EAC-PM Report on Domestic Migration | 27 Dec 2024
For Prelims: Migration, Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana , Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme, One Nation One Ration Card
For Mains: Declining domestic migration and its implications, migration in India, Welfare schemes in Addressing Migrants in India.
Why in News?
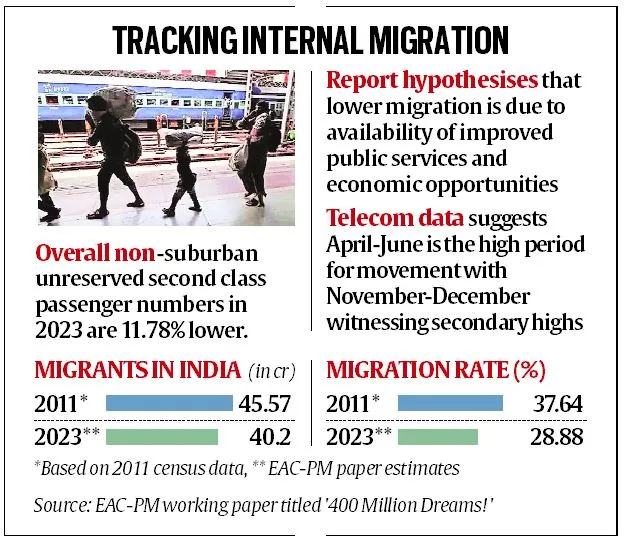
The Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM) released a working paper titled "400 Million Dreams!" which highlights a 12% decline in domestic migration since 2011.
- This shift, reflecting broader socio-economic changes, is attributed to improved economic opportunities and infrastructure in traditionally high migration source areas.
What are the Key Highlights of the EAC-PM Report on Domestic Migration?
- Reduction in Migration: The number of domestic migrants in India has decreased by 12% since 2011, with the estimated number of migrants in 2023 standing at 40.20 crore.
- This is an 11.78% decline from the 45.58 crore migrants reported in Census 2011.
- The migration rate (difference between the number of persons entering and leaving) has fallen from 37.64% of the total population in 2011 to 28.88% in 2023, indicating a slowdown in migration.
- Migration Dynamics:
- Migrant States: West Bengal, Rajasthan, and Karnataka have experienced the highest growth in attracting migrants.
- Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh have seen a reduction in their percentage share of total migrants.
- Urban Concentration of Migration: Major urban agglomerations like Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Bengaluru, and Kolkata continue to be the primary destinations for migrants.
- Mumbai, Bengaluru Urban, and Howrah are among the top districts attracting the most migrant arrivals.
- Emerging Migration Routes: Primary migration corridors include Uttar Pradesh-Delhi, Gujarat-Maharashtra, Telangana-Andhra Pradesh, and Bihar-Delhi.
- Seasonal Migration Trends: Migration is most frequent during April to June, with secondary peaks in November-December, likely due to festivals and marriages.
- January experiences the lowest levels of migration, suggesting a seasonal pattern.
- Migrant States: West Bengal, Rajasthan, and Karnataka have experienced the highest growth in attracting migrants.
- Reasons for Decline in Migration: The decline in domestic migration is attributed to improved local economic opportunities through schemes like Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY), enhanced infrastructure via Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY), better healthcare through Ayushman Bharat - Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY), and advancements in education and connectivity through Digital India in migration-origin regions.
Migration
- Migration refers to the movement of people from their usual place of residence to a new one, either across international borders or within a state.
- While there is no universally agreed definition, the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs defines a long-term migrant as someone who lives outside their country of origin for at least 12 months.
- Two Primary Types of Migration: International migration involves crossing state boundaries to live in another country for a minimum duration, while internal migration occurs within the same country.
- Urbanization is a specific form of internal migration, where people move from rural to urban areas.
What are the Implications of Decreased Domestic Migration?
- Economic Implications: Reduced migration can lead to labor shortages in certain regions, especially in industries that rely heavily on migrant workers.
- This can increase wages in those areas but may also lead to higher production costs and reduced competitiveness.
- Improved economic opportunities in smaller cities may reduce income inequality between urban and rural areas. Boost to local economies as the workforce stays in their home regions.
- Social Implications: Reduced migration can lead to increased demand for quality education, healthcare, and infrastructure in rural and semi-urban areas.
- However, it limits access to better employment and education opportunities in urban centers.
- Women who traditionally stay back may face prolonged economic dependence if migration opportunities for male family members shrink.
- Demographic Implications: Reduced inflow of migrants to urban areas could slow down urbanization, impacting cities’ economic dynamism.
- Decline in population growth in metro cities might affect their consumer base and economic activities.
- Policy and Governance Implications: Lower migration rates can reduce the pressure on urban areas, potentially easing issues like overcrowding, housing shortages, and strain on public services.
- National employment schemes like Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) may need to scale up to address reduced employment migration.
- Staying in rural areas might increase pressure on local land and water resources, leading to unsustainable agricultural practices.
India's Initiatives for the Welfare of Migrants
- PM Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi)
- Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maan-Dhan Yojana (PMSYM)
- Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Yojana (PMGKY)
- One Nation One Ration Card (ONORC)
- Mera Ration App
Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM)
- The EAC-PM is an independent advisory body providing economic and related advice to the Government of India, specifically the Prime Minister.
- Its Terms of Reference include analyzing and advising on issues referred by the Prime Minister, addressing macroeconomic matters, and performing tasks assigned by the Prime Minister.
- The EAC-PM’s role is advisory and non-binding, with additional efforts to foster economic understanding among the public through reports, presentations, and stakeholder interactions.
- The NITI Aayog (National Institution for Transforming India) acts as its nodal agency for administrative and logistical support.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Critically analyze the socio-economic implications of declining domestic migration in India. How does it affect regional development and urbanization trends? |
UPSC Civil Services Exam, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Mains
Q. What are the main socio-economic implications arising out of the development of IT industries in major cities of India? (2021)
Q. Discuss the changes in the trends of labour migration within and outside India in the last four decades. (2015)