Delhi High Court Reverses Abortion Approval Order | 31 Jan 2024
For Prelims: Medical Termination of Pregnancy, MTP Amendment Act, 2021, Ambit of Article 21, Suchita Srivastava vs. Chandigarh Administration case, Roe V/s Wade case.
For Mains: Status of Medical Termination of Pregnancy in India, Key Features of MTP Amendment Act 2021.
Why in News?
Recently, the Delhi High Court has reversed its order that permitted a 26-year-old woman to terminate her 29-week-old pregnancy.
- The court, now advocating for the unborn child's right to life, has directed the woman to undergo delivery at either AIIMS or any central or state hospital.
What is the Status of Medical Termination of Pregnancy in India?
- Background: In the 1960s, in the wake of a high number of induced abortions taking place, the Union government ordered the constitution of the Shantilal Shah Committee to deliberate on the legalisation of abortion in the country
- Resulting from its recommendations, the Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act, 1971 was enacted, permitting safe and legal abortions to protect women's health and decrease maternal mortality.
- MTP Act and Subsequent Amendment:
- The MTP Act, 1971 permits licensed medical professionals to perform safe and legal abortions in specific predetermined situations (as provided under the legislation), to protect women's health and decrease maternal mortality.
- It underwent subsequent amendments through the MTP Amendment Act, 2021.
- The MTP Act, 1971 permits licensed medical professionals to perform safe and legal abortions in specific predetermined situations (as provided under the legislation), to protect women's health and decrease maternal mortality.
- Provisions for Terminating Pregnancy:
| Time Since Conception | MTP Act, 1971 | MTP (Amendment) Act, 2021 |
| Up to 12 weeks | On the advice of one doctor | On advice of one doctor |
| 12 to 20 weeks | On advice of two doctors | On advice of one doctor |
| 20 to 24 weeks | Not allowed | On advice of two doctors for special categories of pregnant women |
| More than 24 weeks | Not allowed | On advice of medical board in case of substantial fetal abnormality |
| Any time during the pregnancy | On advice of one doctor, if immediately necessary to save pregnant woman's life | On advice of one doctor, if immediately necessary to save pregnant woman's life |
Note
Under MTP Amendment Act 2021, special categories of women, includes survivors of rape, victims of incest and other vulnerable women like differently abled and minors.
- Other Key Features of MTP Amendment Act 2021:
- Termination Due to Failure of Contraceptive Method or Device: The MTP Act permitted married women to terminate pregnancies up to 20 weeks in case of contraceptive method or device failure.
- The MTP Amendment Act extended the allowance to unmarried women as well.
- Medical Boards: The board will assess pregnancies beyond 24 weeks for substantial foetal abnormalities.
- It should comprise specialists like gynaecologists, paediatricians, and radiologists, and will be established by all state and union territory governments.
- Privacy Measures: A registered medical practitioner can only disclose details of a terminated pregnancy to individuals authorised by law. Violation carries penalties of imprisonment up to a year, fines, or both.
- Termination Due to Failure of Contraceptive Method or Device: The MTP Act permitted married women to terminate pregnancies up to 20 weeks in case of contraceptive method or device failure.
- Constitutional Stance:
- Although the Constitution does not explicitly mention the right to abortion, certain fundamental rights have been associated with reproductive rights and women’s healthcare.
- Article 21 - Right to Life and Personal Liberty: The Supreme Court interprets this broadly to encompass reproductive autonomy and healthcare (Suchita Srivastava vs. Chandigarh Administration case, 2009)
- Also, recently the Supreme Court observed that the rights of an unborn child must be balanced with a woman's reproductive right.
Note
The fetus's moral status, legal standing, and constitutional rights still remain a grey area in India. However, section 20 of the Hindu Succession Act, 1956, protects the fetus's life from conception.
- Global Trends:
- Worldwide, there is a noticeable trend toward the liberalisation of abortion laws and improved accessibility to abortion services.
- Since the early 1990s, approximately 60 countries globally have relaxed abortion laws, broadening the legal grounds for abortion.
- Notably, only four countries: the United States, El Salvador, Nicaragua, and Poland, have tightened abortion laws during this period by removing legal grounds for the procedure.
- A significant development occurred in 2022 when the U.S. Supreme Court eliminated the constitutional right to abortion (Roe v. Wade case).
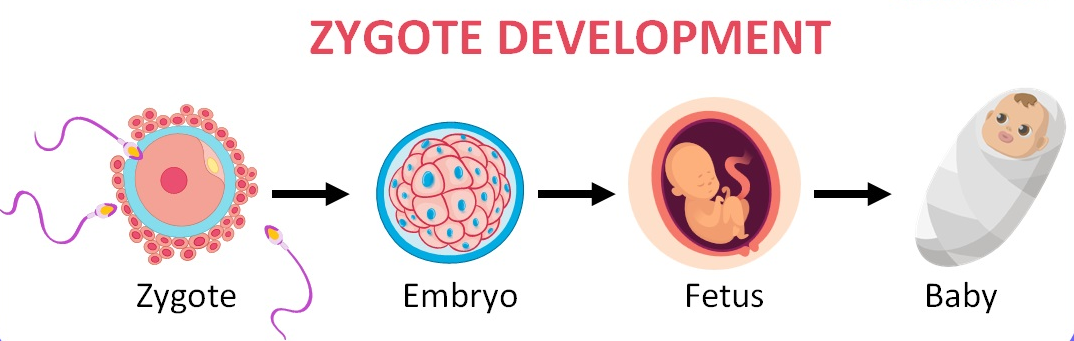
- Zygote: The initial cell formed by the fusion of sperm and egg during fertilisation.
- Embryo: Early stage of development, from the moment of fertilisation until about the 8th week of pregnancy.
- Fetus: The later stage of prenatal development, starting from the ninth week until birth, characterised by the development of organs and systems.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question:
Mains
Q. What are the continued challenges for Women in India against time and space? (2019)
