Important Facts For Prelims
Cooperative Bank
- 17 Feb 2025
- 5 min read
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) intervened in New India Cooperative Bank over fund misappropriation concerns, appointing an administrator and imposing restrictions to protect depositors.
- This move reflects a broader trend of consolidation and financial discipline in the cooperative banking sector.
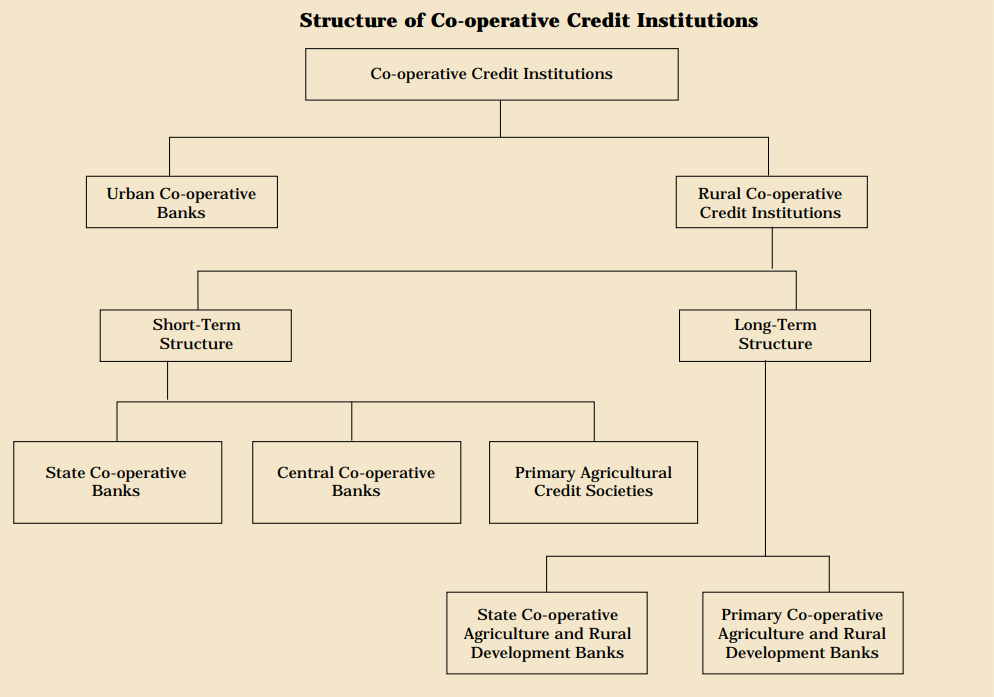
What are the Cooperative Banks?
- Definition: A Co-operative Bank is a Co-operative Society, either registered under State Cooperative Societies Acts or the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 2002, engaged in banking business.
- Cooperative banks in India are classified into Urban Cooperative Banks (UCBs), and Rural Cooperative Banks (RCBs).
- Ownership: Cooperative banks are owned and operated by members, who are its customers.
- Members usually have equal voting rights, according to the cooperative principle of “one person, one vote”.
- Objective: Provide rural financing and micro-financing. Primarily support agriculture, small-scale industries, and self-employed workers
- Regulation and Supervision: Cooperative banks in India function under a dual regulatory framework, dividing banking and managerial oversight between the RBI and the Registrar of Cooperative Societies (RCS).
- RBI’s Role: Regulates banking functions under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949, and Banking Laws (Application to Cooperative Societies) Act, 1965. This includes capital adequacy, risk management, lending norms, and financial supervision.
- RCS’s Role: Oversees managerial aspects under the State/Central Government, including incorporation, registration, governance, audit, board supersession, and liquidation of cooperative banks.
- License Cancellation: RBI can revoke the license of a Co-operative Bank if it ceases banking operations or fails to meet the conditions set by RBI.
- Importance: UCBs cater to the financial needs of small businesses and individuals, fostering growth in urban and semi-urban areas.
- Cooperative banks play a vital role in providing credit to farmers, boosting rural economic development.
- Cooperative banks are more resilient to economic downturns, as they avoid high-risk assets, demonstrated by UCBs during the 2008 global financial crisis.
- They cater to the unbanked and underbanked sections, promoting inclusive growth by Financial Inclusion.
|
Aspect |
Commercial Banks |
Cooperative Banks |
|
Governing Act |
Commercial banks are constituted by a uniform act passed by the parliament |
Cooperative banks are constituted by different states under different acts. |
|
Regulation |
RBI directly |
Regulated by RBI, NABARD and Registrar of Co-operative Societies. |
|
Services Offered |
Larger scope in offering a variety of banking services |
Lesser scope in offering a variety of banking services. |
|
Area of Operation |
Large-scale operation, usually countrywide. Commercial banks can also open branches in foreign countries. |
Small-scale operation, usually limited to a region. Cooperative banks cannot open branches in foreign countries. |
|
Borrowers |
Borrowers are only account holders and have no voting power, so they cannot influence the lending policy |
Borrowers are member shareholders, so they have some influence on the lending policy of the bank |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With reference to ‘Urban Cooperative Banks’ in India, consider the following statements:
- They are supervised and regulated by local boards set up by the State Governments.
- They can issue equity shares and preference shares.
- They were brought under the purview of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 through an Amendment in 1966.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)