Coal Gasification | 04 Jun 2024
Why in News?
The Ministry of Coal requested proposals from public and private sector participants for coal gasification projects as part of an Rs 8,500 crore viability gap funding (VGF) scheme.
- Viability Gap Funding (VGF) is a financial tool used to support projects that are economically justified but not financially viable on their own.
What is Coal Gasification?
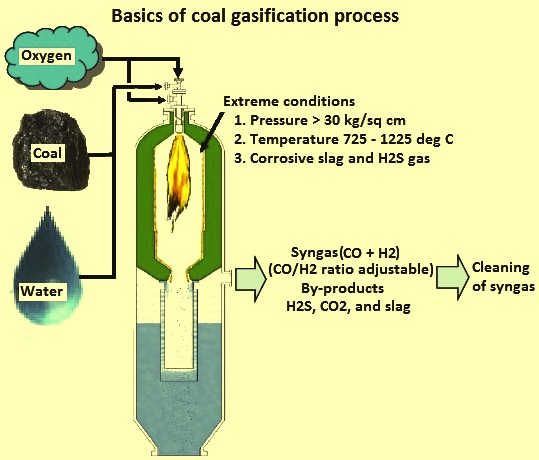
- Coal gasification is a process that transforms Coal into a Synthetic gas (Syngas), consisting of mixture of gasses such as Carbon monoxide (CO), Hydrogen (H2), Carbon dioxide (CO2), Methane (CH4) and Water vapor (H2O).
- Coal is reacted at high temperatures (typically 1,000–1,400°C) with a controlled amount of oxygen and steam.
- Syngas can be used to produce a wide range of Fertilizers, Fuels, solvents and synthetic materials.
- The Process is as given:
- Preparation: Coal is crushed into a fine powder to increase its surface area and enhance the chemical reactions during the process.
- Gasification Reactor: The crushed coal is introduced into a high-temperature and high-pressure reactor along with limited oxygen or air and steam.
- Chemical Reactions: In the absence of sufficient oxygen for complete combustion, the coal undergoes a series of complex chemical reactions.
- These reactions break down the coal molecules into the components of syngas.
- Gas Cleaning: The raw syngas produced from the reactor contains impurities like tar, sulfur, and dust. These impurities need to be removed through a gas cleaning process before the syngas can be used further.
- Benefits of Coal Gasification:
- Cleaner Alternative to Coal Combustion: Coal gasification burns cleaner than coal for electricity. It captures pollutants before using the gas for power generation.
- Versatile Syngas Usage: The syngas produced can be used for various purposes, including electricity generation, production of cleaner fuels like hydrogen and production of chemicals like ammonia and methanol.
Note
- The Government is promoting coal-to-chemical and gasification processes due to the expected surplus of domestic coal in the future after meeting the power and other sectors' needs.
- India aims for 100 million tonnes (MT) coal gasification by 2030 with investments worth over Rs. 4 lakh crores.
- In addition to VGF, the government is supporting the coal industry in 2 ways:
- Long-term linkage window: This creates a stable market for coal producers.
- Coal utilization for gasification: Coal mine owners can use their coal for gasification projects and get a discount on revenue sharing.
- Production of coal and lignite reached 1 billion tonnes in FY 2024, target of 1.08 billion tonnes is set for the current fiscal year 2024-25.
- India has the fourth largest coal reserves in the world, with reserves of 361.41 billion tonnes.
- Top 3 Coal Reserves: US, Russia and Australia.
- Top 3 Coal Production: China, India and US.
Read more: Coal Gasification, Coal Logistics Plan and Policy
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following statements: (2019)
- Coal sector was nationalized by the Government of India under Indira Gandhi.
- Now, coal blocks are allocated on lottery basis.
- Till recently, India imported coal to meet the shortages of domestic supply, but now India is self-sufficient in coal production.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Q2. Which of the following is/are the characteristic/characteristics of Indian coal? (2013)
- High ash content
- Low sulphur content
- Low ash fusion temperature
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)