Disclosure of Political Funding | 01 Dec 2023
For Prelims: Representation of the People Act 1951, Supreme Court, Electoral Bonds, Publicity Act of USA, European Union, Regulation of the European Parliament, Political Parties, Elections and Referendums Act, 2000 of UK, Democracy, Rule of Law, Election Commission.
For Mains: Importance of disclosing political donations for promoting transparency in the democratic process and preventing electoral corruption.
Why in News?
In light of the current political circumstances and concerns regarding donations, the conclusion of the Supreme Court hearings on the challenge to electoral bonds prompts a critical examination of the potential impact this challenge's resolution may have on democracy and the rule of law in India.
What is Political Funding?
- About:
- Political funding refers to the financial contributions provided to political parties or candidates to support their activities, campaigns, and overall functioning.
- Political funding is crucial for political parties to effectively participate in democratic processes, conduct election campaigns, and engage in various political activities.
- Statutory Provisions in India:
- Representation of the People Act, 1951: RPA Act outlines the rules and regulations regarding elections in India, including provisions related to the declaration of election expenses, contributions, and the maintenance of accounts.
- Income Tax Act, 1961: The Income Tax Act governs the tax treatment of political parties and their donors.
- Political parties need to comply with tax regulations, and individuals or entities making political donations may be eligible for tax benefits under certain conditions.
- Companies Act, 2013: The Companies Act regulates corporate donations to political parties, specifying the maximum amount a company can contribute, and mandates disclosure of political contributions in financial statements.
- Methods of Raising Political Funding:
- Individual Persons: Section 29B of RPA allows political parties to receive donations from individual persons while allowing taxpayers to claim a 100% deduction
- State/Public Funding: Here, the government provides funds to parties for election related purposes. State Funding is of two types:
- Direct Funding: The government provides funds directly to the political parties. However, direct funding is prohibited in India.
- Indirect Funding: It includes other methods except direct funding, like free access to media, free access to public places for rallies, free or subsidized transport facilities. It is allowed in India in a regulated manner.
- Corporate Funding: In India, donations by corporate bodies are governed under section 182 of the Companies Act, 2013.
- Electoral Bonds Scheme: The electoral bonds system was introduced in 2017 by way of a Finance bill and it was implemented in 2018.
- They serve as a means for individuals and entities to make donations to registered political parties while maintaining donor anonymity.
- Electoral Trusts Scheme, 2013: It was notified by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT).
- An Electoral Trust is a Trust set up by companies with the sole objective to distribute the contributions received by it from other Companies and individuals to the political parties.
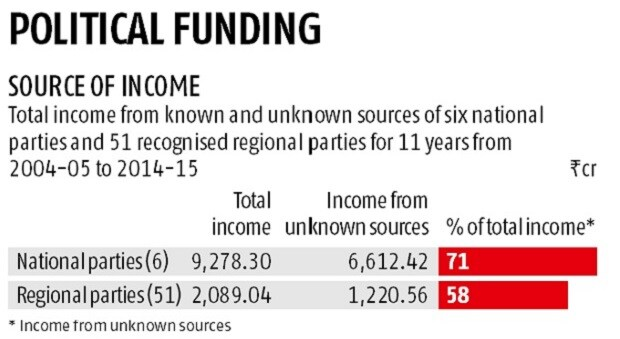
Why is There a Need for Disclosure of Political Funding?
- Global Standards on Political Funding Disclosure:
- The amendments to the Representation of the People Act 1951 in India, allowing for electoral bonds, have established complete anonymity for political donors.
- This stands in stark contrast to international practices, where the prevailing requirement is full disclosure of political donations.
- Across the world, including the United States, regulations mandate transparency in political funding, with disclosure requirements dating back to 1910.
- The European Union, in 2014, enacted regulations on the funding of European political parties, incorporating limits on donations, disclosure mandates, and immediate reporting for large contributions.
- The amendments to the Representation of the People Act 1951 in India, allowing for electoral bonds, have established complete anonymity for political donors.
- Fundamental Requirements in Political Funding Regulations:
- Most legal regulations globally converge on two fundamental requirements for political party funding:
- comprehensive disclosure of donors above specific minimal amounts and the imposition of limits or caps on donations.
- These measures aim to ensure transparency, prevent corruption, and maintain public confidence in the political system and democracy.
- Most legal regulations globally converge on two fundamental requirements for political party funding:
- Upholding Citizen’s Trust:
- Public disclosure of political funding is imperative as political parties serve as the foundation of representative democracy.
- Transparent financial accounts play a crucial role in upholding citizens' trust in both parties and politicians, safeguarding the rule of law, and combating corruption within the electoral and political processes.
- This transparency ensures accountability, reinforcing the democratic principles that rely on openness and fairness.
- Preventing Undue Influence:
- Without disclosure, money can become a tool for some to unduly influence the political process. Disclosure helps prevent the co-optation of politics by business interests and widespread vote buying.
- Maintaining a Level Playing Field:
- The equitable playing field gets eroded when one party has indomitable access to excess campaign finance. Disclosure ensures that all parties have equal opportunities.
Exemption From Disclosure Under Electoral Bonds Scheme
- Through an amendment to the Finance Act 2017, the Union government has exempted political parties from disclosing donations received through electoral bonds.
- This means the voters will not know which individual, company, or organization has funded which party, and to what extent.
- However, in a representative democracy, citizens cast their votes for the people who will represent them in Parliament.
Supreme Court’s Observations
- Recently, the Supreme Court has instructed the Election Commission of India (ECI) to provide the recent data on funds received by political parties through electoral bonds
- The Indian Supreme Court has long held that the “right to know”, especially in the context of elections, is an integral part of the right to freedom of expression (Article 19) under the Indian Constitution.
What are the Reforms Required in Political Funding?
- Electoral Justice:
- Electoral justice plays a pivotal role in upholding the core tenets of democracy, ensuring that all aspects of the electoral process align with the law and safeguard the enjoyment of electoral rights.
- This system, essential for a healthy democracy, is instrumental in maintaining and facilitating free, fair, and genuine elections.
- Addressing the Issues of Electoral Bonds:
- Electoral bonds, allowing for undisclosed donor details, pose a threat to democratic transparency and the integrity of free and fair elections.
- Apart from making them constitutionally sound, addressing this issue requires a comprehensive approach that goes beyond legality and focuses on preserving the democratic essence of transparency in the electoral process.
- Mechanism for Reporting and Independent Audit:
- This includes the identification of donors above a specified nominal limit, immediate reporting of significant donations to the election commission.
- It also entails publicizing political party accounts, independent auditing of party accounts, and establishing limits on funding and expenditure.
- State Funding of Elections:
- State funding of elections refers to a system in which the government provides financial support to political parties and candidates to facilitate their participation in the electoral process.
- This funding is typically derived from public resources and aims to reduce the reliance on private donations, minimizing the potential influence of vested interests in political campaigns.
Legal Insights: Electoral Bonds Case
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2017)
- The Election Commission of India is a five-member body.
- Union Ministry of Home Affairs decides the election schedule for the conduct of both general elections and bye-elections.
- The Election Commission resolves the disputes relating to splits/mergers of recognized political parties.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 3 only
Ans : D
Mains
Q. In the light of recent controversy regarding the use of Electronic Voting Machines (EVM), what are the challenges before the Election Commission of India to ensure the trustworthiness of elections in India? (2018)