Commercial Cultivation of HT Basmati Rice | 06 Aug 2024
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian government for the first time allowed the commercial cultivation of two non-transgenic varieties of herbicide-tolerant (HT) basmati rice: Pusa Basmati 1979 and Pusa Basmati 1985.
- It has been developed by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) to promote sustainable paddy cultivation practices that conserve water and reduce carbon
emissions.
Note:
- Transgenic refers to a Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) or cell whose genome has been altered by the introduction of one or more foreign DNA sequences or genes from
another species by artificial means.- GMO is an organism that contains a genetically modified genome.
- All transgenic organisms are GMOs.
- Non-Transgenic does not involve inserting any foreign DNA.
What are the Key Features of the New Varieties of Rice?
- These new varieties contain a mutated AcetoLactate Synthase (ALS) gene making it possible for farmers to spray Imazethapyr (a herbicide) to control weeds.
- Mutated ALS gene prevents the ALS enzymes from having binding sites for Imazethapyr, ensuring that amino acid synthesis remains unaffected.
- The ALS gene in rice encodes an enzyme responsible for synthesising amino acids essential for the crop's growth and development.
- While, in normal rice plants, the herbicide binds to the ALS enzymes, inhibiting amino acid production.
- Imazethapyr effectively targets a variety of broadleaf, grassy, and sedge weeds but cannot distinguish between the crop and invasive plants.
- As a result, these plants can tolerate the herbicide, which kills only the weeds.
- Since no foreign genes are involved in the process, herbicide tolerance is achieved through mutation breeding, making these plants non-Genetically Modified Organisms (non-GMOs).
- Significance: These HT rice varieties offer several benefits such as eliminating the need for nursery preparation, puddling, transplanting, and field flooding, reducing methane emissions, a major greenhouse gas by supporting Direct Seeding of Rice (DSR).
Concerns Regarding the Use of HT Variety of Rice
- There is a risk of developing "super weeds" that become resistant to herbicides through repeated use, making them harder to control.
- There are worries about potential herbicide residue accumulation in food products, despite developers' assurances that the grain is residue-free.
- While India permits certain herbicides like imazethapyr, the European Union bans them, which could impact international trade and safety standards.
- Questions arise about the long-term sustainability of HT crops, as increased herbicide use over time might lead to ecological concerns.
|
Paddy Transplantation vs Direct Seeding of Rice (DSR) |
|
|
Paddy Transplantation |
DSR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rice:
- It is a kharif crop that requires high temperature (above 25°C) and high humidity with annual rainfall above 100 cm.
- In southern states and West Bengal, the climatic conditions allow the cultivation of two or three crops of rice in an agricultural year.
- In West Bengal farmers grow three crops of rice called ‘aus’, ‘aman’ and ‘boro’.
- About one-fourth of the total cropped area in India is under rice cultivation.
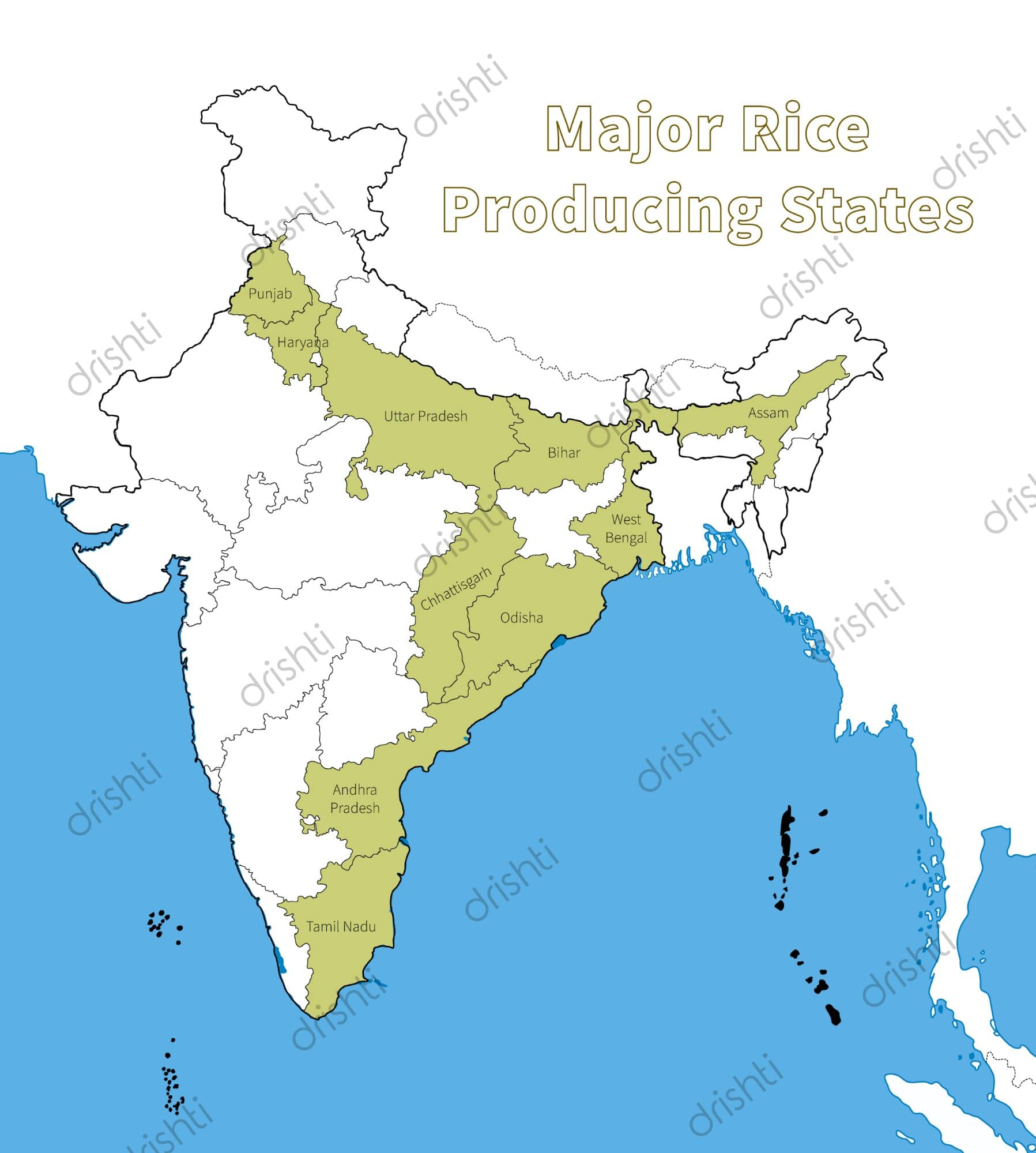
- Leading producer states: West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh, and Punjab.
- High Yielding States: Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Haryana, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, West Bengal and Kerala.
- India is the second-largest producer of rice after China.
- Basmati rice is India’s top agricultural-export produce. In 2022-23, India exported 4.56 million tonnes of this valued at USD 4.78 billion.
- Basmati's distinctive fragrance is attributed to 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline (2-AP), an organic compound produced during maturation that gives this rice grain its nutty and
fragrant aroma.
- Basmati's distinctive fragrance is attributed to 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline (2-AP), an organic compound produced during maturation that gives this rice grain its nutty and
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. What is/are the advantages/advantages of zero tillage in agriculture? (2020)
- Sowing of wheat is possible without burning the residue of the previous crops.
- Without the need for a nursery of rice saplings, direct planting of paddy seeds in the wet soil is possible.
- Carbon sequestration in the soil is possible.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: D
