Global Burden of Cancer: WHO | 08 Feb 2024
For Prelims: Global Burden of Cancer: WHO, World Cancer Day (4th February), Cancer.
For Mains: Global Burden of Cancer: WHO, Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
Why in News?
Ahead of World Cancer Day (4th February), the World Health Organization (WHO)’s cancer agency, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), released the latest estimates of the Global Burden of Cancer in 2022.
- The IARC estimates highlighted the growing burden of cancer, the disproportionate impact on underserved populations, and the urgent need to address cancer inequities worldwide.
What are the Key Highlights of the Global Burden of Cancer in 2022 by WHO?
- Global Burden:
- In 2022, there were an estimated 20 million new cancer cases and 9.7 million deaths.
- The estimated number of people alive within 5 years following a cancer diagnosis was 53.5 million.
- About 1 in 5 people develop cancer in their lifetime.
- Common Cancer Types:
- 10 types of cancer collectively comprised around two-thirds of new cases and deaths globally in 2022.
- Lung cancer was the most commonly occurring cancer worldwide with 2.5 million new cases accounting for 12.4% of the total new cases.
- Female breast cancer ranked second (2.3 million cases, 11.6%), followed by colorectal cancer, prostate cancer, and stomach cancer.
- Leading Causes of Death:
- Lung cancer was the leading cause of cancer death (1.8 million deaths, 18.7% of the total cancer deaths) followed by colorectal cancer (900 000 deaths, 9.3%), liver cancer, breast cancer and stomach cancer.
- Lung cancer’s re-emergence as the most common cancer is likely related to persistent tobacco use in Asia.
- Lung cancer was the leading cause of cancer death (1.8 million deaths, 18.7% of the total cancer deaths) followed by colorectal cancer (900 000 deaths, 9.3%), liver cancer, breast cancer and stomach cancer.
- Cancer Inequities:
- There have been striking inequities in the cancer burden according to human development. This is particularly true for breast cancer.
- In countries with a very high HDI (Human Development Index), 1 in 12 women will be diagnosed with breast cancer in their lifetime and 1 in 71 women die of it.
- By contrast, in countries with a low HDI; while only one in 27 women is diagnosed with breast cancer in their lifetime, one in 48 women will die from it.
- Women in lower HDI countries are 50% less likely to be diagnosed with breast cancer than women in high HDI countries, yet they are at a much higher risk of dying of the disease due to late diagnosis and inadequate access to quality treatment.
- Projected Burden Increase:
- Over 35 million new cancer cases are predicted in 2050, a 77% increase from the estimated 20 million cases in 2022.
- The rapidly growing global cancer burden reflects both population ageing and growth, as well as changes to people’s exposure to risk factors, several of which are associated with socioeconomic development.
- Tobacco, alcohol and obesity are key factors behind the increasing incidence of cancer, with air pollution still a key driver of environmental risk factors.
- In terms of the absolute burden, high HDI countries are expected to experience the greatest absolute increase in incidence, with an additional 4.8 million new cases predicted in 2050 compared with 2022 estimates.
- Call for Action:
- There is an urgent need for major investments to address global inequities in cancer outcomes and to ensure access to affordable, quality cancer care for all individuals regardless of their geographical location or socioeconomic status.
What are the Key Findings Related to India?
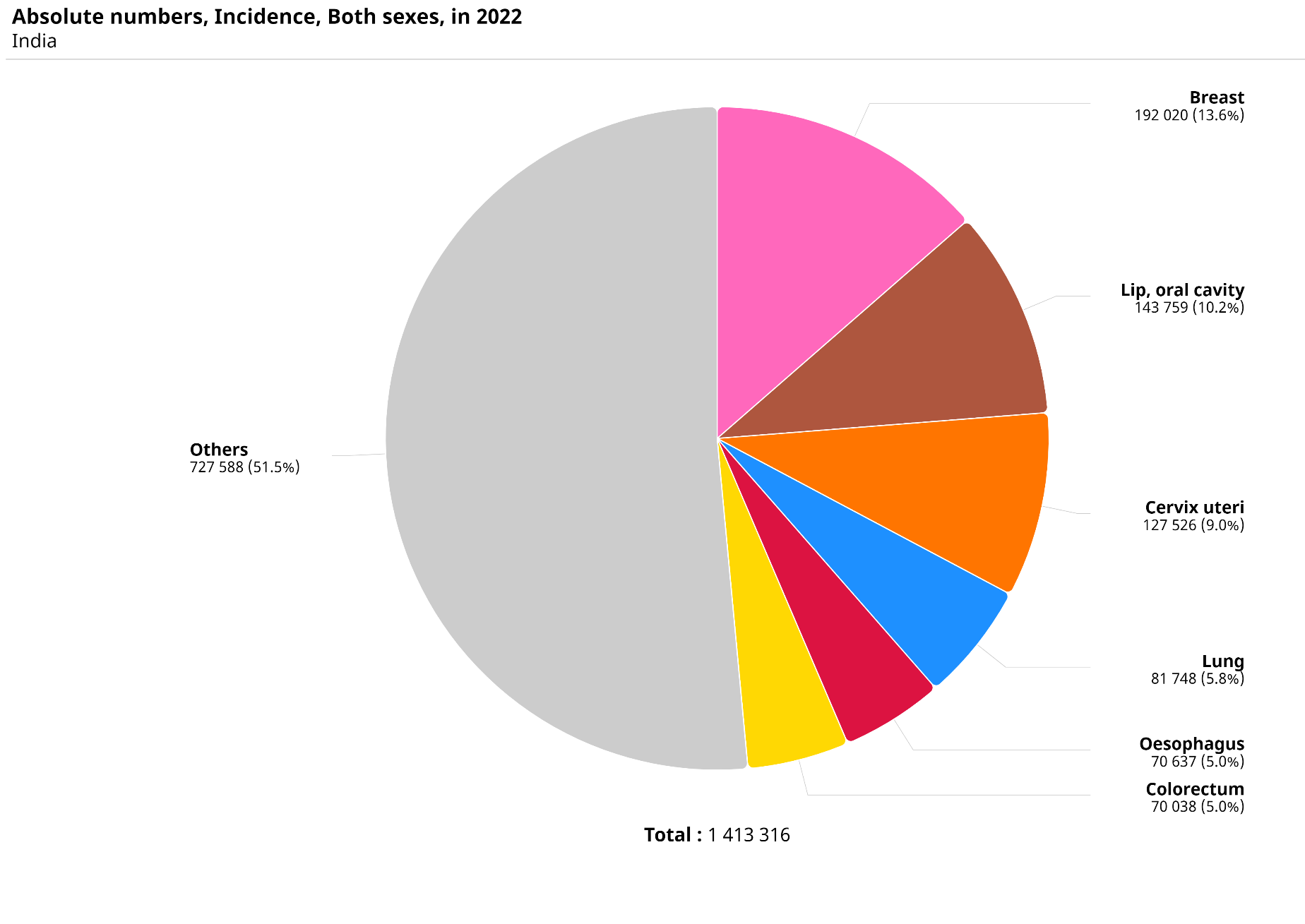
- India reported 1,413,316 new cases in 2022 with a higher proportion of female patients — 691,178 men and 722,138 women.
- Breast cancer had the highest proportion in the country, with 192,020 new cases, accounting for 13.6% of all patients and over 26% in women.
- In India, breast cancer was followed by lip and oral cavity (143,759 new cases, 10.2%), cervix and uterine, lung, and oesophagal cancers.
- A recent study by WHO assessing the cancer burden in Asia, published in The Lancet Regional Health, found that India alone accounted for 32.9% of global deaths and 28.1% of new cases of lip and oral cavity cancer in 2019.
- This was on account of the widespread consumption of smokeless tobacco (SMT) such as khaini, gutkha, betel quid and paan masala in South Asian countries like India, Bangladesh and Nepal. Worldwide, SMT is responsible for 50% of the oral cancer burden.
- As per the Lancet Global Health 2023, India accounted for 23% of deaths that occurred due to cervical cancer globally.
- In India, cervical cancer’s five-year survival rate was 51.7%. However, survival rates in India are lower compared to high-income countries such as the United States.
What are the Key Facts Related to World Cancer Day?
- About:
- World Cancer Day is an international awareness day led by the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) celebrated on 4th February every year.
- Cancer is caused by an uncontrolled, abnormal growth of cells in the body that causes lump or tumour in most causes.
- It was first celebrated on 4th February 2000 at the World Summit Against Cancer for the New Millennium in Paris.
- The Paris Charter's mission is to promote research, prevent cancer, improve patient services, raise awareness and mobilise the global community to make progress against cancer, and includes the adoption of World Cancer Day.
- World Cancer Day is an international awareness day led by the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) celebrated on 4th February every year.
- Theme 2024:
- Close the Care Gap.
- The theme aims to mobilise the necessary attention and resources to ensure that the rising burden of cancer can be addressed in an equal manner across the globe and that all people in the world have access to systematic testing, and early diagnosis and treatment.
- Close the Care Gap.
Cancer
- It is a complex and broad term used to describe a group of diseases characterised by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the body.
- These abnormal cells, known as cancer cells, have the ability to invade and destroy healthy tissues and organs.
- In a healthy body, cells grow, divide, and die in a regulated manner, allowing for the normal functioning of tissues and organs.
- However, in the case of cancer, certain genetic mutations or abnormalities disrupt this normal cell cycle, causing cells to divide and grow uncontrollably.
Cervical Cancer
- Cervical cancer develops in a woman's cervix (the entrance to the uterus from the vagina).
- Almost all cervical cancer cases (99%) are linked to infection with high-risk human papillomaviruses (HPV), an extremely common virus transmitted through sexual contact.
- Two HPV types (16 and 18) are responsible for nearly 50% of high grade cervical pre-cancers.
- Cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer among women globally. About 90% of the new cases and deaths worldwide in 2020 occurred in low- and middle-income countries.
What are the Government Initiatives related to Cancer?
- The interim Budget 2024-25 encouraged the vaccination of girls aged 9-14 years to prevent cervical cancer.
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke
- National Cancer Grid
- National Cancer Awareness Day
- HPV Vaccine
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q 1. Consider the following statements: (2010)
- The Taxus tree is naturally found in the Himalayas.
- The Taxus tree is listed in the Red Data Book.
- A drug called “taxol” is obtained from Taxus trees and is effective against Parkinson’s disease.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q.1 What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of the society? (2021)
Q.2 What do you understand by nanotechnology and how is it helping in health sector? (2020)
Q.3 Why is there so much activity in the field of biotechnology in our country? How has this activity benefitted the field of biopharma? (2018)
Q.4 Stemcelltherapy is gaining popularity in India to treat a wide variety of medical conditions including Leukaemia, Thalassemia, damaged cornea and several burns. Describe briefly what stem cell therapy is and what advantages it has over other treatments? (2017)