Indian Economy
Card Tokenisation
- 25 Jun 2022
- 6 min read
For Prelims: RBI, Card Tokenisation, Card-on-File
For Mains: Reports of RBI, Card Tokenisation, Card-on-File
Why in News?
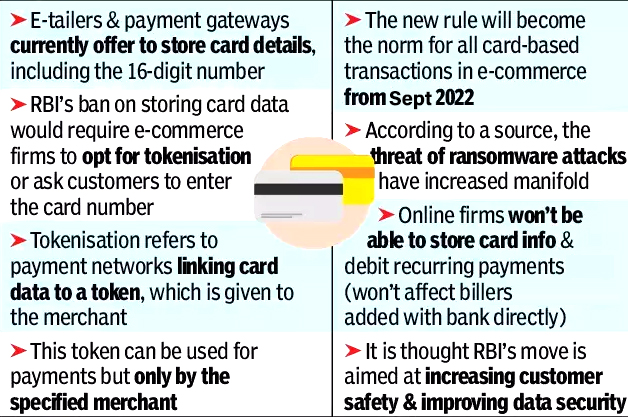
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) extended the timeline for tokenisation of debit and credit cards by three months till 30th September, 2022 to avoid disruption and inconvenience to cardholders.
- After 30th September, no entity in the card transaction or payment chain, other than the card issuers and card networks, should store the CoF (Card-on-File data or storage of actual card data) and any such data stored previously will be done away with.
What is Tokenisation and Card-on-File?
- Tokenisation: It refers to replacement of actual credit and debit card details with an alternate code called the “token”, which will be unique for a combination of card, token requestor and device.
- A tokenised card transaction is considered safer as the actual card details are not shared with the merchant during transaction processing.
- Customers who do not have the tokenisation facility will have to key in their name, 16-digit card number, expiry date and CVV each time they order something online.
- As of now, about 19.5 crore tokens have been created. Opting for CoFT (creating tokens) is voluntary for the cardholders.
- Card-on-File: A CoF transaction is a transaction where a cardholder has authorised a merchant to store the cardholder’s Mastercard or Visa payment details.
- The cardholder then authorises that same merchant to bill the cardholder’s stored Mastercard or Visa account.
- E-commerce companies and airlines and supermarket chains normally store card details in their system.
Why is Tokenisation of Cards Required?
- Many entities involved in an online card transaction chain store card data like card number and expiry date — Card-on-File (CoF) for undertaking transactions in future. While this practice does render convenience, availability of card details with multiple entities increases the risk of card data being stolen or misused.
- There have been instances where such data stored by merchants have been compromised.
- Many jurisdictions do not mandate Additional Factor of Authentication (AFA) for authenticating card transactions, stolen data in the hands of fraudsters may result in unauthorised transactions and resultant monetary loss to cardholders. Within India as well, social engineering techniques can be employed to perpetrate frauds using such data.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) acts as a ‘bankers’ bank. This would imply which of the following? (2012)
- Other banks retain their deposits with the RBI.
- The RBI lends funds to the commercial banks in times of need.
- The RBI advises the commercial banks on monetary matters.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 2 and 3 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
- The origin of the Reserve Bank of India can be traced to 1926, when the Royal Commission on Indian Currency and Finance (also known as the Hilton- Young Commission) recommended the creation of a central bank for India to separate the control of currency and credit from the Government and to augment banking facilities throughout the country. The Reserve Bank of India Act of 1934 established the Reserve Bank.
- Role of RBI as a Bankers’ Bank and Supervisor
- RBI holds a part of the cash reserves of banks, lends them funds for short periods and provides them with centralized clearing and cheap and quick remittance facilities. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- The RBI is authorized statutorily to require scheduled commercial banks to deposit with it a stipulated ratio of their Net Demand Time Liabilities (NDTL). Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- As a Banker to Banks, the Reserve Bank also acts as the ‘lender of last resort’. It can come to the rescue of a bank that is solvent but faces temporary liquidity problems by supplying it with much needed liquidity when no one else is willing to extend credit to that bank.
- The RBI is supposed to function as the lender of the last resort.
- RBI also supervise and advise the commercial banks in monetary matters. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.