Science & Technology
China’s EAST Reactor and Nuclear Fusion
- 20 Feb 2025
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Tokamak, Nuclear fusion, Difference between Nuclear Fusion & Nuclear Fission.
For Mains: Advantages of Nuclear Fusion, Challenges in Harnessing Nuclear Energy
Why in News?
China’s Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST) nuclear fusion reactor set a new milestone in nuclear fusion by sustaining plasma at 100 million°C for 1,066 seconds.
- This achievement advances the pursuit of clean and sustainable fusion energy for future energy security.
Tokamak: A tokamak is an experimental device designed to generate energy through nuclear fusion.
- Inside the tokamak, the heat produced from the fusion of atoms is absorbed by the vessel’s walls.
- Similar to conventional power plants, this heat is then used to produce steam, which drives turbines and generators to generate electricity.
What is Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST)?
- About:
- EAST is an advanced nuclear fusion research facility located at the Institute of Plasma Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (ASIPP) in Hefei, China.
- It became operational in 2006.
- Purpose:
- It aims to replicate the nuclear fusion process that powers the Sun, contributing to the development of sustainable energy (without any harmful radioactive waste).
- It is a part of the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) initiative, which will be the world's largest fusion reactor when operational by 2035.
- The ITER, established in 1985, is a collaboration of 35 nations located in France. It aims to build the world’s largest tokamak to demonstrate the feasibility of fusion as a large-scale, carbon-free energy source.
- Its members include China, the European Union, India, Japan, Korea, Russia and the US.
- Working Mechanism:
- EAST is based on the nuclear fusion process, where deuterium and tritium nuclei (isotopes of hydrogen) fuse to form a helium nucleus, releasing a large amount of energy.
- Hydrogen fuel is heated to over 150 million°C to form a hot plasma (ionized gas).
- A strong magnetic field confines the plasma, preventing heat loss and enabling sustained fusion reactions.
- Achievements & Significance:
- EAST has achieved significant milestones such as sustaining plasma at 50 million°C for over 60 seconds (2016) and 100 seconds (2017), achieving steady-state high-confinement plasma for 403 seconds (2023).
- Despite these, EAST has yet to achieve ignition (self-sustaining fusion) or produce electricity.
- It serves as a testbed for ITER, a multinational project, including India and the EU, aimed at developing a tokamak capable of achieving net energy gain.
What are Nuclear Reactions?
- About: A nuclear reaction is an interaction between two nuclear particles or two nuclei that results in the formation of new nuclei different from the original ones.
- Nuclear reactions can be classified into two main types: nuclear fission and nuclear fusion.
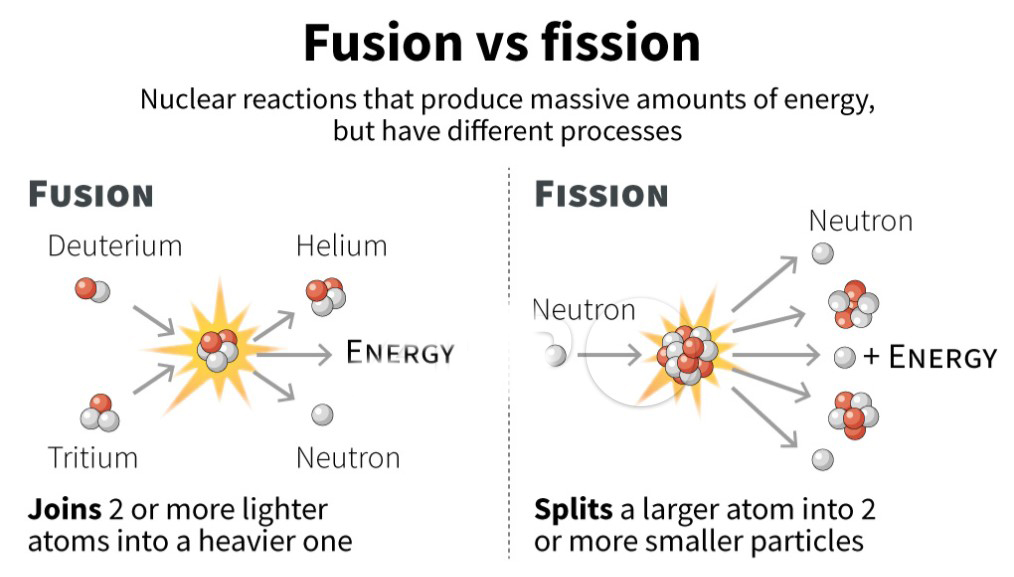
- Nuclear Fission: It is a reaction that occurs when an atom's nucleus splits into smaller nuclei, releasing energy.
- It can occur naturally (radioactive decay) or be induced in a lab by bombarding the nucleus with neutrons or other particles.
- The combined mass of the resulting fragments is less than the original nucleus, with the lost mass converted into energy.
- All commercial nuclear reactors operate on nuclear fission.
- Nuclear Fusion: It is the process where two light atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier one, releasing massive energy.
- This reaction occurs in plasma state (high-temperature & charged state of matter).
- The Sun and other stars are powered by fusion, requiring temperatures of around 10 million°C to overcome electrical repulsion between nuclei.
- The hydrogen bomb operates on thermonuclear fusion, with a fission bomb (uranium/plutonium-based) providing the initial energy to trigger the reaction.
What are the Challenges in Achieving Nuclear Fusion Reaction?
- Extreme Temperature Requirements: Fusion requires temperatures exceeding those found at the Sun’s core (over 100 million degrees Celsius) to sustain fusion reaction.
- Magnetic Confinement: Maintaining the high-energy plasma in a stable state requires strong magnetic fields, as used in tokamak reactors, to prevent energy loss and sustain reactions.
- Tritium Scarcity: While deuterium is readily available in seawater, tritium is scarce and primarily obtained from specific nuclear fission reactions, raising concerns about long-term fuel supply.
- Current sources of tritium include heavy-water reactors in Canada, India, and South Korea, but ITER’s demands could exhaust global reserves.
- Ignition Milestone: A self-sustaining fusion reaction, where energy output exceeds energy input, remains a major goal yet to be achieved.
- Sustained Reactions: Currently, maintaining stable plasma conditions for prolonged periods remains a major challenge.
Alternative Approaches to Fusion Energy: Apart from tokamaks, researchers are exploring other fusion methods.
- Stellarators: It offers a complex yet promising magnetic confinement method that eliminates the need for a poloidal field (a kind of magnetic field) in tokamak, though they are harder to build.
- Laser Inertial Fusion: It involves the use of high-power laser beams to compress a deuterium-tritium pellet, triggering fusion. The energy released can generate steam to drive turbines, producing electricity.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the role of nuclear energy in achieving global decarbonization goals. What are the key advantages and challenges associated with nuclear energy as a clean energy source? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. The function of heavy water in a nuclear reactor is to (2011)
(a) Slow down the speed of neutrons
(b) Increase the speed of neutrons
(c) Cool down the reactor
(d) Stop the nuclear reaction
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. With growing energy needs should India keep on expanding its nuclear energy programme? Discuss the facts and fears associated with nuclear energy. (2018)