Governance
Dam Management in India
- 18 Aug 2022
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Karam River, Narmada River, Dams of India, Regulation of Dams in India
For Mains: Concerns regarding the ageing dams of India and related steps that can can be taken
Why in News?
Recently, the outer part of the “Karam Dam”, which is being built on the Karam river, a tributary of the Narmada, collapsed.
- The Dam Safety Act 2021 covers those dams having a height of over 15m and between 10m and 15m with certain stipulations.
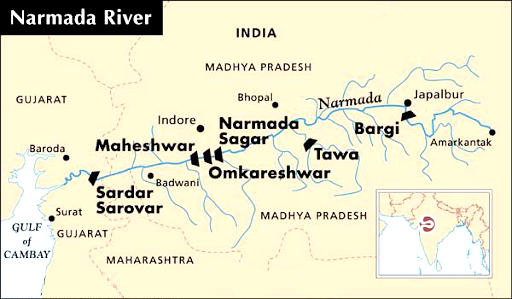
What are the Key Points of Narmada River?
- About: Narmada is the largest west flowing river of the peninsular region flowing through a rift valley between the Vindhya Range on the north and the Satpura Range on the south.
- Source: It rises from Maikala range near Amarkantak in Madhya Pradesh.
- Drainage: It drains a large area in Madhya Pradesh besides some areas in the states of Maharashtra and Gujarat.
- The river near Jabalpur (Madhya Pradesh) forms the DhuanDhar Falls.
- There are several islands in the estuary of Narmada of which Aliabet is the largest.
- Major Tributaries: Hiran, Orsang, the Barna and the Kolar.
- Major Hydro Power Projects in the basin: Indira Sagar, Sardar Sarovar etc.
- Narmada Bachao Andolan (NBA):
- It is an Indian social movement spearheaded by native tribes (adivasis), farmers, environmentalists and human rights activists against a number of large dam projects across the Narmada River.
- Sardar Sarovar Dam in Gujarat is one of the biggest dams on the river and was one of the first focal points of the movement.
What is the Dam Safety Act 2021?
- About:
- Dam Safety Act 2021 aims at surveillance, inspection, operation and maintenance of all specified dams across the country.
- The Act applies to all specified dams in the country i.e., those dams having a height of over 15m and between 10m and 15m with certain design and structural conditions.
- Provisions:
- It constitutes two National Bodies:
- National Committee on Dam Safety:
- Its functions include evolving policies and recommending regulations regarding dam safety.
- National Dam Safety Authority:
- Its functions include implementing policies of the National Committee, and resolving matters between State Dam Safety Organisations (SDSOs), or between a SDSO and any dam owner in that state.
- National Committee on Dam Safety:
- It also constitutes two state bodies:
- State Dam Safety Organizations (SDSOs):
- Its functions include keeping perpetual surveillance, inspecting, and monitoring dams.
- State Committee on Dam Safety:
- It will supervise state dam rehabilitation programs, review the work of the SDSO, and review the progress on measures recommended in relation to dam safety, among others.
- State Dam Safety Organizations (SDSOs):
- Obligations of Dam Owners:
- As per the Dam Safety Act 2021, all the specified dams are required to be inspected twice a year during the pre-monsoon and post-monsoon periods.
- Dam owners will be responsible for the safe construction, operation, maintenance and supervision of a dam.
- They must provide a dam safety unit in each dam.
- This unit will inspect the dams:
- Before and after monsoon season
- During and after every earthquake, flood, calamity, or any sign of distress.
- Functions of dam owners include:
- Preparing an emergency action plan
- Carrying out risk assessment studies at specified regular intervals
- Preparing a comprehensive dam safety evaluation through a panel of experts.
- Punishment:
- Anyone obstructing a person in the discharge of his functions under the Act or refusing to comply with directions may be imprisoned for a year. In case of loss of life, the person may be imprisoned for two years.
- Issues with the Act:
- Jurisdiction of Parliament to frame a law on intra-state river dams:
- The Act applies to all specified dams in the country. As per the Constitution, states can make laws on water including water storage and water power (Entry 17 of State List).
- However, Parliament may regulate and develop inter-state river valleys if it deems it necessary in public interest (Entry 56 of Union List).
- The question is whether Parliament has the jurisdiction to regulate dams on rivers flowing entirely within a state.
- Jurisdiction of Parliament to frame a law on intra-state river dams:
- Functions of authorities may be changed through notification:
- The functions of the National Committee on Dam Safety, the National Dam Safety Authority, and the State Committee on Dam Safety are listed in Schedules to the Act.
- These Schedules can be amended by the government through a notification.
- The question is whether core functions of authorities should be amended through a notification or whether such amendments should be passed by Parliament.
- It constitutes two National Bodies:
Way Forward
- The most important aspect in ensuring dam safety is the existence of accountability and transparency while taking into consideration the views of the real stakeholders--the people living downstream from the dams, who are the most at-risk group in case of a breach.
- In terms of the operational safety, the rule curve, that decides how a dam is supposed to be operated and is created when a dam is proposed, needs to be upgraded at regular intervals on the basis of environmental changes such as siltation and rainfall pattern since these would change the frequency and intensity of incoming flood into the dam as well as the spillway capacity.
- The rule curve also needs to be in the public domain so that the people can keep a check on its correct functioning and can raise questions in its absence.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Mains
Q. Suppose the Government of India is thinking of constructing a dam in a mountain valley bound by forests and inhabited by ethnic communities. What rational policy should it resort to in dealing with unforeseen contingencies? (2018)