Important Facts For Prelims
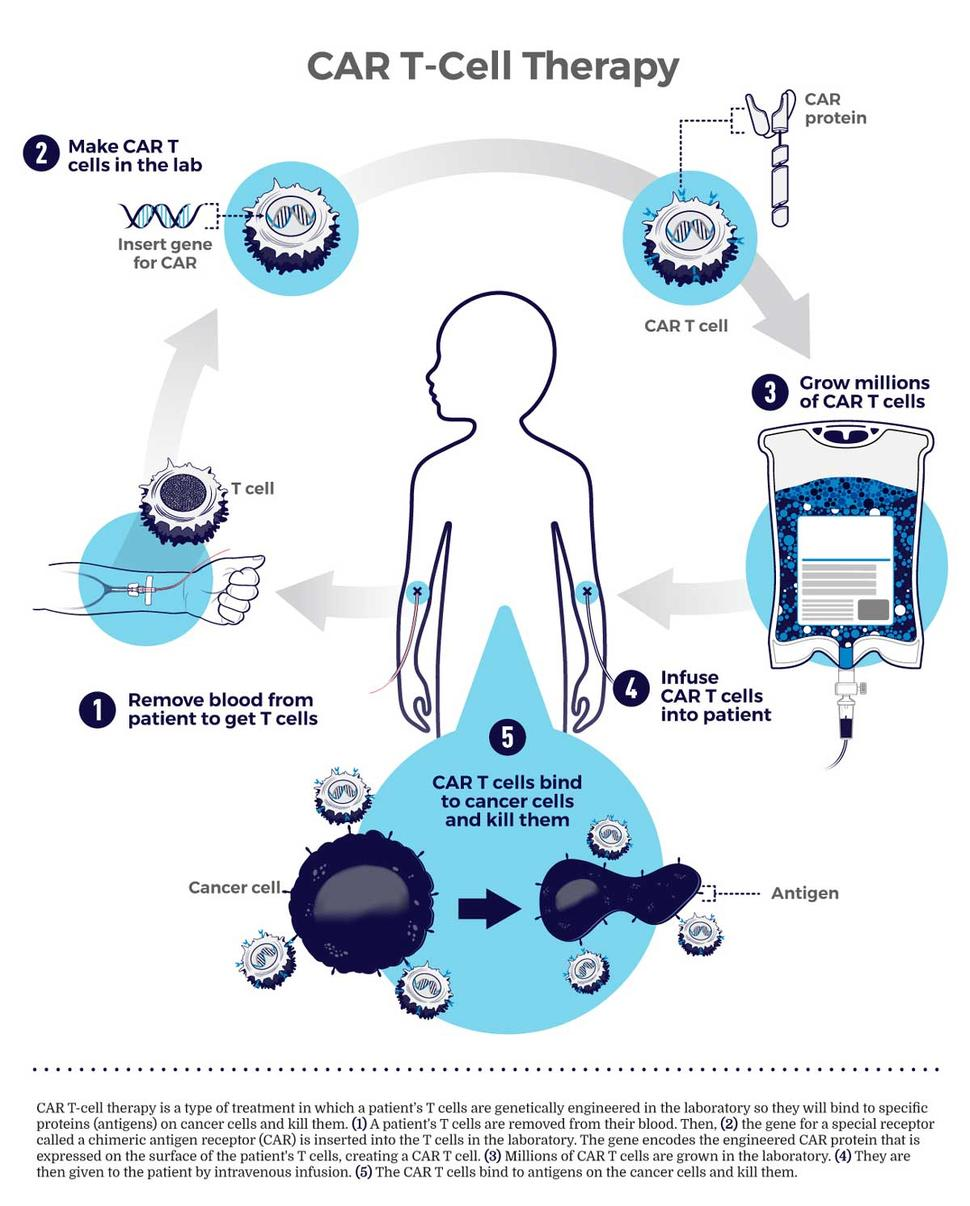
CAR-T Cell Therapy
- 04 Nov 2023
- 2 min read
Why in News?
Recently, The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) has granted market authorisation for NexCAR19, India’s first indigenously-developed Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cell (CAR-T cell) Therapy.
- India is now one of the first developing countries to have its indigenous CAR-T and gene therapy platform.
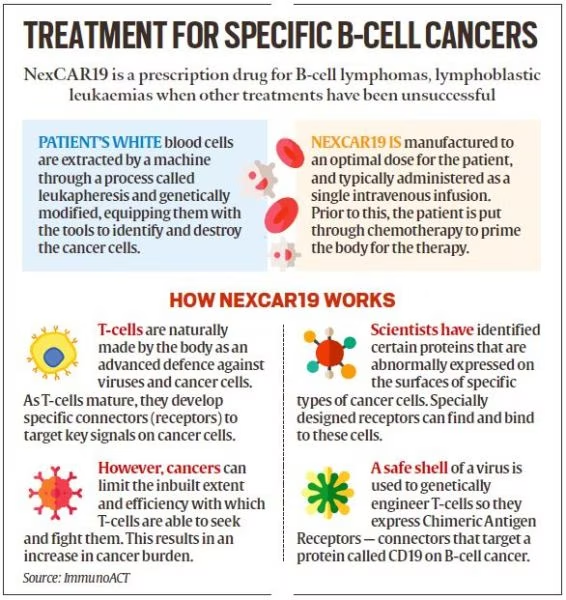
What is NexCAR19?
- About:
- NexCar19 is a type of CAR-T and gene therapy developed indigenously in India by ImmunoACT, which is a company incubated at IIT Bombay.
- It is designed to target cancer cells that carry the CD19 protein.
- This protein acts like a flag on cancer cells, which allows CAR-T cells to recognise and attach themselves to the cancer cells and start the process of elimination.
- Even some developed nations don’t have their own CAR-T therapies; they import them from the United States or Europe.
- Patient Eligibility:
- NexCAR19 therapy is intended for people with B-cell lymphomas who have not responded to standard treatments like chemotherapy and have experienced relapse or recurrence of cancer.
- Initially, the therapy is approved for patients aged 15 years and older.
- Procedure:
- The process commences with the patient donating blood at a transfusion center. The T-cells are genetically modified and reinfused into the patient within a period of 7-10 days.
- Efficacy:
- It leads to significantly lower drug-related toxicities. It causes minimal damage to neurons and the central nervous system, a condition known as neurotoxicity.
- Neurotoxicity can sometimes occur when CAR-T cells recognise the CD19 protein and enter the brain, potentially leading to life-threatening situations.
- This therapy also results in Minimal Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS), which is characterized by inflammation and hyperinflammation in the body due to the death of a significant number of tumour cells, as CAR-T cells are designed to target and eliminate cancer cells.
- It leads to significantly lower drug-related toxicities. It causes minimal damage to neurons and the central nervous system, a condition known as neurotoxicity.