Social Justice
Decline in Muslim Enrollment in Higher Education
- 01 Dec 2023
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Decline in Muslim Enrollment in Higher Education, Unified District Information System for Education Plus (UDISE+), All India Survey of Higher Education (AISHE), Naya Savera- Free Coaching and Allied Scheme.
For Mains: Decline in Muslim Enrollment in Higher Education, Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes.
Why in News?
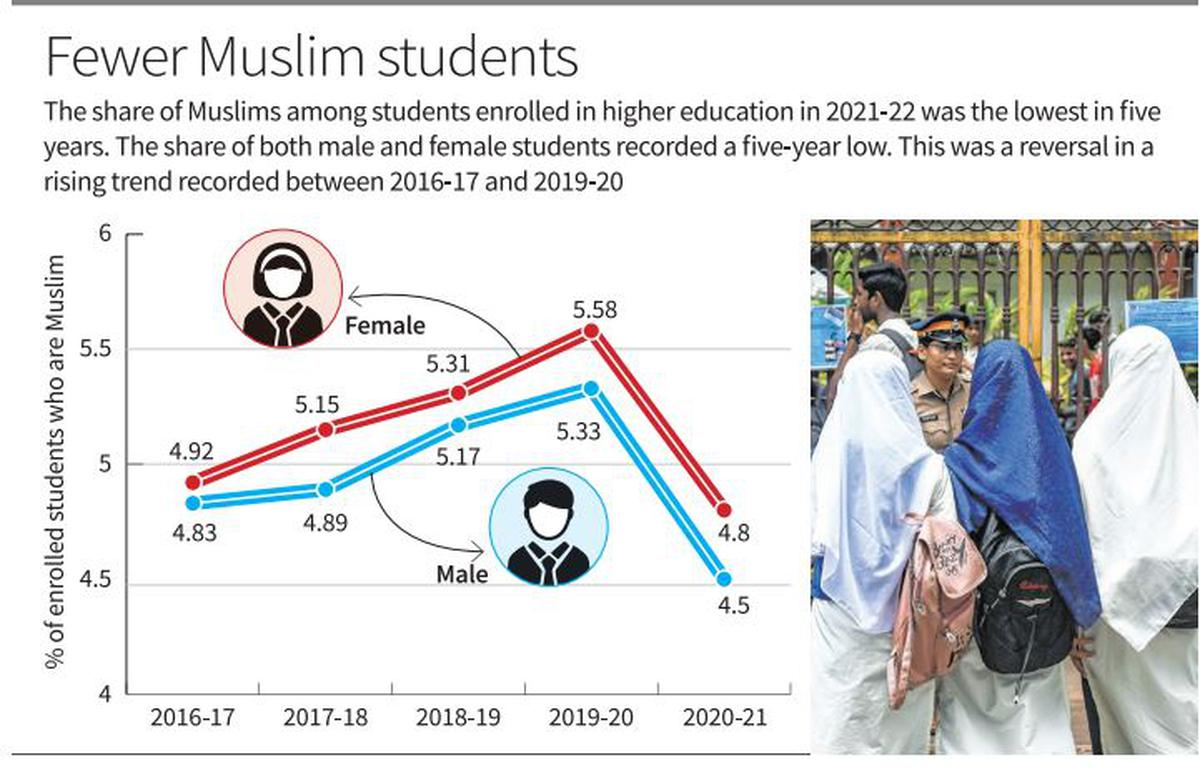
According to a report prepared from the analysis of data from the Unified District Information System for Education Plus (UDISE+) and the All India Survey of Higher Education (AISHE), the enrollment in higher education among Muslim students has dropped significantly.
What is the UDISE Plus Report?
- It is a comprehensive study that provides information on enrollment and dropout rates of school students, number of teachers in schools, and information on other infrastructural facilities like toilets, buildings and electricity.
- It was launched in 2018-2019 to speed up data entry, reduce errors, improve data quality and ease its verification.
- It is an application to collect the school details about factors related to a school and its resources.
- It is an updated and improved version of UDISE, which was initiated in 2012-13 by the Ministry of Education.
What is the All India Survey for Higher Education?
- AISHE is an initiative by the Ministry of Education. The annual web-based survey aims to determine the state of higher educational institutions in India and find areas for improvement. Students enrolled in higher educational institutions will respond to the AISHE survey.
- This survey can rate their college on different categories like teachers, exam results, education finance, programmes, student enrolment, and infrastructure. The data collected in this survey is used to make informed policy decisions and conduct better research in higher education.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report on Dropout Among Muslims?
- Enrollment Data:
- There is a significant drop of over 8.5% in enrollment of Muslim students (age group 18-23) in higher education in 2020-21.
- Enrollment decreased from 21 lakh students in 2019-20 to 19.21 lakh in 2020-21.
- From 2016-17 to 2020-21, there was an overall increase in enrollment, but a decline in the latest year, marking a decrease of 1,79,147 students from 2019-20 to 2020-21.
- Relative Enrollment Percentage:
- The percentage of Muslim students enrolled in higher education compared to the total student population saw a slight decrease from 4.87% in 2016-17 to 4.64% in 2020-21.
- Enrollment Pattern across Education Levels:
- Across States and Union Territories, a consistent trend is observed where Muslim student representation gradually declines from Class 6 onwards, reaching its lowest in Classes 11 and 12.
- Enrollment percentage of Muslim students drops from 14.42% in upper primary (Class 6-8) to 10.76% in higher secondary (Class 11-12).
- State Disparities:
- States like Bihar and Madhya Pradesh have relatively low Gross Enrolment Ratio for Muslim students, which indicates that many Muslim children in these States are still out of the education system.
- Assam (29.52%) and West Bengal (23.22%) recorded high dropout rates among Muslim students, while Jammu and Kashmir recorded 5.1% and Kerala 11.91%.
- Recommendations:
- There is a need for enhancing scholarships, grants, and financial aid explicitly tailored for Muslim students to alleviate financial burdens and increase access to higher education.
- Many Muslim students come from low-income families and struggle to afford the cost of higher education.
- Implementing inclusive policies and targeted support is crucial to bridge the education gap and provide equal opportunities for all students, irrespective of religious background or economic status.
- There is a need for enhancing scholarships, grants, and financial aid explicitly tailored for Muslim students to alleviate financial burdens and increase access to higher education.
What are the Major Schemes in India for the Welfare of Minorities?
- Pre-Matric Scholarship Scheme, Post-Matric Scholarship Scheme, Merit-cum-Means based Scholarship Scheme: For educational empowerment of students, through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) mode.
- Naya Savera- Free Coaching and Allied Scheme: The Scheme aims to provide free coaching to students/candidates belonging to economically weaker sections of minority communities for preparation of entrance examinations of technical/ professional courses and competitive examinations.
- Padho Pardesh: Scheme of interest subsidy to students of economically weaker sections of minority communities on educational loans for overseas higher studies.
- Nai Roshni: Leadership development of women belonging to minority communities.
- Seekho Aur Kamao: It is a skill development scheme for youth of 14 - 35 years age group and aiming at improving the employability of existing workers, school dropouts etc.
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK): It is a Scheme designed to address the development deficits of the identified Minority Concentration Areas.
- The areas of implementation, under PMJVK, have been identified on the basis of minority population and socio-economic and basic amenities data of Census 2011 and will be known as Minority Concentration Areas.
- USTTAD (Upgrading the Skills and Training in Traditional Arts/Crafts for Development): Launched in May 2015 aims to preserve the rich heritage of traditional skills of indigenous artisans/craftsmen.
- Under this scheme HunnarHaats are also held all over the country to provide a nation-wide marketing platform to Minority artisans & entrepreneurs and to create employment opportunities.
- Prime Minister-Virasat Ka Samvardhan (PM Vikaas): New PM Vikas has been added to the Ministry of Minority Affairs' Budget in 2023.
- It is a skilling initiative focussing on the skilling, entrepreneurship and leadership training requirements of the minority and artisan communities across the country.
- The scheme is intended to be implemented in conjunction with the ‘Skill India Mission’ of the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship and through integration with the Skill India Portal (SIP).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1 In India, if a religious sect/community is given the status of a national minority, what special advantages it is entitled to? (2011)
- It can establish and administer exclusive educational institutions.
- The President of India automatically nominates a representative of the community to Lok Sabha.
- It can derive benefits from the Prime Minister’s 15-Point Programme.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Q.2 In India, which of the following review the independent regulators in sectors l ike telecommunications, insurance, electricity, etc.? (2019)
- Ad Hoc Committees set up by the Parliament
- Parliamentary Department Related Standing Committees
- Finance Commission
- Financial Sector Legislative Reforms Commission
- NITI Aayog
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 1, 3 and 4
(c) 3, 4 and 5
(d) 2 and 5
Ans: (a)