Differential Rotation of the Sun | 07 Nov 2024
The Sun exhibits a unique rotational pattern called differential rotation, where different parts rotate at varying speeds.
- The Sun's rotation period varies by latitude, with the equator rotating in 26.5 days, the sunspot zone (16° north) in 27.3 days, and the poles in 31.1 days.
- The Sun has a north and south pole, and rotates on its axis. However, unlike Earth which rotates at all latitudes every 24 hours, the Sun rotates every 25 days at the equator and takes progressively longer to rotate at higher latitudes. This is known as differential rotation.
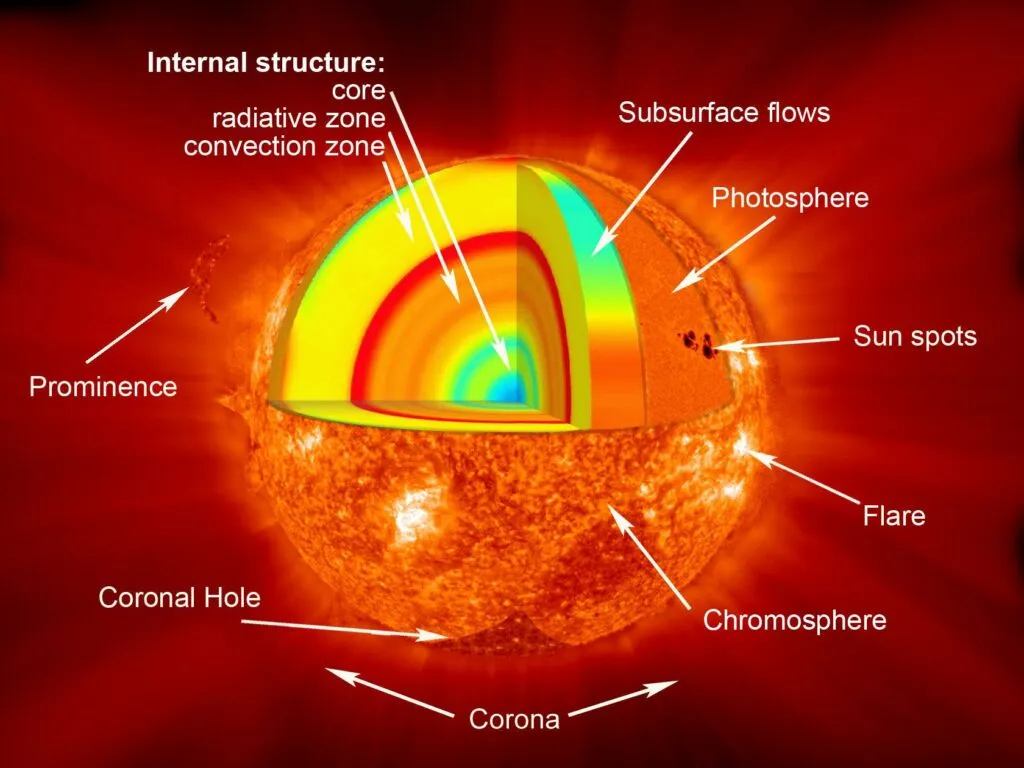
- Sunspots are areas that appear dark on the surface of the Sun. They appear dark because they are cooler than other parts of the Sun’s surface.
- The Sun's core temperature is 15 million degrees K, and its surface temperature is 6,000 degrees K, creating a high-pressure gaseous state known as plasma.
- The Sun has a north and south pole, and rotates on its axis. However, unlike Earth which rotates at all latitudes every 24 hours, the Sun rotates every 25 days at the equator and takes progressively longer to rotate at higher latitudes. This is known as differential rotation.
- Despite extensive research, the underlying cause of differential rotation remains an unsolved puzzle for solar physicists.