Discoveries in Biology Using C. Elegans | 15 Jan 2025
The roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans has played a pivotal role in numerous Nobel Prize-winning discoveries, shedding light on fundamental biological processes.
- Nobel Winning Research on C. Elegans:
- Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun (2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine): Discovered microRNAs and their crucial role in gene expression control.
- Osamu Shimomura, Martin Chalfie, and Roger Tsien (2008 Nobel Prize in Chemistry): Developed green fluorescent protein (GFP), enabling live-cell imaging and revolutionizing biological research.
- GFP is a tool used in molecular and cell biology for visualizing and tracking biological processes.
- Andrew Fire and Craig Mello (2006 Nobel Prize in Medicine): Discovered RNA interference (RNAi), revolutionizing gene-silencing techniques.
- It led to the discovery that double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) can silence specific genes, offering potential therapeutic applications.
- Sydney Brenner (2002 Nobel Prize in Medicine): His research contributed to understanding programmed cell death.
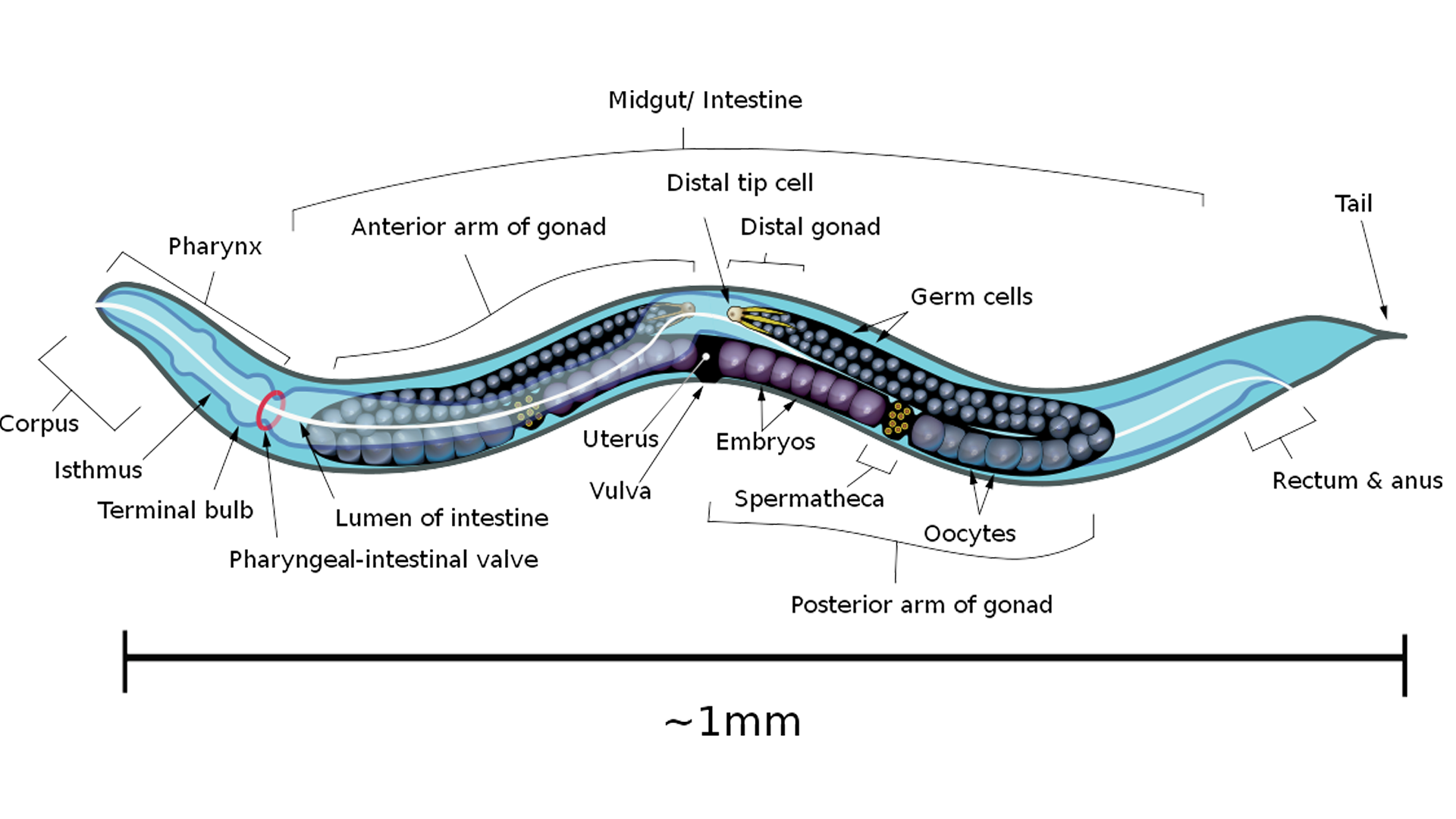
- About C. Elegans: It is a tiny invertebrate, measuring just 1 mm in length, and transparent nematode.
- Nematodes, also called roundworms, are unsegmented, cylindrical, and often microscopic organisms and a major component of soil and sediment ecosystems.
- They are parasitic in animals or plants or free-living in soil or water.
Read More: Nobel Prize 2024 in Physiology or Medicine