Rapid Fire
Fluoride Contamination
- 08 Apr 2025
- 2 min read
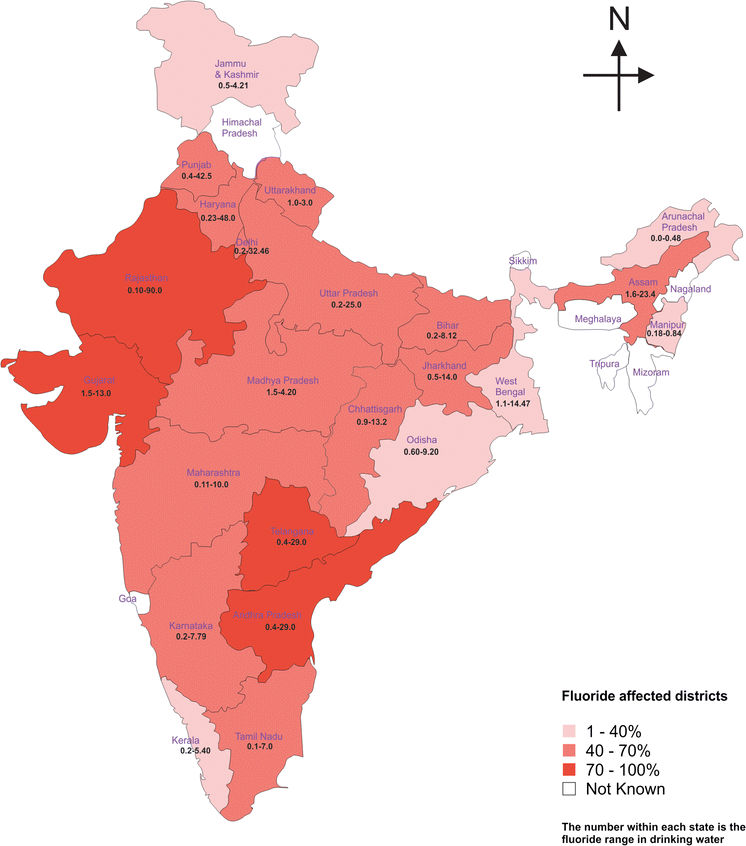
Excess Fluoride in Sonbhadra's groundwater (Uttar Pradesh), has triggered a growing public health crisis.
- Fluoride: It is a highly reactive element that does not occur in elemental form in nature.
- It makes up 0.3 g/kg of the Earth’s crust and is found as fluoride (oxidation state -1) in minerals like fluorspar, cryolite, and fluorapatite.
- Major Uses: Widely used in aluminium production, and as fluxes in steel and glass fibre industries. They are also released during the manufacture of phosphate fertilizers, bricks, tiles, and ceramics.
- Compounds like fluorosilicic acid, sodium hexafluorosilicate, and sodium fluoride are used in municipal water fluoridation.
- Health Impacts: Fluoride has a dual impact, it is beneficial in small amounts (prevents dental caries), but harmful in excess (causes dental fluorosis (mottling of teeth enamel, mainly in children) and skeletal fluorosis (bone/joint issues) ).
- As per the Bureau of Indian Standards, the safe fluoride level in water is 1 to 1.5 mg/L (milligrams per liter), levels above this are considered hazardous to health.
- Schemes for Fluoride Control in India: India launched the National Programme for Prevention and Control of Fluorosis (NPPCF) during the 11th Five Year Plan. Additionally, the Jal Jeevan Mission aims to ensure safe drinking water.
| Read more: Fluoride & Iron Removal technology of CMERI |