
- Energy Security: Oil and natural gas are essential for energy security; countries prioritise ensuring a steady and reliable supply of energy to increased production to meet domestic demand and reduce dependence on imports.
- Geopolitical Considerations: Some nations may use energy production as a tool for political leverage or to exert influence over other nations, which can impact production control efforts.
- Domestic Political Factors: Political considerations, including domestic pressure and competing interests, can influence production decisions. Governments may face opposition from stakeholders, including industry groups, local communities, or political factions, which can complicate efforts to control production.
How can the Dependence on Oil and Gas be Reduced?
- Setting Concrete Targets: Developed countries have absolutely no excuse - new oil and gas investments should have ended already. All the countries, especially richer countries, need to lead on this, and set phase-out dates for all fossil fuel production.
- Embrace Renewable Energy Innovation: Countries shall invest in research and development to accelerate the advancement of renewable energy technologies.
- This includes funding for breakthrough technologies such as next-generation solar panels, advanced wind turbines, and energy storage solutions.
- Foster International Collaboration: Countries can collaborate on research, knowledge sharing, and joint initiatives to develop innovative solutions for reducing oil and natural gas consumption.
- Sharing best practices and lessons learned can accelerate progress globally.
- Aid for Capacity Building: Developed countries shall assist developing countries in building their capacity to implement sustainable energy projects through technical assistance, training programs, and knowledge sharing.
- Green Industrialisation: Countries shall promote the development of green industries, such as renewable energy manufacturing, to create local job opportunities, increase energy self-sufficiency, and reduce dependence on fossil fuel imports.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q.1 With reference to furnace oil, consider the following statements: (2020)
- It is a product of oil refineries.
- Some industries use it to generate power.
- Its use causes sulphur emissions into environment.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q.2 The term ‘West Texas Intermediate’, sometimes found in news, refers to a grade of (2020)
(a) Crude oil
(b) Bullion
(c) Rare earth elements
(d) Uranium
Ans: (a)
Mains:
Q. The question of India’s Energy Security constitutes the most important part of India’s economic progress. Analyse India’s energy policy cooperation with West Asian countries. (2017)