Gender Parity and Women's Empowerment Gap | 21 Jul 2023
For Prelims: United Nations, Women's Empowerment Index (WEI), Global Gender Parity Index (GGPI)
For Mains: Challenges and gaps in achieving women's empowerment and gender parity, Issues Related to Women
Why in News?
A recent report by the United Nations sheds light on the status of women's empowerment and gender parity around the world.
- The comprehensive analysis, jointly created by UN Women and UN Development Programme, evaluated 114 countries based on the Women's Empowerment Index (WEI) and the Global Gender Parity Index (GGPI).
- The findings emphasize the urgent need for comprehensive policy action to address the existing gaps and propel progress toward a more equitable and inclusive world.
What are the Key Findings of the Report?
- Only 1% of women globally live in countries with high women's empowerment and gender parity.
- Leadership roles and decision-making remain predominantly male-dominated, restricting opportunities for women.
- On average, women achieve only 60% of their full potential, according to the WEI.
- Women lag behind men by 28% across key dimensions of human development, as measured by the GGPI.
- None of the 114 countries analyzed achieved complete women's empowerment or gender parity.
- Over 90% of women worldwide reside in countries with low or middle women's empowerment and low or middle performance in achieving gender parity.
- Gender equality challenges persist even in highly developed countries. Among the 114 countries analyzed, over 85, including more than half in the high or very high human development categories, show low or moderate women's empowerment and gender parity. Economic progress alone does not ensure gender equality.
- India has low women's empowerment and gender parity despite moderate human development, highlighting the need for concerted efforts to bridge the gender gap and uplift women's status.
- Gender equality alone does not guarantee women's empowerment. The report shows that no country with a gender gap has achieved high women's empowerment.
- Additionally, about 8% of women live in countries with low empowerment but high gender parity.
UN Women:
- UN Women was established in 2010 by the UN General Assembly to accelerate progress on meeting the needs and rights of women and girls worldwide.
- UN Women supports UN Member States as they set global standards for achieving gender equality and works with governments and civil society to design and implement laws, policies, programs and services that benefit women and girls.
- UN Women focuses on four strategic priorities: women’s leadership and political participation, women’s economic empowerment, ending violence against women, and peace, security and humanitarian action.
What are the Recommendations for Comprehensive Policy Action?
- Health Policies: Governments should support and promote universal access to sexual and reproductive health, aiming for long and healthy lives for all.
- Equality in Education: Addressing gaps in skills and the quality of education, particularly in fields like STEM, will empower women and girls in the digital age.
- Work-life Balance and Support for Families: Policies and services addressing work-life balance, including affordable quality childcare, parental leave schemes, and flexible working arrangements, should be invested in.
- Women's Equal Participation: Targets and action plans should be established to achieve gender parity in all spheres of public life, while discriminatory laws and regulations holding women back must be eliminated.
- Violence Against Women: Implementing comprehensive measures focused on prevention, changing social norms, and eliminating discriminatory laws and policies is crucial.
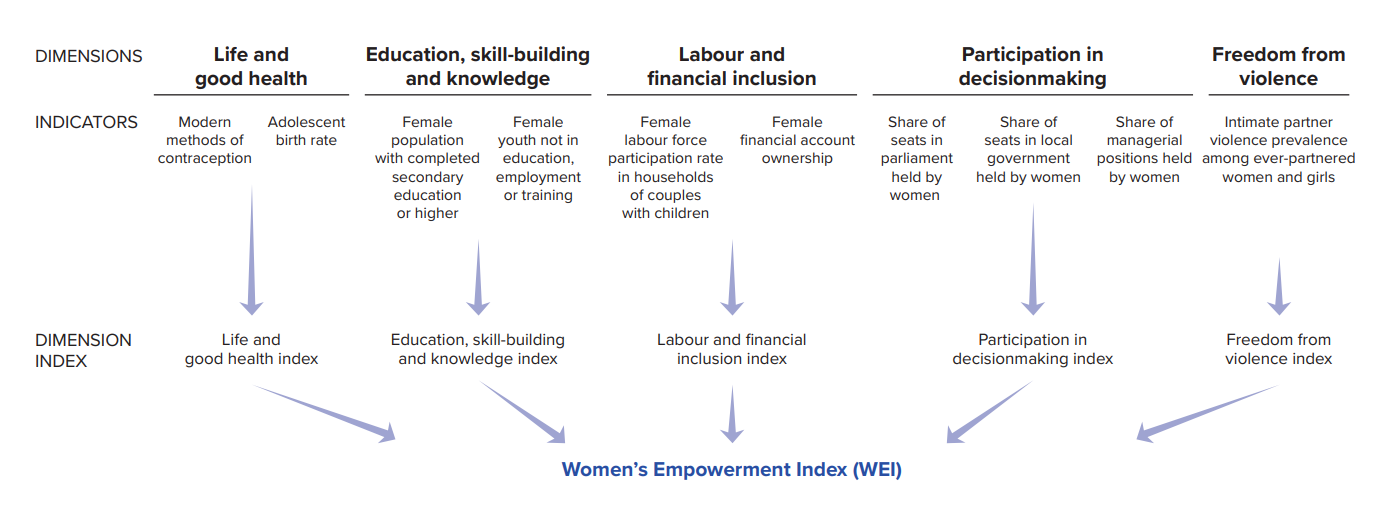
What is the Women's Empowerment Index (WEI)?
- The WEI is a composite index developed by UN Women and UNDP.
- It measures women's empowerment across five dimensions: life and good health, education, skill-building and knowledge, labor and financial inclusion, participation in decision-making, and freedom from violence.
- The WEI captures women's power and freedom to make choices and seize life opportunities.
- The development of the WEI marks a significant milestone in evidence-based policymaking and serves as a baseline for monitoring the government's progress towards Sustainable Development Goal 5 (SDG5) on gender equality and empowerment of women and girls.
What is the Global Gender Parity Index (GGPI)?
- The GGPI is a composite index that assesses gender disparities in key dimensions of human development, including health, education, inclusion, and decision-making.
- The GGPI is developed by UN Women and UNDP as part of a new global report titled ‘The Path to Equality: Women’s Empowerment and Gender Parity in Human Development’, which was launched in July 2023.
- The GGPI aims to capture the status of women relative to men across different contexts and dimensions. It also reflects the multidimensional and interrelated nature of gender equality.
What are the Indian Initiatives to reduce Gender Gap in Social, Economic and Political Life?
- Economic Participation and Health and Survival:
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao: It ensures the protection, survival and education of the girl child.
- Mahila Shakti Kendra: Aims to empower rural women with opportunities for skill development and employment.
- Rashtriya Mahila Kosh: It is an apex micro-finance organization that provides micro-credit at concessional terms to poor women for various livelihood and income generating activities.
- Sukanya Samriddhi Yojna: Under this scheme girls have been economically empowered by opening their bank accounts.
- Female Entrepreneurship: To promote female entrepreneurship, the Government has initiated Programmes like Stand-Up India and Mahila e-Haat (online marketing platform to support women entrepreneurs/ SHGs/NGOs), Entrepreneurship and Skill Development Programme (ESSDP).
- Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalaya: They have been opened in Educationally Backward Blocks (EBBs).
- Political Reservation: Government has reserved 33% of the seats in Panchayati Raj Institutions for women.
- Capacity Building of Elected Women Representatives: It is conducted with a view to empowering women to participate effectively in the governance processes.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following gives ‘Global Gender Gap Index’ ranking to the countries of the world? (2017)
(a) World Economic Forum
(b) UN Human Rights Council
(c) UN Women
(d) World Health Organization
Ans: (a)