Important Facts For Prelims
Electroencephalography (EEG)
- 16 Jul 2024
- 5 min read
Why in News?
Recently, electroencephalography has been in the news due to the centenary year of the first human EEG, pioneered by German physiologist Hans Berger.
- Vladimir Pravdich-Neminsky achieved the first mammalian EEG in 1912 with a dog's brain, followed by Hans Berger in 1924 with the first human EEG.
What is EEG?
- About:
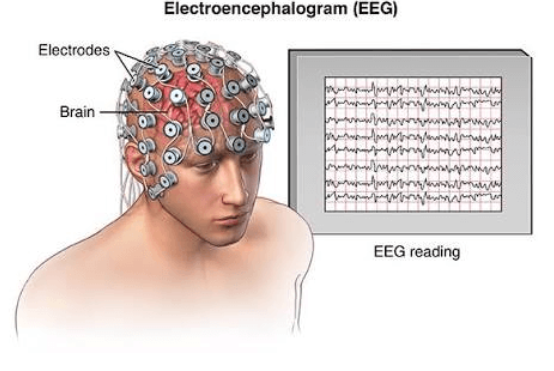
- EEG stands for electroencephalography. ‘Electro-’ pertains to electricity; ‘-encephalo-’ refers to the brain; and ‘-graphy’ is a suffix meaning to show or to represent.
- The EEG is a remarkable tool in physics and neurobiology, offering a straightforward glimpse into the human brain's workings, without invasive procedures.
- An EEG setup is simple, cost-effective, non-invasive, portable, space-efficient, and doesn't emit high-energy radiation or sounds, unlike MRI.
- Working:
- Volume conduction is the interference that happens between the source of an electrical potential and the electrode measuring that potential.
- It occurs when electrical potentials is measured at a distance from their source.
- Neurons in the brain constantly exchange ions with their surroundings, creating waves of electrical activity that electrodes on the scalp track to produce an electroencephalogram.
- Volume conduction is the interference that happens between the source of an electrical potential and the electrode measuring that potential.
- Applications:
- It is the best test available to diagnose epilepsy (a neurological condition involving the brain that makes people more susceptible to having recurrent unprovoked seizures).
- An EEG test can also reveal the effects of anaesthesia, sleeping patterns, neurological activity during a coma, and availability of oxygen.
- EEG can also help confirm brain death.
- Also used for neuroscience, cognitive psychology, neurolinguistics, and neuromarketing studies and to develop brain-computer interfaces.
- Researchers have linked EEG data to various brain activities, distinguishing effectively between normal and abnormal states.
- Challenges:
- EEG is great at tracking rapid brain activity in milliseconds but is biased towards signals from the brain's surface and dendrites, making pinpointing activity origin complex.
- Researchers use EEG with MRI and advanced methods to overcome these challenges.
EEG And Other Similar Technologies
|
Feature |
EEG (Electroencephalography) |
fMRI (functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging) |
PET Scan (Positron Emission Tomography Scan) |
MEG (Magnetoencephalography) |
|
What it measures |
Electrical activity of neurons |
Blood flow changes in the brain |
Metabolic activity of brain cells |
Magnetic fields generated by electrical currents in the brain |
|
Safety |
Safe, non-invasive |
Safe, non-invasive (with some limitations) |
Requires low-dose radiation exposure |
Safe, non-invasive |
|
Cost |
Relatively inexpensive |
Very expensive |
Expensive |
Expensive |
|
Portability |
Portable, can be used in various settings |
Not portable, requires a large scanner room |
Not portable, requires a specialized scanner |
Somewhat portable, requires a magnetically shielded room |
|
Applications |
Epilepsy diagnosis, sleep studies, brain function monitoring |
Studying brain function during tasks, brain mapping |
Identifying metabolic changes associated with diseases, cancer detection |
Studying brain function during tasks, epilepsy localisation |
Read More: MRI
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. With reference to Visible Light Communication (VLC) technology, which of the following statements are correct? (2020)
- VLC uses electromagnetic spectrum wavelengths 375 to 780 nm.
- VLC is known as long-range optical wireless communication.
- VLC can transmit large amounts of data faster than Bluetooth.
- VLC has no electromagnetic interference.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 1, 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 2, 3 and 4 only
Ans: (c)
Q. With reference to ‘Near Field Communication (NFC) Technology’, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2015)
- It is a contactless communication technology that uses electromagnetic radio fields.
- NFC is designed for use by devices which can be at a distance of even a metre from each other.
- NFC can use encryption when sending sensitive information.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)