Indian Economy
E-commerce As Export Hub
- 20 Jun 2024
- 11 min read
For Prelims: Merchandise exports, Government e-marketplace (GeM) , e-Commerce, Foreign Direct Investment, Consumer Protection, Data Privacy, Intellectual Property, The Information Technology Act, Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules 2021, Consumer Protection (E-Commerce) Rules 2020, Foreign Direct Investment Policy
For Mains: Significance E-Commerce export policy.
Why in News?
Recently, the commerce ministry's 100-day agenda roadmap for the new government includes plans to harness E-Commerce for export. India set a target to achieve USD 1 trillion in merchandise exports by 2030, identifying cross-border e-commerce as a key strategy to achieve this goal.
What are the 100-day agenda in E-Commerce?
- 100-day Agenda: This is the programme to developing e-commerce hubs to support online exports is a key focus of the government’s 100-day agenda.
- The Commerce Department works with the Department of Revenue on duty-free returns and faster customs clearances.
- Economic Potential: In 2023, the cross-border e-commerce trade was about USD 800 billion and is estimated to reach USD 2 trillion by 2030.
- China's e-commerce exports are about USD 350 billion, whereas India's shipments through online medium is only USD 2 billion.
- Return Logistics Challenge: In e-commerce, about 25 per cent of goods are re-imported.necessitating duty-free imports for these items.
- Identifying these items for duty-free status is challenging.
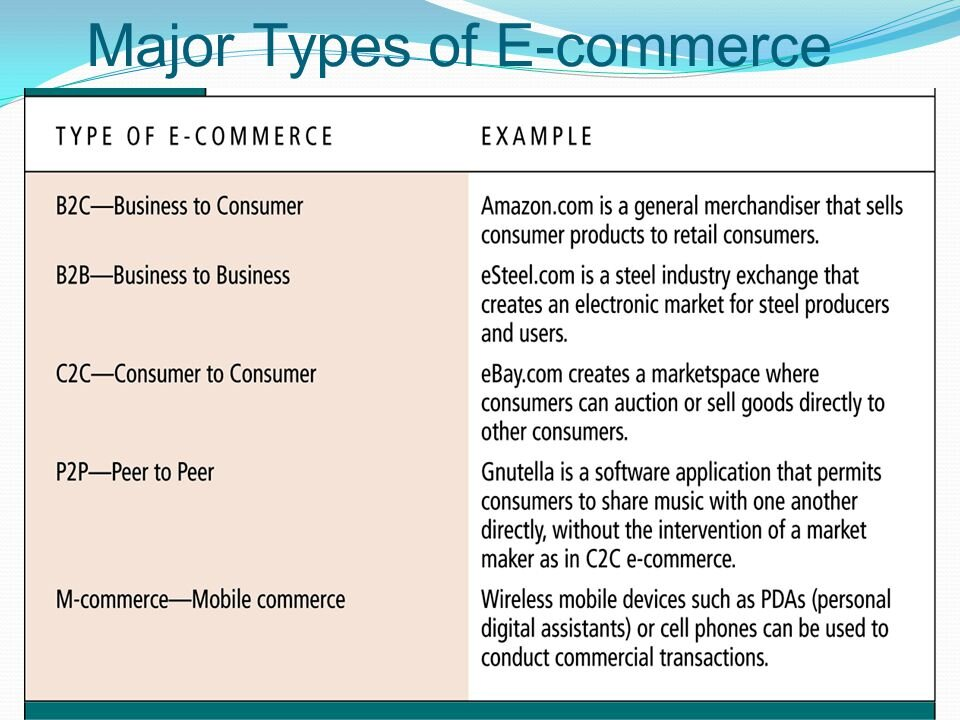
What is E-Commerce?
- About: E-commerce involves buying and selling goods and services over the Internet.
- As of 2023, India ranks as the eighth-largest e-commerce market globally.
- E-commerce encompasses a broad spectrum of activities, ranging from online retail platforms that facilitate the purchase and sale of products, to digital payment systems that enable secure and convenient financial transactions.
- Classification:
- The Market-based Model: It involves an e-commerce entity providing an IT platform to connect buyers and sellers, exemplified by companies like Amazon and Flipkart.
- The Inventory-based Model: It entails an e-commerce entity owning and directly selling goods and services from its inventory to consumers, as seen with platforms such as Myntra and Nykaa.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is not permitted in inventory based model of e-commerce.
- Current Status: India's e-commerce platforms achieved a significant milestone, hitting a Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) of USD 60 billion in fiscal year 2023, marking a 22% increase from the 2022.
- The export of India’s toy story has grown at nearly 30% Compound annual growth rate (CAGR) over the last seven years.
- In the fiscal year 2022-23, the Government e-marketplace (GeM) achieved its highest-ever Gross Merchandise Value of USD 2011 billion.
- As of 2023, the e-commerce sector in India is valued at USD 70 billion, constituting approximately 7% of the country’s total retail market.
- India has approximately 800 million internet subscribers, including about 350 million mature online users actively engaging in transactions.
- Future Potential: The Indian e-commerce industry is projected to reach USD 300 billion by 2030.
- Third-party logistics providers are anticipated to manage approximately 17 billion shipments within the next seven years.
- It is anticipated to surpass the United States, becoming the world's second-largest e-commerce market.
- The e-retail market in India is projected to surpass USD160 billion by 2028.
What is the Significance of the E-Commerce Industry In the Indian Economy?
- Employment Provider: The e-commerce sector in India offers substantial employment opportunities, both directly and indirectly, spanning various sectors such as MSMEs, textiles, leather, agriculture (farmers), and craftsmanship.
- Additionally, it supports forward linkages including logistics, packaging, transport, storage, and advertising, contributing to economic growth and job creation.
- Fashion, grocery, and general merchandise are projected to dominate the Indian e-commerce market, capturing nearly two-thirds of the market share by 2027, underscoring the sector's emergence as a pivotal growth area in India's retail landscape.
- Enhancing the Competitiveness of Indian Products in Global Markets: E-commerce has enabled Indian manufacturers and sellers to showcase their products on international platforms, increasing their reach and exposure to global markets.
- According to industry reports, e-commerce exports from India stood at around USD 49 billion in the financial year 2022-23.
- Catalysing Export Growth: The rise of e-commerce has significantly boosted India's export potential, providing a platform for Indian businesses to tap into international markets. As per data from the Reserve Bank of India, major export destinations include the USA, UAE, China, Hong Kong, and several European nations.
- Facilitating Efficient Service Delivery: Services like online education, telemedicine, and professional consultations have become more accessible, bridging geographical barriers.
- According to industry estimates, the online education sector in India is projected to grow at a CAGR of around 20% between 2020-2025.
- Transforming Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Government initiatives like the National Logistics Policy have streamlined deliveries, enhancing logistical efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
What are the Various Regulatory Frameworks for E-commerce in India?
- Taxation Related: E-commerce entities operating in India are subject to taxation under the Income Tax Act, of 1961. Goods and Services Tax (GST) applies to e-commerce transactions within India.
- Taxation agreements under the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement facilitate international transactions.
- Business Regulation: The B2B (Business to Business) e-commerce sector in India is governed by the Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) policy and the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), which regulates foreign investments and business setups.
- Additional regulations impacting e-commerce include provisions under the Companies Act 2013, Payment and Settlement Act 2007, RBI regulations on payment mechanisms, and rules on labeling and packaging.
- Data and Associated Issues: The Information Technology Act, of 2000 (IT Act), regulates various aspects of e-commerce, including electronic contracts, digital signatures, and cybercrime prevention.
- Sections 84A and 43A of the IT Act impose obligations on entities handling sensitive personal data or information.
- The Information Technology (Guidelines for Intermediaries and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021, introduced new regulations aimed at digital media intermediaries, including e-commerce platforms.
What are the Government Initiatives Related to the E-Commerce Sector in India?
What are the Various Challenges and Way Forward in E-Commerce Sector Export?
| Challenges | Way Forward |
| 1. Logistics and Supply Chain Inefficiencies: Logistics and supply chain infrastructure in India is still developing, leading to inefficiencies and higher costs, which can hinder export competitiveness. | 1. Continued Investment in Logistics infrastructure: Investment such as dedicated freight corridors, modern warehousing facilities, and seamless multimodal connectivity. Adoption of advanced technologies like automation, IoT, and data analytics can optimise supply chain operations. |
| 2. Cross-Border Trade Facilitation: Challenge: Complexities in cross-border trade procedures, such as customs clearance, documentation, and payment gateways, can hinder e-commerce exports. |
2. E-commerce under WTO: Need to update WTO e-commerce moratorium (1998) to regulate e-commerce under WTO rules to facilitate cross-border trade. (WTO e-commerce moratorium prohibit charging customs duties on electronic transmissions). |
| 3. Cybersecurity: E-commerce websites are vulnerable to cyber attacks, which can lead to loss of sensitive information and negatively impact the reputation of the business. | 3. Developing a Strong Data Privacy Network: A strong data network is crucial for e-commerce exports, and India needs to develop robust cybersecurity measures and promote consumer awareness campaigns to build confidence in e-commerce platforms. |
|
Drishti Mains Question Examine the role of e-commerce in India's export sector and What should be the strategies to maximize its potential for bolstering the nation's global competitiveness. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. With reference to India’s decision to levy an equalization tax of 6% on online advertisement services offered by non-resident entities, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2018)
- It is introduced as a part of the Income Tax Act.
- Non-resident entities that offer advertisement services in India can claim a tax credit in their home country under the “Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements”.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. The emergence of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Digital Revolution) has initiated e-Governance as an integral part of the government”. Discuss. (2020)