Convention on Migratory Species | 08 May 2023
For Prelims: Bonn Convention (UNEP/CMS), Central Asian Flyway, micro-plastic and single-use plastic, Wildlife Crime Control Bureau, Wildlife Protection Act, 1972
For Mains: Convention on migratory species and Efforts made by India
Why in News?
The Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change in collaboration with the United Nations Environment Programme/ Convention on Migratory Species (UNEP/CMS) had organized a meeting of Range Countries to strengthen conservation efforts for migratory birds and their habitats in the Central Asian Flyway (CAF).
- The meeting was attended by 11 countries, including Armenia, Bangladesh, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Kuwait. The delegates agreed on an institutional framework for the CAF and a draft roadmap for updating the CMS CAF Action Plan.
What is CMS?
- About:
- It is an intergovernmental treaty under the UNEP- popularly known as Bonn Convention.
- It was signed in 1979 and in force since 1983.
- As of 1 March 2022, the CMS has 133 Parties.
- India is also a party to CMS since 1983.
- Aim:
- It aims to conserve terrestrial, marine and avian migratory species throughout their range.
- It lays the legal foundation to conduct conservation measures on a global scale.
- The legal instruments under CMS may range from legally binding Agreements to less formal MoU.
- Two appendices under CMS:
- Appendix I lists ‘Threatened Migratory Species’.
- Appendix II lists ‘Migratory Species requiring international cooperation’.
- India and the CMS:
- India has signed a non-legally binding Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with CMS on conservation and management of Siberian Cranes (1998), Marine Turtles (2007), Dugongs (2008), and Raptors (2016).
- With 2.4% of the world’s land area, India contributes to around 8% of the known global biodiversity.
- India also provides temporary shelter to several migratory species including Amur Falcons, Bar-headed Geese, Black-necked Cranes, Marine Turtles, Dugongs, Humpback Whales, etc.
What is a Migratory Species?
- A species or lower taxon of wild animals of which the entire population or any geographically separate part of the population cyclically and predictably cross one or more national jurisdictional boundaries.
- The word ‘cyclically’ relates to a cycle of any nature, such as astronomical (circadian, annual, etc.), life or climatic, and of any frequency.
- The word ‘predictably’ implies that a phenomenon can be anticipated to recur in a given set of circumstances, though not necessarily regularly in time.
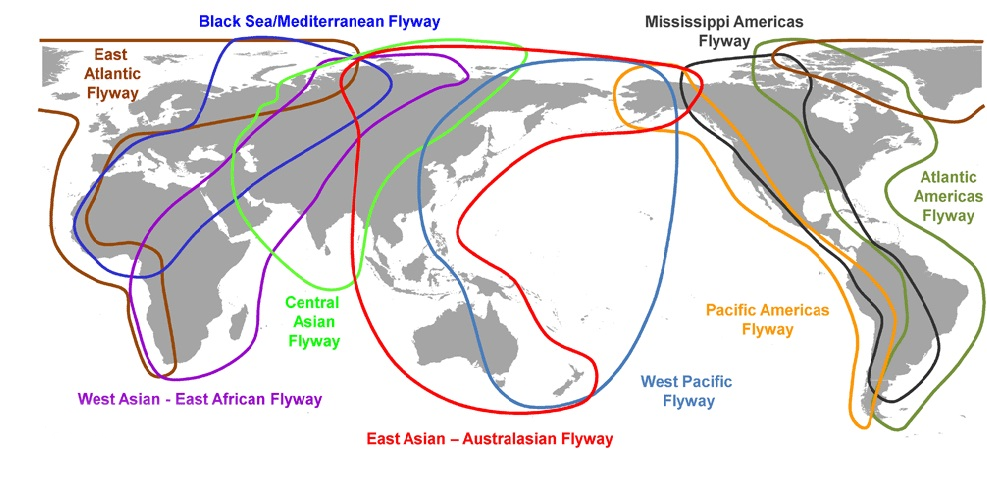
What is Central Asian Flyway?
- The CAF is a major migratory route for birds, covering 30 countries from the Arctic Ocean to the Indian Ocean.
- Indian subcontinent is a part of a CAF with at least 279 populations of 182 migratory waterbird species (including 29 globally threatened species).
- It is home to more than 400 species of migratory birds, including threatened and endangered species such as the Siberian crane and the lesser white-fronted goose.
What are Flyways?
- Flyways are the area used by a group of birds during their annual cycle which includes their breeding areas, stopover areas, and wintering areas.
- The CMS Secretariat has identified nine major flyways globally with respect to bird migration.
What are some Efforts made by India for Migratory Species?
- National Action Plan for the Conservation of Migratory Birds (2018-2023): India has launched the National Action Plan for the conservation of migratory species along the Central Asian Flyway.
- To reduce pressure on critical habitats and migratory routes by addressing the various challenges faced by migratory birds, including habitat loss, degradation and fragmentation, hunting, poaching, pollution, and climate change.
- To stop the decline of migratory birds and reverse the scenario by 2027.
- To avoid threats to habitats and migratory routes and ensure their sustainability for future generations.
- To support trans-boundary cooperation among various countries along the Central Asian Flyway to conserve migratory birds and their habitats.
- To improve the database on migratory birds and their habitats to enhance our understanding of their conservation needs.
- India also Announced:
- Conservation of marine turtles- by launching its Marine Turtle Policy and Marine Stranding Management Policy, by 2020,
- Reduction of pollution from micro-plastic and single-use plastic,
- Transboundary protected areas for conservation of species like Tigers, Asian elephants, Snow Leopard, the Asiatic Lion, the one-horned rhinoceros, and the Great Indian Bustard, and
- Sustainable infrastructure development like Linear Infrastructure Policy Guidelines to tailor development in ecologically fragile areas.
- Project Snow Leopard (PSL): PSL was launched in 2009 to promote an inclusive and participatory approach to conserve snow leopards and their habitat.
- Dugong Conservation Reserve: India has established its first Dugong conservation reserve in Tamil Nadu.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972:
- Rare and endangered species of birds including migratory birds are included in Schedule-I of the Act thereby according them highest degree of protection.
- Stringent punishments have been provided in the Act for violation of provisions of the Act.
- Important habitats of birds, including migratory birds have been notified as protected Areas under the Act for better conservation and protection of birds and their habitats.
- Other Initiatives:
- Focused protection measures involving the local communities have been taken up in the State of Nagaland for protection of Amur Falcons that migrate to Northeast India on their route to Southern Africa.
- India has taken several steps to conserve vultures like imposing ban on veterinary use of diclofenac, establishment of Vulture breeding centres etc.
- Wildlife Crime Control Bureau has been established for control of illegal trade in wildlife and its parts and products.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2020)
| International agreement/set-up | Subject | |
| 1. | Alma-Ata Declaration | Healthcare of the people |
| 2. | Hague Convention | Biological and chemical weapons |
| 3. | Talanoa Dialogue | Global climate change |
| 4. | Under2 Coalition | Child rights |
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2, 3 and 4 only
Ans: (c)
- Alma-Ata Declaration: It was adopted at the International Conference on Primary Health Care (PHC) which was held in Almaty, Kazakhstan in 1978. It urged all the governments, health care workers and development workers to promote and protect the primary health of all the people. Hence, pair 1 is correctly matched.
- Hague Convention: There are a series of Hague Convention on different subjects such as Convention for the Protection of Cultural Property in the Event of Armed Conflict, Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction, etc. But it is not related to biological and chemical weapons. Hence, pair 2 is not correctly matched.
- Talanoa Dialogue: The Dialogue was launched at the UN Climate Change Conference (COP 23) in Bonn (Germany) in 2017. Talanoa is a traditional word used in Fiji and across the Pacific to reflect a process of inclusive, participatory and transparent dialogue. The purpose of Talanoa is to share stories, build empathy and to make wise decisions for the collective good. Hence, pair 3 is correctly matched.
- Under2 Coalition: The Under2 Coalition is a global community of state and regional governments committed to ambitious climate action in line with the Paris Agreement. The coalition brings together more than 220 subnational governments who represent over 1.3 billion people and 43% of the global economy. Currently, Maharashtra, Jammu & Kashmir, West Bengal, Telangana and Chhattisgarh are signatories to this pact from India. Signatories commit to keeping global temperature rises to well below 2°C with efforts to reach 1.5°C. Hence, pair 4 is not correctly matched.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.