Copper Plates Discovered from Vijayanagara Kingdom | 23 Oct 2024
For Prelims: Vijayanagara Kingdom, Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), King Krishandevaraya, Hampi, World Heritage site by UNESCO, Hazara Rama temple,Ugra Narasimha idol.
For Mains: Cultural and litreary developments during Vijayanagara Empire, Literary Contributions of Krishnadevaraya.
Why in News?
Recently, a collection of copper plate inscriptions featuring two leaves from the 16th Century CE was discovered at the Sri Singeeswarar temple in Mappedu village, Tiruvallur district of Tamil Nadu.
- The two leaves of the copper plates strung together using a ring featuring the seal of the Vijayanagara Kingdom.
- The inscription, donating a village to Brahmins by the Raja of Chandragiri, is written in Sanskrit and the Nandinagari script. It was engraved in 1513 during the reign of King Krishnadevaraya.
Who was King Krishandevaraya?
- Reign of Krishnadevaraya:
- The Kingdom of Vijayanagar was ruled by Krishnadevaraya from 1509 to 1529 AD.
- After Krishna Deva Raya, Achyuta Raya took over in 1530, followed by Sada Siva Raya in 1542.
- He was known by various titles, including “Kannadaraya” and “Kannada Rajya Ramaramana.”
- He is regarded as one of the greatest statesmen in Indian history and is considered one of the most significant rulers of mediaeval South India.
- The Kingdom of Vijayanagar was ruled by Krishnadevaraya from 1509 to 1529 AD.
- Literary Contributions:
- He was an eminent scholar and authored works such as Madalasa Charita, Satyavedu Parinaya, Rasamanjari, Jambavati Kalyana, and Amuktamalkyada.
- Fluent in multiple languages, he supported poets writing in Sanskrit, Telugu, Tamil, and Kannada.
- Patronage of Learning and Literature:
- His court included the Ashtadiggajas, eight prominent scholars, among them Allasani Peddana, known as the Andhra-kavitapitamaha, famous for his work Manucharitamu.
- Kannada poet Thimmanna completed the Kannada Mahabharatha, originally started by Kumara Vyasa, at Krishnadevaraya's request.
- Other notable poets patronised during his reign.
- Kannada poet Mallanarya, author of Veerasaivamrita and Bhavachintaratna.
- Chatu Vittalanatha, who wrote Bhagvatha.
- Timmanna Kavi, is known for his eulogy Krishnaraya Bharata.
- Peddanna, a Telugu poet, was honoured for his proficiency in Telugu and Sanskrit.
- Cultural Development:
- Krishnadevaraya played a significant role in nurturing the Carnatic musical tradition.
- He also encouraged classical dance forms, including Bharatanatyam and Kuchipudi.
- Infrastructural Development:
- He is credited with building some fine temples and adding impressive gopurams to many important south Indian temples.
- He also founded a suburban township near Vijayanagar called Nagalapuram after his mother.
What are the Key Facts of the Vijaynagar Empire?
- Foundation and Duration of the Empire:
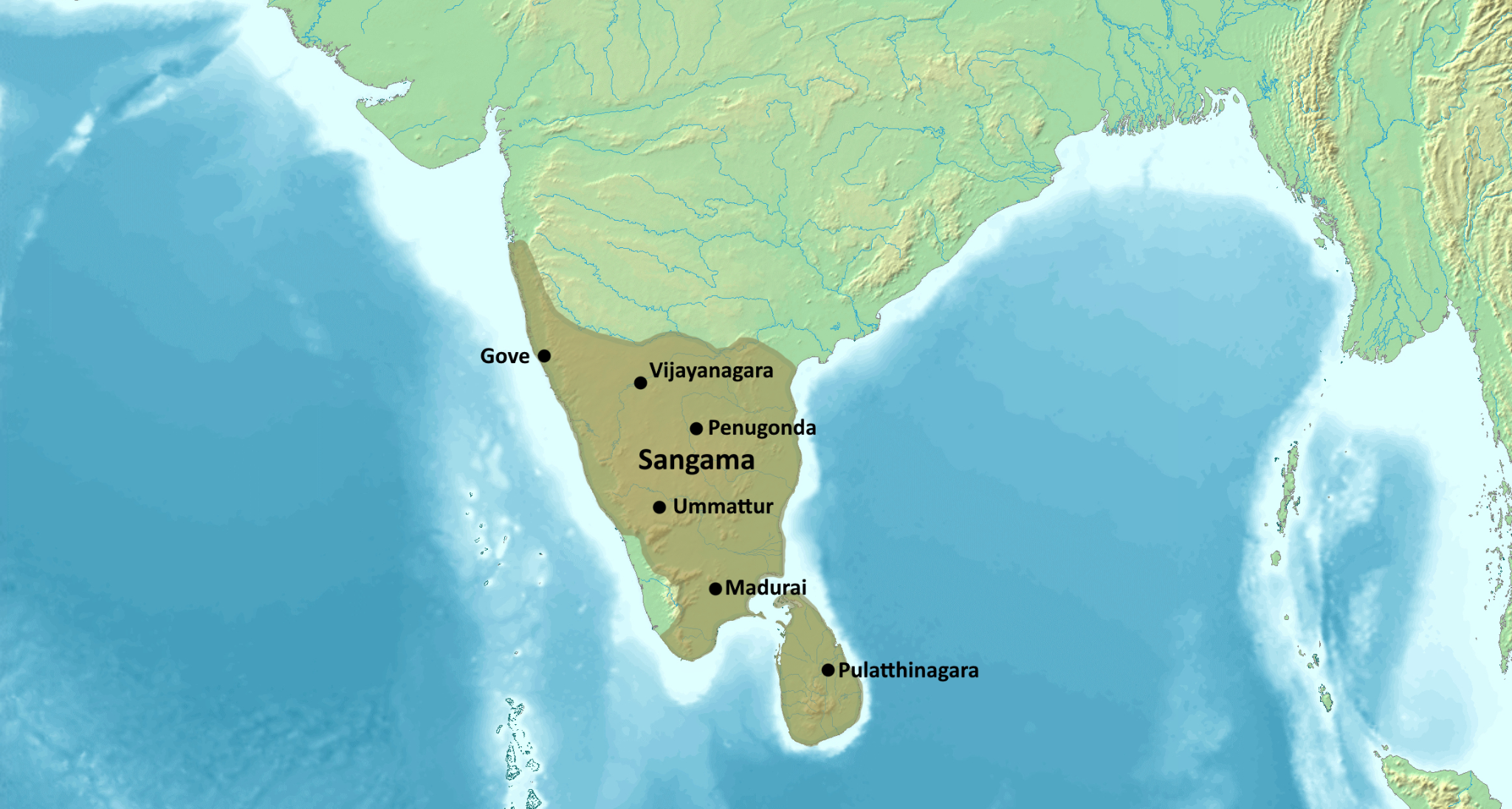
- The Vijayanagara Empire was established in the Deccan region from 1336 onwards, founded by Harihara (also known as Hakka) and his brother Bukka Raya.
- They made Hampi the capital city (declared a World Heritage site by UNESCO in 1986).
- Vijayanagar Empire was ruled by four important dynasties (Sangama, Saluva, Tuluva, Aravidu).
- The empire lasted from 1336 until around 1660, although it faced a gradual decline in its final century following a devastating defeat by an alliance of deccan sultanates, leading to the capital being captured, looted, and destroyed.
- The Vijayanagara Empire was established in the Deccan region from 1336 onwards, founded by Harihara (also known as Hakka) and his brother Bukka Raya.
- Portuguese Relations:
- Around 1510, the Portuguese captured Goa, which had been under the Sultan of Bijapur, with the support of Vijayanagara.
- The Portuguese supplied the Vijayanagara Empire with guns and Arabian horses, while the empire exported cotton, rice, sugar, spices, indigo, and wooden goods.
- Cultural and Architectural Flourishing:
- The empire is generally regarded as reaching its zenith during the reign of Krishna Deva Raya, who conquered territories east of the Deccan that were formerly part of Orissa.
- Many of the empire's notable monuments, including the Hazara Rama temple, Krishna temple, and Ugra Narasimha idol, date back to his time.
- Vijayanagara rulers promoted the construction of grand temples, such as the Virupaksha Temple and Vittala Temple, known for their intricate carvings and stunning architecture.
- Dominance in Southern India:
- Over two centuries, the Vijayanagara Empire dominated southern India and was the strongest power in the Indian subcontinent during this period.
- The empire served as a defense against invasions from the Turkic Sultanates of the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
- Tussle with the Deccan Sultanates and Mughals:
- The foundation of the Vijayanagara Empire was partly in response to the weakening of the Delhi Sultanate under Muhammad bin Tughlaq, whose policies led to unrest in the Deccan.
- His attempt to shift his capital from Delhi to Daulatabad and his harsh taxation policies caused revolts, contributing to the rise of independent regional states, including Vijayanagara.
- The empire frequently clashed with the Bahmani Sultanate, which had emerged after the collapse of Tughlaq's control in the Deccan.
- Territorial conflicts with the Deccan Sultanates, particularly over the Raichur Doab, were driven by competition for strategic and economic resources rather than purely religious differences.
- The foundation of the Vijayanagara Empire was partly in response to the weakening of the Delhi Sultanate under Muhammad bin Tughlaq, whose policies led to unrest in the Deccan.
- Area of Rule under Vijayanagar:
- At its peak, the Empire covered a vast area across southern India, including parts of present-day Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Telangana.
- It extended from the Krishna River in the north to the southernmost tip of the Indian Peninsula, and from the Arabian Sea on the west to the Bay of Bengal on the east.
- Decline and Fall:
- In 1565, the Battle of Talikota (Battle of Rakkasagi–Tangadagi) resulted in a decisive defeat for the Vijayanagara army by the allied Deccan sultanates.
Nayakas
- The Nayakas were military commanders who were granted land (amaram) by the king in return for maintaining troops and financial contributions.
- They held substantial autonomy in their territories, managing local administration and defense while remaining loyal to the central authority.
- The Nayakas were responsible for local governance, including land distribution and tax collection, creating a feudal-like system.
- Over time, some Nayakas gained significant power, leading to conflicts with the central authority, especially during the decline of the empire.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the socio-economic and cultural contributions of the Vijayanagara Empire to southern India. How did these contributions influence subsequent Indian history? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Where is the famous Virupaksha temple located? (2009)
(a) Bhadrachalam
(b) Chidambaram
(c) Hampi
(d) Srikalahasti
Ans: (c)
Mains:
Q. Krishnadeva Raya, the king of Vijayanagar, was not only an accomplished scholar himself but was also a great patron of learning and literature. Discuss. (2016)