Buddha's Relevance to the Modern Youth | 05 Jul 2023
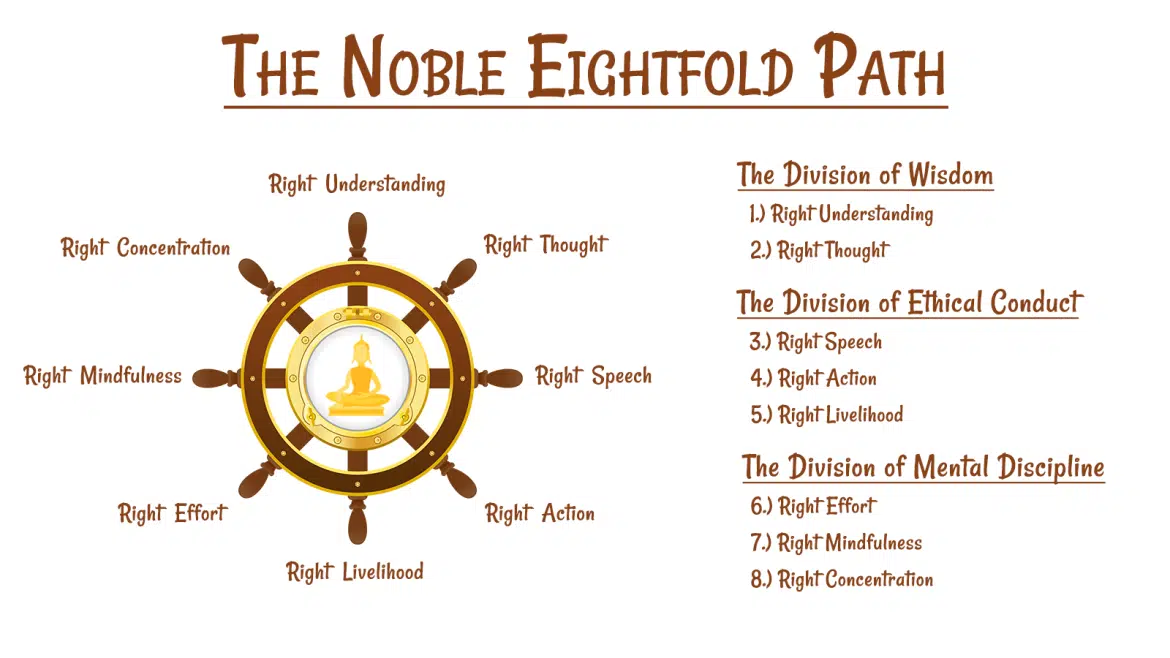
For Prelims: Dharma Chakra Pravartana Divas, Lord Buddha, Maha Bodhi Temple, Four Noble Truths, Noble Eightfold Path, Four Sublime States.
For Mains: Major Teachings of Lord Buddha, Buddha's Relevance to the Modern Youth.
Why in News?
The President of India, urged the youth to draw inspiration from the teachings of Lord Buddha, on the occasion of Dharma Chakra Pravartana Divas (3rd July 2023).
- The President reflected on how Lord Buddha's first sermon on Asadha Purnima planted the seeds of the middle path of the Dhamma.
Lord Buddha
- About:
- Lord Buddha (Siddhartha Gautam) was born into royal family of Sakya clan who ruled from Kapilvastu, in Lumbini located in the Terai plains of southern Nepal.
- At the age of 29, Gautama left home and rejected his life of riches and embraced a lifestyle of asceticism, or extreme self-discipline.
- After 49 consecutive days of meditation, Gautama attained Bodhi (enlightenment) under a pipal tree at Bodhgaya, a village in Bihar.
- Buddha gave his first sermon in the village of Sarnath, near Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh on Asadha Purnima. This event is known as Dharma Chakra Pravartana (turning of the wheel of law).
- The day is also observed as Guru Poornima by both Buddhists and Hindus as a day to mark reverence to their Gurus.
- Major Teachings of Lord Buddha:
- The Three Marks of Existence: These are the characteristics of all phenomena that one should understand and accept. They are impermanence (anicca), unsatisfactoriness (dukkha), and non-self (anatta).
- The Four Noble Truths: These are the truths about the nature of suffering, its cause, its cessation, and the path to its cessation. The cause of suffering is ignorance, attachment, and aversion.
- The Four Sublime States: These are the positive mental qualities that one should cultivate and radiate to all beings. They are loving-kindness (metta), compassion (karuna), sympathetic joy (mudita), and equanimity (upekkha).
- By developing these states, one can foster harmony, empathy, altruism, and peace.
- The Five Precepts: These are the basic ethical principles that Buddha laid down for his lay followers.
- They are: to abstain from killing, stealing, sexual misconduct, lying and intoxication.
- They help us to avoid harming ourselves and others, to respect life and property, to maintain purity and honesty and to preserve clarity and awareness.
How can Youth Draw Inspiration from Buddha to Navigate Life's Challenges?
- Mindfulness as a Foundation: One of the central tenets of Buddha's teachings is the practice of mindfulness.
- Mindfulness encourages individuals to cultivate a deep awareness of the present moment, fostering an enhanced understanding of their thoughts, emotions, and actions.
- In a world saturated with distractions, young people can draw inspiration from Buddha's emphasis on being fully present and engaged.
- By practicing mindfulness, youth can learn to manage stress, improve focus and concentration, and nurture a greater sense of self-awareness, leading to improved mental well-being and personal growth.
- Impermanence and Non-Attachment: Buddha's teachings emphasize the impermanence (the state or fact of lasting for only a limited period of time) of all phenomena and the futility of attachment.
- In a materialistic society driven by instant gratification, youth can find solace and inspiration in the understanding that everything is transient.
- By recognizing the impermanence of both joy and suffering, young individuals can cultivate a mindset that is adaptable, resilient, and open to change.
- Learning to let go of attachment to outcomes, possessions, and even relationships can free the youth from unnecessary suffering and allow them to embrace life with greater equanimity.
- Compassion and Empathy: In a world where divisions and conflicts persist, young people can find inspiration in Buddha's teachings on loving-kindness and compassion.
- By cultivating empathy, youth can develop a deeper understanding of others' struggles, fostering a sense of unity and connection.
- Self-Discovery and Inner Transformation: Young people, often grappling with questions of identity and purpose, can draw inspiration from Buddha's teachings on self-exploration.
- By engaging in introspection and self-reflection, youth can gain insights into their true nature, passions, and aspirations.
- Engaging in Social and Environmental Responsibility: Buddha's teachings emphasize the interconnectedness of all beings and advocate for responsible action.
- The youth can actively engage in social and environmental responsibility by working towards equality, justice, and sustainable practices.
- They can participate in community initiatives, advocate for marginalized groups, and champion environmental conservation.
- By embodying these teachings, they contribute to building a more equitable, harmonious, and environmentally conscious society.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the religious history of India, consider the following statements: (2020)
- Sthaviravadins belong to Mahayana Buddhism.
- Lokottaravadin sect was an offshoot of Mahasanghika sect of Buddhism.
- The deification of Buddha by Mahasanghikas fostered the Mahayana Buddhism.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q. With reference to the religious history of India, consider the following statements: (2016)
- The concept of Bodhisattva is central to Hinayana sect of Buddhism.
- Bodhisattva is a compassionate one on his way to Enlightenment.
- Bodhisattva delays achieving his own salvation to help all sentient beings on their path to it.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Pala period is the most significant phase in the history of Buddhism in India. Enumerate. (2020)