Environmental Performance Index 2024 | 18 Jun 2024
For Prelims: Environmental Performance Index 2024, air quality, emissions, and biodiversity conservation, climate change category, net-zero emissions by 2070, additional carbon sinks, India's forests, wetlands, agro-biodiversity, soil health, food loss.
For Mains: Significance of Environmental Performance Index 2024.
Why in News?
The Yale Center for Environmental Law and Policy and the Columbia Center for International Earth Science Information Network released the Environmental Performance Index (EPI) for 2024.
What are the Key Highlights of EPI 2024?
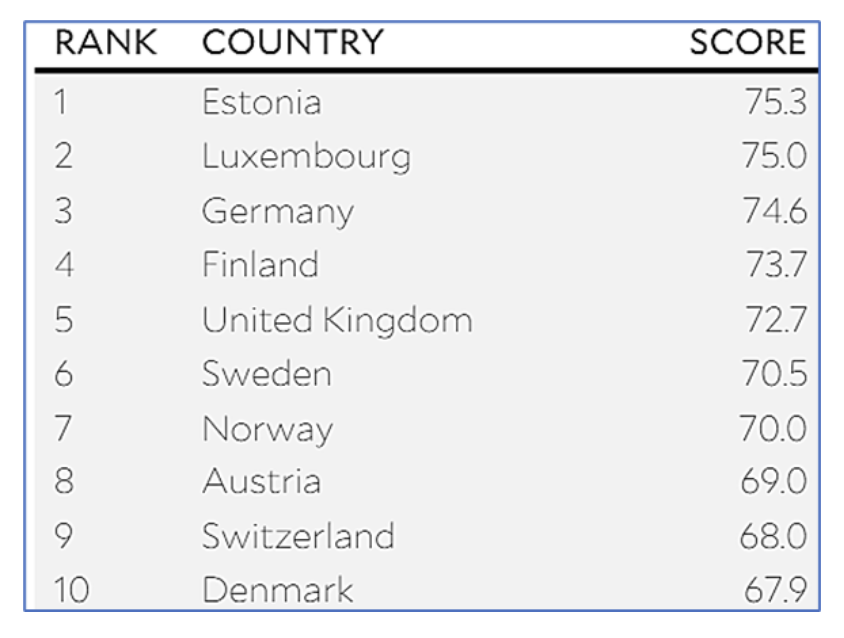
- Global Scenario: Estonia leads the index by reducing its greenhouse gas emissions by 59% from 1990 levels.
- The report shows that only five countries — Estonia, Finland, Greece, Timor-Leste, and the United Kingdom — cut their GHG emissions at the rate needed to reach net zero by 2050.
- In contrast, Sub-Saharan Africa and Southern Asia rank lowest among the eight regions assessed.
- Apart from the United Kingdom, all countries identified in the 2022 Environmental Performance Index (EPI) report as being on track to achieve net zero emissions by 2050, and have either seen slow progress, as in the United States, or their emissions are still increasing, as seen in China, India, and Russia.
- India’s Performance: India ranks 176th out of 180 countries with 27.6 points, placing above only Pakistan, Vietnam, Laos, and Myanmar.
- It performs poorly in Air quality, Emissions, and Biodiversity Conservation, largely due to its heavy reliance on coal, which contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution levels.
- Specifically, India ranks 177th in air quality and 172nd in projected emissions by 2025.
- It performs poorly in Air quality, Emissions, and Biodiversity Conservation, largely due to its heavy reliance on coal, which contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution levels.
- The Largest Emitter Of Transboundary Pollution: In South Asia, India is identified as the largest emitter of transboundary pollution, impacting neighbouring Bangladesh and affecting residents' well-being.
- Despite its low overall ranking, India fares relatively better (133rd) in the climate change category, due to investments in renewable energy and a commitment to achieving net-zero emissions by 2070.
- However, achieving these goals will require an additional USD 160 billion annually in climate change mitigation investments.
- Despite its low overall ranking, India fares relatively better (133rd) in the climate change category, due to investments in renewable energy and a commitment to achieving net-zero emissions by 2070.
- New Metrics Introduced: The 2024 EPI introduces pilot indicators to measure the effectiveness and stringency of protected areas.
What are the Issues Related to EPI?
- Issues Raised By India:
- Projected GHG Emissions Calculation: The calculation of projected GHG emissions by 2050 is based on the average rate of change in emissions, which India considers inadequate.
- Measurement of biodiversity loss or ecosystem health can be challenging due to the intricate dynamics involved and the lack of standardised methodologies across all regions.
- Carbon Sinks Exclusion: India's forests and wetlands, which act as crucial carbon sinks, have not been factored into the computation of projected GHG emissions trajectory up to 2050 in the EPI 2024.
- Ecosystem Condition Overlooked: While the index computes the extent of ecosystems, it does not evaluate their condition or productivity.
- Lack of Relevant Indicators: The index does not include indicators like agro-biodiversity, soil health, food loss, and waste, developing nations may lack robust monitoring systems or face difficulties in collecting comprehensive environmental data, which are important for developing countries with large agrarian populations.
- Issues In General:
- Balancing National Priorities: Countries may prioritise economic development over environmental protection, leading to potential conflicts or resistance in implementing EPI recommendations.
- Nations heavily reliant on resource extraction or fossil fuel-based industries may face challenges in transitioning to more sustainable practices.
- Funding and Resource Constraints: Developing countries may struggle to allocate sufficient funds or expertise for environmental projects, hindering progress and developed countries have not allocated sufficient money to the developing nation for mitigation.
- Cross-Border Environmental Impacts: Addressing transboundary issues such as air pollution, water management, or wildlife protection may require multilateral agreements and joint efforts.
- Balancing National Priorities: Countries may prioritise economic development over environmental protection, leading to potential conflicts or resistance in implementing EPI recommendations.
What is the Environmental Performance Index?
- About: The Environmental Performance Index (EPI) is a biennial index, initially launched by the World Economic Forum in 2002 under the name Environmental Sustainability Index (ESI).
- Evaluation Target: It evaluates nations' efforts to meet international environmental policy targets such as the U.N. sustainability goals, the Paris Climate Change Agreement (2015), and the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework.
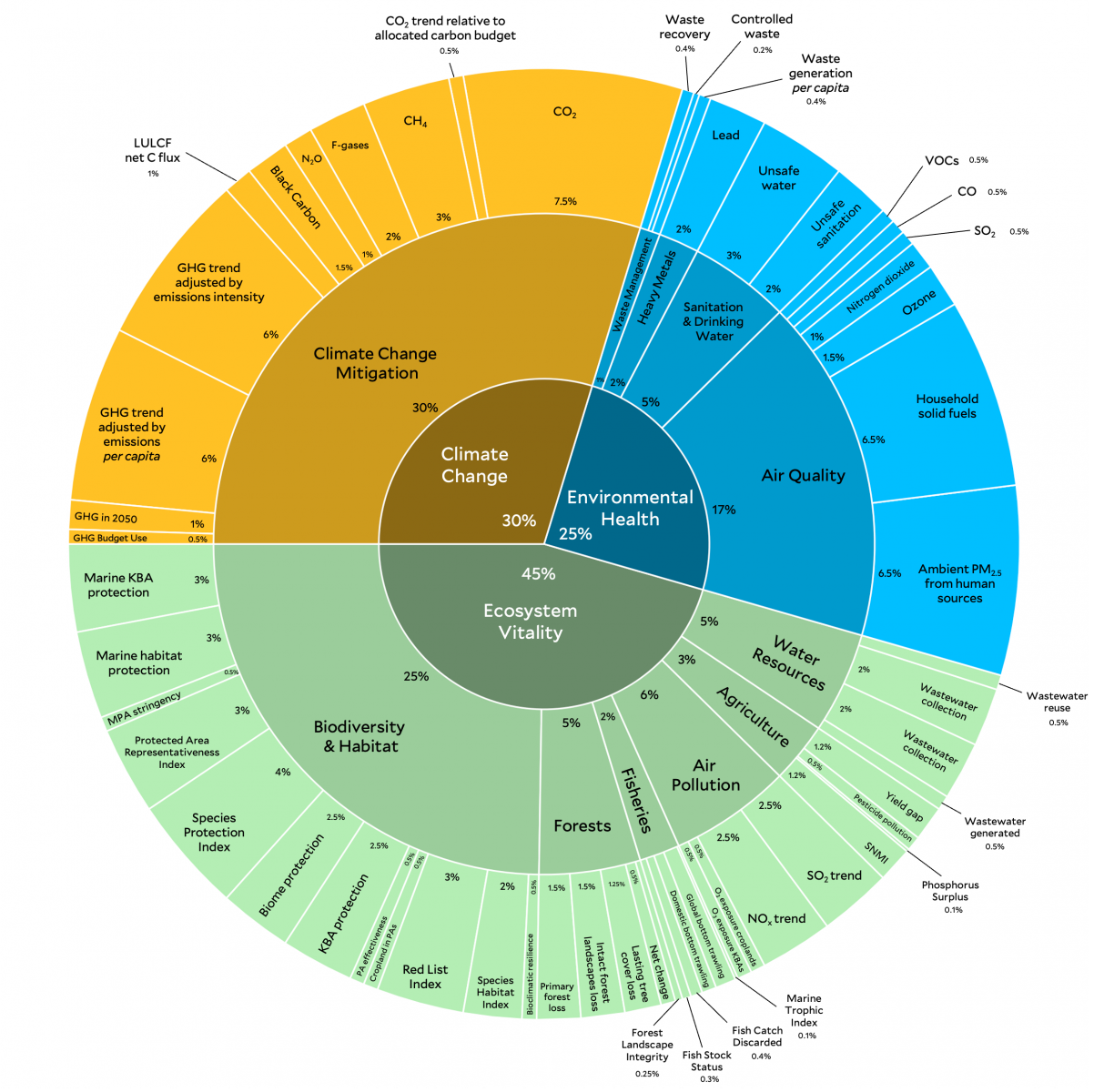
- Framework: The 2024 EPI leverages 58 performance indicators grouped into 11 issue categories with 3 policy objectives:
- Environmental Health
- Ecosystem Vitality
- Climate Change
- The EPI team transforms the raw environmental data into indicators that place countries on a 0–100 scale from worst to best performance.
- Significance:
- Good Governance: Strong governance frameworks, characterised in the EPI framework such as transparency, accountability, and effective policymaking, are essential for promoting and enforcing environmental regulations and policies.
- Financial Resources: Adequate financial resources play a pivotal role in implementing and sustaining environmental initiatives, enabling countries to invest in sustainable practices and infrastructure.
- Human Development: Countries with higher levels of human development, including factors such as education, healthcare, and overall well-being, tend to prioritise environmental sustainability and can implement effective measures.
- Regulatory Quality: Robust and well-designed environmental regulations, coupled with effective enforcement mechanisms, are critical for mitigating environmental degradation and ensuring compliance with sustainability standards.
What are the Environmental Conservation Programmes in India?
- Climate Change: National Action Plan on Climate Change
- Desertification: National Action Programme to Combat Desertification
- Pollution Control: National Clean Air Program
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Environment Management Plan
- Forest Protection: National Afforestation Programme
- Species Conservation: Project Elephant, Project Tiger
Way Forward
- Enhance Methodology and Carbon Sequestration: Incorporate a longer time frame (e.g., 20-30 years) to calculate the projected GHG emissions trajectory, instead of relying solely on the average rate of change over the last 10 years.
- Efforts to enhance carbon sequestration through initiatives like the Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA) should be recognised.
- Expand Set of Indicators: Include indicators that are relevant to developing countries with large agrarian populations, such as agro-biodiversity, soil health, food loss, and waste management.
- For India, the EPI could incorporate indicators like the area under organic farming, crop diversification, and measures to reduce post-harvest losses, reflecting the country's efforts toward sustainable agriculture.
- Transparent Weighting and Funding: Provide clear and transparent explanations for any changes in the weighting of indicators, addressing concerns raised by countries like India.
- Engage in consultations with stakeholders, including government representatives and experts, to ensure that the weighting of indicators aligns with global priorities and national contexts.
|
Drishti Mains Question; Discuss the Key findings of the Environmental Performance Index (EPI) 2024 and and what global challenges exist in mitigating the environmental impacts identified in the report? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 Which of the following best describes/describe the aim of ‘Green India Mission’ of the Government of India? (2016)
- Incorporating environmental benefits and costs into the Union and State Budgets thereby implementing the ‘green accounting’.
- Launching the second green revolution to enhance agricultural output so as to ensure food security to one and all in the future.
- Restoring and enhancing forest cover and responding to climate change by a combination of adaptation and mitigation measures.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Q.2 With reference to ‘Global Climate Change Alliance’, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2017)
- It is an initiative of the European Union.
- It provides technical and financial support to targeted developing countries to integrate climate change into their development policies and budgets.
- It is coordinated by World Resources Institute (WRI) and World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD).
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q.1 Describe the major outcomes of the 26th session of the Conference of the Parties (COP) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). What are the commitments made by India in this conference? (2021)