Criticality of Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor | 02 Aug 2024
Why in News?
Recently, the Atomic Energy Regulatory Board (AERB) has officially granted permission for the "First Approach to Criticality" of the 500 MWe Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor (PFBR) at Kalpakkam, Tamil Nadu, India’s first indigenous PFBR.
Note
- Criticality: Criticality in a nuclear reactor is when enough neutrons are produced by fission to replace those lost through leakage or absorption, ensuring the number of neutrons remains constant.
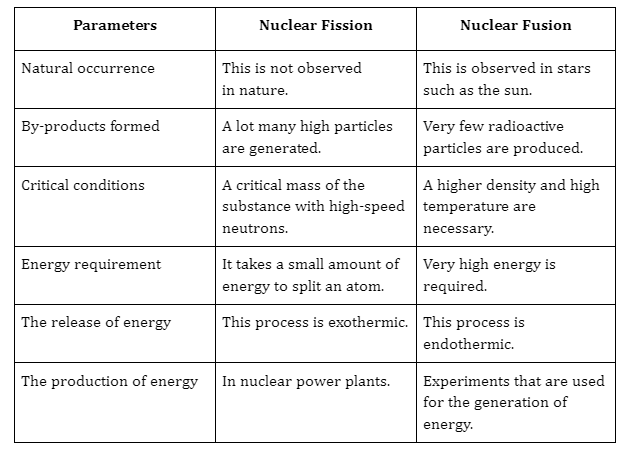
- Fission Vs Fusion:
|
|
.png) |
What is India’s FBR Programme?
- Efforts to build an FBR were initiated two decades ago.
- It is a step towards India developing comprehensive capabilities that span the entire nuclear fuel cycle, by which electricity is produced from uranium in nuclear power reactors.
- The Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) aims to increase the share of nuclear power in the energy mix by 2032 by producing 22,400 MWe from its nuclear power plants.
- It has approved the construction of 10 new PHWRs in ‘fleet mode’, in which a plant is expected to be built in five years from the first pouring of concrete.
- FBRs reactors generate more nuclear fuel than they consume due to the gainful conversion of fertile isotopes into fissile material.
- In 2003, the Bharatiya Nabhikiya Vidyut Nigam Ltd or BHAVINI was incorporated to build and operate India’s most advanced nuclear reactor, the Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor (PFBR).
- Once commissioned, India will be the second country after Russia to have a commercial operating FBR.
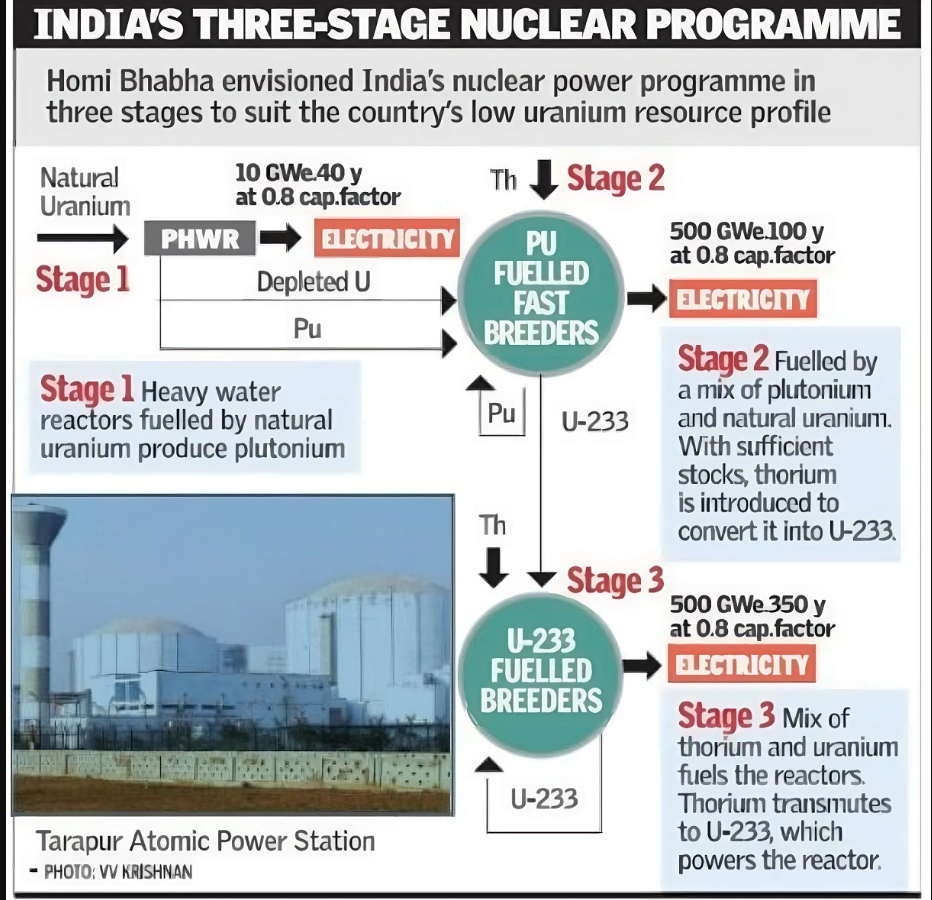
What are the Three stages of India’s Nuclear Energy Program?
- The First Stage: The installation of Pressurised Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) is underway, with PHWRs using natural uranium as fuel and heavy water as coolant and moderator.
- The Second Stage: It involves the setting up of FBRs backed by reprocessing plants and plutonium fabrication plants, primarily to multiply the inventory of fissile material.
- Multiplication of fissile inventory is also needed to establish a higher power base for using thorium in the third stage of the programme.
- The Third Stage: It will be based on the Thorium and Uranium Cycle. For producing Uranium-233 (U233), obtained by irradiation of thorium in PHWRs and FBRs, an Advanced Heavy Water Reactor (AHWR) is proposed.
- The combination of power reactors from all three stages is expected to ensure long-term energy security for the country.
- But the commercial utilisation of thorium on a significant scale can begin only when abundant supplies of either Uranium-233 (U233) or Plutonium-239 (Pu239) are available.
- The progress on the FBR has made the passage to the third phase visible.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Which one of the following statements best reflects the idea behind the “Fractional Orbital Bombardment System” often talked about in media?
(a) A hypersonic missile is launched into space to counter the asteroid approaching the Earth and explode it in space.
(b) A spacecraft lands on another planet after making several orbital motions.
(c) A missile is put into a stable orbit around the Earth and deorbits over a target on the Earth.
(d) A spacecraft moves along a comet with the same speed and places a probe on its surface.
Ans: (c)
Q. In the context of Indian news in recent times, what is MCX-SX? (2009)
(a) A kind of supercomputer
(b) Title of Moon Impact Probe
(c) Stock exchange
(d) Nuclear-powered submarine
Ans: (c)
Q. Which among the following has the world’s largest reserves of Uranium? (2009)
(a) Australia
(b) Canada
(c) Russian Federation
(d) USA
Ans: (a)

.png)