Social Justice
Female Genital Mutilation
- 15 Feb 2024
- 5 min read
For Prelims: Female Genital Mutilation, International Day of Zero Tolerance for Female Genital Mutilation, United Nations Population Fund, United Nations Children's Fund
For Mains: Challenges Related to Women, Challenges in Eradicating FGM
Why in News?
Recently, the UN agencies stated that in 2024, nearly 4.4 million girls are at risk of female genital mutilation around the world.
What is Female Genital Mutilation?
- About: Female genital mutilation (FGM) comprises all procedures that involve altering or injuring the female genitalia for non-medical reasons and is recognised internationally as a violation of the human rights, the health and the integrity of girls and women.
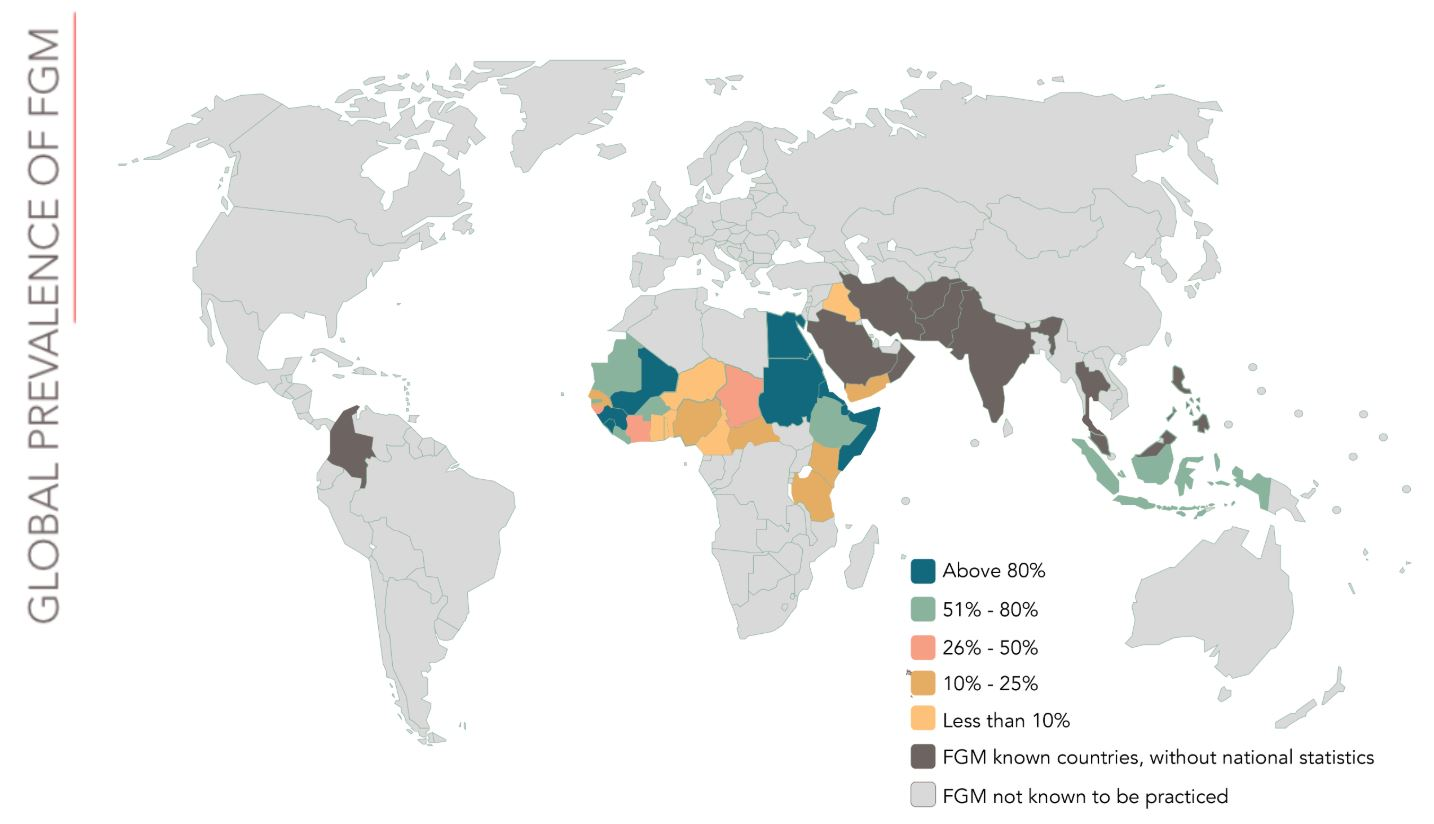
- Prevalence: It is concentrated primarily in Western, Eastern, and North-Eastern Africa, as well as select Middle Eastern and Asian nations.
- However, with increased migration, FGM has become a global concern, affecting girls and women in Europe, Australia, and North America as well.
- Impacts: Girls who undergo female genital mutilation face short-term complications such as severe pain, shock, excessive bleeding, infections, and difficulty in passing urine, as well as long-term consequences for their sexual and reproductive health and mental health.
- Status in India: Presently, there is no legislation that bans the FGM practice in the country.
- In 2017, in response to a petition in the Supreme court, the Ministry of Women and Child Development had said that “at present there is no official data or study which supports the existence of FGM in India.”
- However, according to some other unofficial reports, procedures of FGM are prevalent amongst the Bohra community, primarily in the states of Maharashtra, Kerala, Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Madhya Pradesh.
- Challenges in Eradicating FGM:
- Cultural and Social Norms: FGM is often deeply rooted in cultural and social norms, with communities practicing it as a tradition passed down through generations.
- Changing these deeply ingrained beliefs and practices can be challenging.
- Lack of Awareness and Education: Many individuals within communities where FGM is practiced may not fully understand the harmful consequences of the practice.
- Lack of awareness and education about the physical and psychological health risks associated with FGM can perpetuate its continuation.
- Lack of Adequate Data Collection and Reporting: Limited data collection and reporting on FGM prevalence hinder efforts to understand the scope of the issue and target interventions effectively.
- Cultural and Social Norms: FGM is often deeply rooted in cultural and social norms, with communities practicing it as a tradition passed down through generations.
- Global Initiatives Towards Eradication:
- United Nations Population Fund and United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF), have co-led the largest global programme on the elimination of female genital mutilation (FGM) since 2008.
- In 2012, the UN General Assembly designated 6th February as the International Day of Zero Tolerance for Female Genital Mutilation, with the aim to amplify and direct the efforts on the elimination of this practice.
- 2024 Theme: Her Voice. Her Future
- The United Nations strives for its full elimination by 2030, following the spirit of Sustainable Development Goal 5.
- SDG 5.3 aims to eliminate all harmful practices, such as child, early and forced marriage and female genital mutilations.
Way Forward
- Legislation and Policy Enforcement: Strengthening existing laws to explicitly bans FGM and imposes penalties for those who perform or facilitate it.
- Governments should ensure effective enforcement of these laws through law enforcement agencies.
- Awareness and Education: Launching a comprehensive awareness campaigns to educate communities about the harmful effects of FGM on physical, psychological, and sexual health.
- These campaigns should target not only individuals within practicing communities but others as well.
- Inclusion in Human Rights Framework: There is a need to ensure that efforts to combat FGM are grounded in human rights principles and respect the rights of women and girls.
- Advocating for the inclusion of FGM prevention and response measures in international human rights framework is the need of the hour.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. Discuss the positive and negative effects of globalisation on women in India? (2015)