G7 Summit: Climate Goals, Gandhi Statue & Quad Climate Initiatives | 23 May 2023
For Prelims: G7 Summit, Quad Leaders' Summit, G7 Countries, Net-Zero Targets, Indo-Pacific region,
For Mains: Role of the G7 summit in addressing global challenges, the significance of the Quad in promoting regional cooperation, India's foreign policy, the relationship between climate change and global security
Why in News?
During the recent 49th G7 summit, member countries had outlined key milestones in their climate Wishlist in response to ongoing studies and reports that continue to raise alarms about the worsening state of climate change, urging immediate action.
- Furthermore, at the same summit, the Prime Minister of India unveiled a bust of Mahatma Gandhi in Hiroshima, Japan.
- Additionally, the Quad Leaders' Summit also took place on the sidelines of the G7 summit, emphasizing shared democratic values, strategic interests, and initiatives for the Indo-Pacific region.
What are the Main Climate Wishlist of the G7?
- Global Peak in Emissions by 2025:
- The G7 emphasized the need for a global peak in emissions by 2025.
- While this is not mandated under the Paris Agreement, achieving it is not implausible.
- Developed countries are witnessing a decline in emissions, although not at the required pace while developing countries' emissions are still increasing.
- If all countries only fulfill their existing commitments, emissions in 2030 would be about 11% higher than 2010 levels.
- The G7 emphasized the need for a global peak in emissions by 2025.
- Ending Fossil Fuel Use:
- The G7 does not set a specific deadline for ending fossil fuel use but commits to accelerating the phase-out of "unabated fossil fuels" in line with 1.5 degree Celsius trajectories.
- They aim to eliminate "inefficient fossil fuel subsidies" by 2025 or earlier without specifying the definition of "inefficient subsidies."
- The G7 countries claim to have stopped financing new fossil fuel-based energy projects, except in limited circumstances.
- Net-Zero Targets:
- The G7 reiterates its commitment to achieve net-zero status by 2050 and urges other major economies to do the same.
- The world as a whole must become net-zero by mid-century to meet the 1.5-degree Celsius target.
- China aims for net-zero by 2060, while India has set 2070 as its target.
- Post-2050 targets of major developing countries may change with evolving technologies and cleaner energy adoption.
What are the Challenges in Implementing the G7 Climate Wishlist?
- Insufficient Action and Inconsistencies:
- G7 countries account for 20% of global emissions but have not effectively fulfilled their pledges.
- Lack of sufficient and consistent actions to align with the 1.5-degree Celsius and 2-degree Celsius temperature goals.
- G7 member countries Failure to update nationally determined contributions (NDCs) . Paris Agreement targets.
- Inadequate Climate Finance Support:
- G7 countries have been slow and insufficient in providing climate finance to developing nations agreed under the Paris Agreement targets.
- Developing countries, disproportionately affected by climate impacts, require support for adaptation and resilience.
- Oxfam reports that only 20% of climate finance from rich countries in 2019 was allocated for adaptation, with minimal reaching least developed countries.
- Continued Reliance on Fossil Fuels:
- Criticism directed at the G7 countries for their ongoing dependence on fossil fuels, particularly coal.
- Fossil fuels, especially coal, are highly carbon-intensive energy sources exacerbating climate change.
- Oil Change International highlights that G7 countries provided significant public finance for fossil fuels, surpassing investments in clean energy.
- Criticism directed at the G7 countries for their ongoing dependence on fossil fuels, particularly coal.
Why did the PM of India Unveil Gandhi’s Bust in Hiroshima?
- Mahatma Gandhi was one of the most influential leaders of the twentieth century, who championed the principles of non-violence, peace, justice and human dignity. His statue was unveiled at Hiroshima Peace Memorial Park , as a tribute to his legacy and a reminder of his relevance in today's world.
- The symbolic gesture was meant to highlight the shared commitment of the G7 and its partners to prevent another nuclear catastrophe and to pursue nuclear disarmament and non-proliferation.
- It was also meant to acknowledge the suffering and resilience of the Hibakusha, the survivors of the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945.
- The statue was also seen as a recognition of India's role and contribution to global peace and security, as well as its partnership with Japan on various issues, including climate change.
- The unveiling ceremony was attended by the G7 leaders, as well as the Prime Minister of India, who was invited as a guest to the summit along with other leaders from Australia, South Korea, and South Africa.
What Were the Outcomes of the Quad Leaders' Summit?
- The Quad Leaders' Summit was held on May 23, 2023, on the sidelines of the G7 summit. It was attended by the Prime Minister of India, President Joe Biden of the US, Prime Minister Scott Morrison of Australia and Prime Minister Yoshihide Suga of Japan.
- The Quad is an informal strategic dialogue among four democracies that share common interests and values in the Indo-Pacific region.
- One of the key areas of cooperation among the Quad members is climate change. The leaders issued a joint statement that reaffirmed their commitment to the Paris Agreement and its full implementation.
- They also announced several initiatives to enhance collaboration on clean energy transition, innovation, adaptation, and resilience. Some of these initiatives are:
- Launching a new Quad Climate Working Group to coordinate their efforts on domestic and international climate policies.
- Establishing a Quad Clean Energy Partnership to support the deployment of clean energy technologies in Indo-Pacific countries through technical assistance, capacity building, and financing mechanisms.
- Supporting a Quad Green Shipping Network to promote decarbonization of maritime transport through information sharing, best practices, and standards development.
- Expanding cooperation on disaster risk reduction and management through joint exercises, training, and information sharing.
- Supporting nature-based solutions for climate mitigation and adaptation through the conservation and restoration of ecosystems such as forests, wetlands, and mangroves.
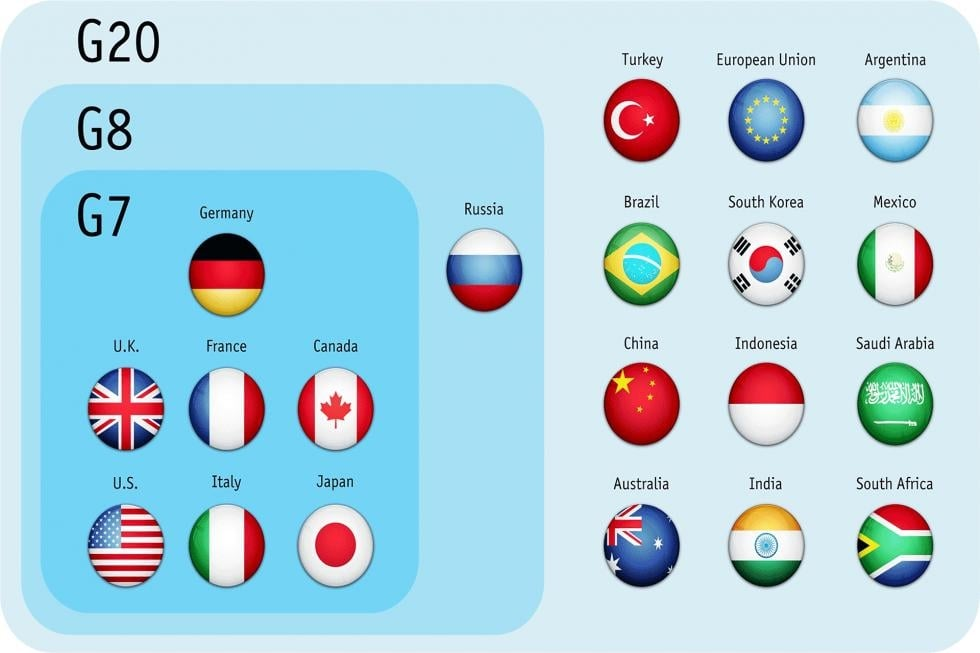
What is the Group of Seven (G7)?
- It is an intergovernmental organization that was formed in 1975.
- The bloc meets annually to discuss issues of common interest like global economic governance, international security and energy policy.
- The G7 countries are the UK, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan and the US.
- All the G7 countries and India are a part of G20.
- The G7 does not have a formal charter or a secretariat. The presidency, which rotates among member countries each year, is in charge of setting the agenda. Sherpas, ministers and envoys hammer out policy initiatives before the summit.
- The 49th G7 summit was held in Hiroshima, Japan.
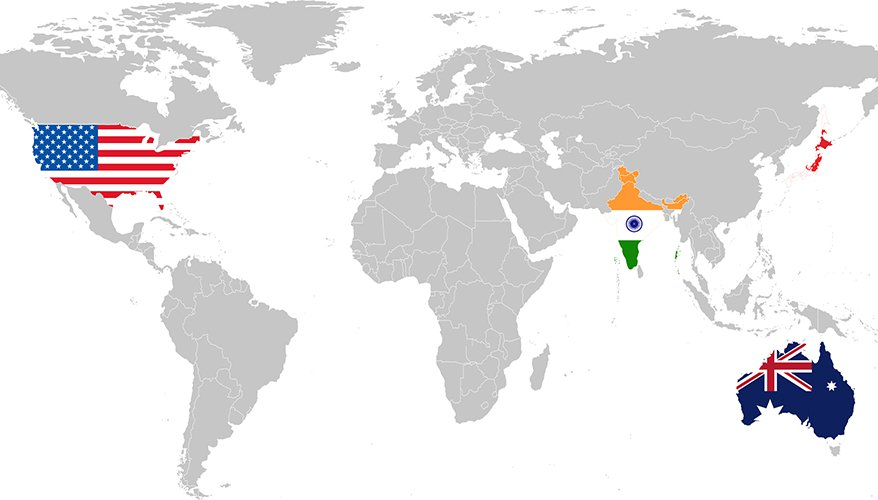
What is QUAD?
- It is the grouping of four democracies –India, Australia, the US, and Japan.
- All four nations find a common ground of being democratic nations and also support the common interest of unhindered maritime trade and security.
- The Quad is billed as four democracies with a shared objective to ensure and support a “free, open, and prosperous” Indo-Pacific region.
- The idea of Quad was first mooted by Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe in 2007. However, the idea couldn’t move ahead with Australia pulling out of it, apparently due to Chinese pressure.
- Finally in 2017, India, Australia, the US and Japan, came together and formed this “quadrilateral” coalition.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. The term ‘Intended Nationally Determined Contributions’ is sometimes seen in the news in the context of (2016)
(a) pledges made by the European countries to rehabilitate refugees from the war-affected Middle East
(b) plan of action outlined by the countries of the world to combat climate change
(c) capital contributed by the member countries in the establishment of Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank
(d) plan of action outlined by the countries of the world regarding Sustainable Development Goals
Answer: (b)
Q. With reference to the Agreement at the UNFCCC Meeting in Paris in 2015, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
- The Agreement was signed by all the member countries of the UN and it will go into effect in 2017.
- The Agreement aims to limit the greenhouse gas emissions so that the rise in average global temperature by the end of this century does not exceed 2°C or even 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
- Developed countries acknowledged their historical responsibility in global warming and committed to donate $1000 billion a year from 2020 to help developing countries to cope with climate change.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (b)
Q. In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20? (2020)
(a) Argentina, Mexico, South Africa and Turkey
(b) Australia, Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
(c) Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
(d) Indonesia, Japan, Singapore and South Korea
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. ‘Climate change’ is a global problem. How India will be affected by climate change? How Himalayan and coastal states of India will be affected by climate change? (2017)
Q. Describe the major outcomes of the 26th session of the Conference of the Parties (COP) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). What are the commitments made by India in this conference? (2021)