Social Issues
Gender Disparity in Organ Transplants
- 17 Nov 2023
- 5 min read
For Prelims: Transplantation of Human Organs Act, 1994,National Organ Transplantation Guidelines, National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation
For Mains: Factors Contributing to the Gender Disparity in Organ Transplants,
Why in News?
In India, a stark gender disparity in organ transplants has been revealed by data from the National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO). Between 1995 and 2021, four out of every five organ recipients were men, indicating a significant healthcare imbalance.
- The low representation of women in organ transplants highlights the need and importance of equitable access to healthcare for all.
Note:
- NOTTO is set up under the Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, located in New Delhi.
- The National Network division of NOTTO functions as the apex centre for all Indian activities for procurement, distribution and registry of organs and tissue donation and transplantation in the country.
What are the Trends in Organ Transplants in India?
- According to the data collated by the NOTTO, the nodal agency for organ and tissue donation and transplantation in India, there is a significant gender disparity among organ recipients and donors in the country.
- The data shows that between 1995 and 2021, out of the total 36,640 patients who underwent organ transplants, 29,695 were men and only 6,945 were women.
- Although studies show that the number of women donors is higher than men.
- This indicates that women who need organ transplants are not getting adequate access to healthcare and treatment, due to various socio-cultural and economic factors.
- The data shows that between 1995 and 2021, out of the total 36,640 patients who underwent organ transplants, 29,695 were men and only 6,945 were women.
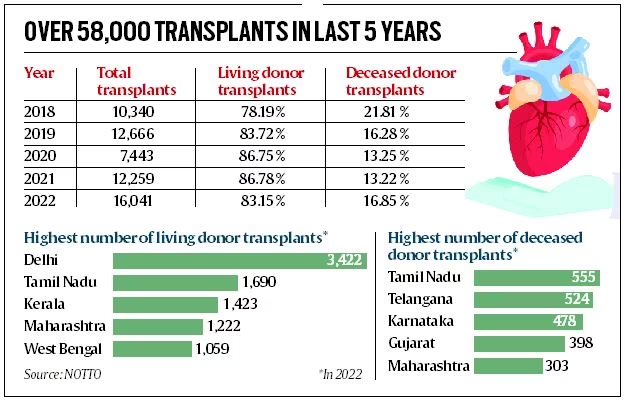
- According to the NOTTO data, there has been an overall increase in the number of organ transplants in India, with a record high of 16,041 such procedures in 2022.
- Among the different types of organ transplants, kidney transplants are the most common, followed by liver, heart, and lung transplants.
- Among the different states, Delhi topped the table in living donor transplants, while Tamil Nadu remained the leader in deceased donor transplants, where organs from brain-dead patients are used.
- Also, India conducts the third highest number of transplants in the world.
What are the Causes and Consequences of Gender Disparity in Organ Transplants?
- Causes of Gender Disparity in Organ Transplants:
- The gender disparity in organ transplants reflects the prevailing gender inequality and discrimination in Indian society, where women’s health and well-being are often neglected or compromised.
- Lack of awareness and education among women and their families about the need and benefits of organ transplants.
- Preference for male members as recipients, especially in cases of living donor transplants, where organs from family members are used.
- Fear and stigma associated with organ donation and transplantation, especially among women, who may face social exclusion or marital problems.
- Financial constraints and affordability issues, as organ transplants are expensive and require long-term follow-up and medication.
- Consequences of Gender Disparity in Organ Transplants:
- Gender bias and discrimination in the healthcare system, where women may face harassment, negligence, or denial of treatment by the medical staff or authorities.
Laws Related to Organ Donation in India
- Transplantation of Human Organs Act, 1994:
- It was enacted to provide a system of removal, storage and transplantation of human organs for therapeutic purposes and for the prevention of commercial dealings in human organs.
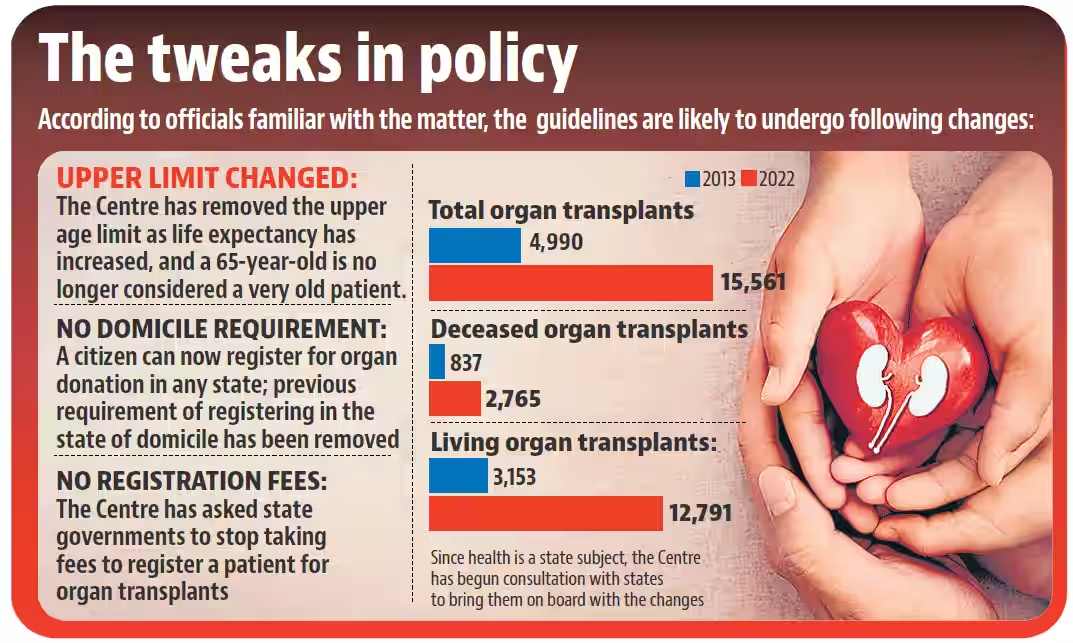
- National Organ Transplantation Guidelines:
Way Forward
- Organize awareness and information campaigns on organ donation and transplantation, targeting women and their families, through various media and platforms.
- Providing counseling and support services to women and their families, to address their doubts, fears, and concerns regarding organ donation and transplantation.
- Strengthening and expanding the network and infrastructure of organ and tissue donation and transplantation, to ensure timely and equitable access and availability of organs and services.
- Implementing and enforcing the legal and ethical norms and guidelines for organ and tissue donation and transplantation, to prevent and punish any malpractices or violations.
- Encouraging and facilitating the participation and empowerment of women as organ donors and recipients, by recognising and rewarding their contributions and achievements.