Branned Millets for Health Benefits | 12 Nov 2024
Why in News?
Recently, a study titled ‘Impact of debranning (the process of removing the outer bran layers from a cereal grain) on the nutritional, cooking, microstructural characteristics of five Indian small millets’ was published.
What are the Key Highlights of the Study?
- Nutritional Impact of De-branning: Removing the bran from millets reduces protein, dietary fibre, fat, mineral, and phytate content while increasing carbohydrates and amylose content.
- This diminishes their health benefits and increases their glycemic load.
- Reasons for De-branning Millets: De-branning and polishing millets extends their shelf life and reduces cooking time by making them softer.
- However, vacuum-sealing can extend the shelf life of whole-grain millets without removing the bran.
- Millets' Health Benefits: Millets contain minerals like iron, zinc, and calcium and have bioactive flavonoids that support health.
- They help prevent diabetes, manage hyperlipidemia, reduce weight, and lower blood pressure, with positive effects on cardiovascular disease (CVD).
- They are gluten-free and have a low glycemic index, beneficial for people with celiac disease or diabetes.
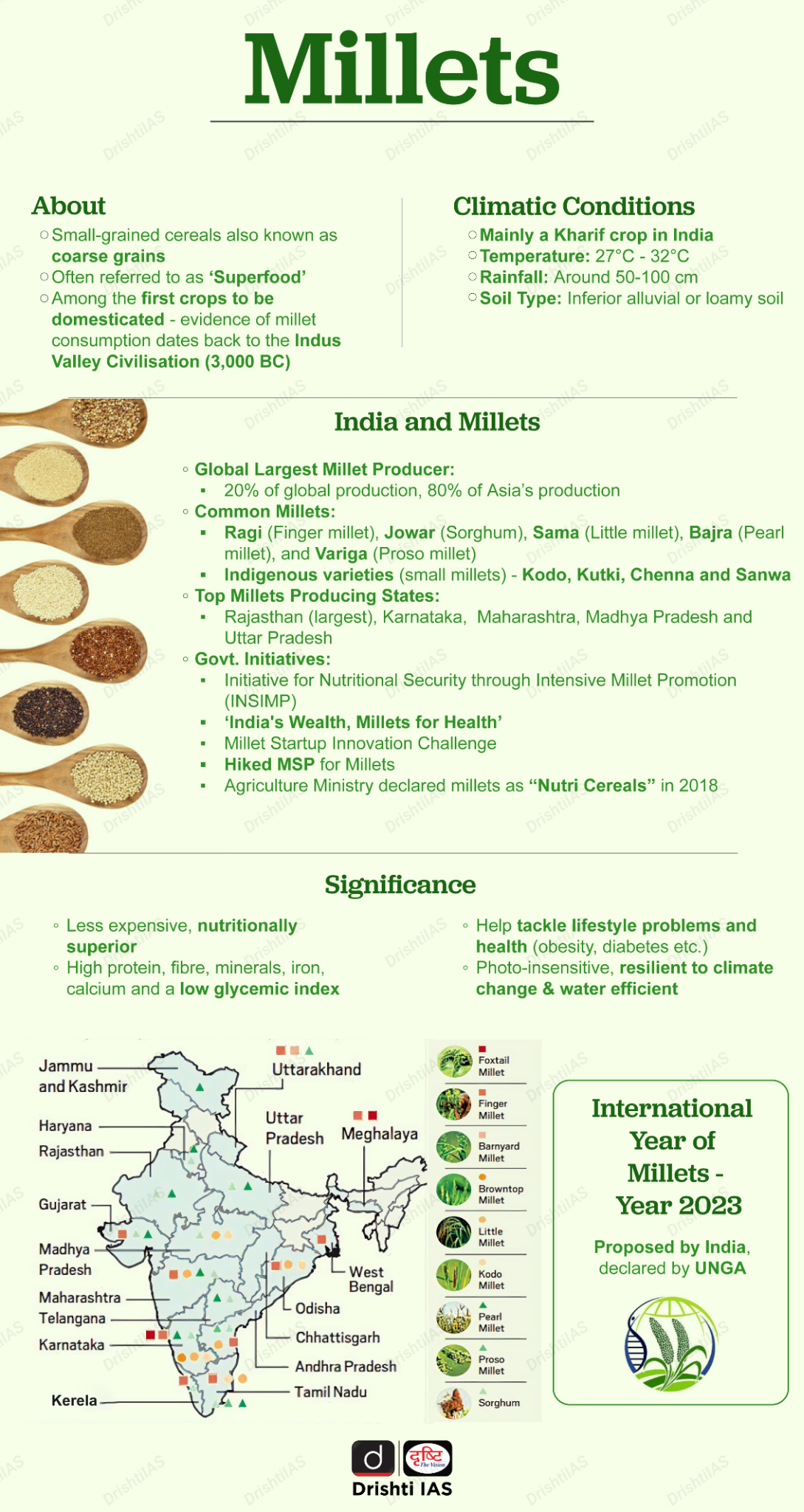
What are the Key Facts About Millet?
- About: It is a collective term referring to a number of small-seeded grasses that are cultivated as grain crops, primarily on marginal lands in dry areas in temperate, subtropical and tropical regions.
- Some of the common millets available in India are Ragi (Finger millet), Jowar (Sorghum), Sama (Little millet), Bajra (Pearl millet), and Variga (Proso millet).
- Global and Indian Production: India is the largest producer and exporter of millets, followed by Niger and China.
- Global millet production stood at 28 million metric tons in 2020, with major consumption in Africa and Asia.
- Millet Promotion: 2023 was recognized as the International Year of Millets by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
- The Indian government promotes millet production under the National Food Security Mission.
- Ecological and Economic Advantages: Millets are drought-tolerant, thrive in arid and semi-arid regions, and require minimal water, fertilisers, and pesticides.
- It serves dual purposes, used as both food and fodder, increasing farming efficiency.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following are the objectives of ‘National Nutrition Mission’? (2017)
- To create awareness relating to malnutrition among pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- To reduce the incidence of anaemia among young children, adolescent girls and women.
- To promote the consumption of millets, coarse cereals and unpolished rice.
- To promote the consumption of poultry eggs.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 3 and 4 only
Ans: (a)
Q.With reference to ‘Initiative for Nutritional Security through Intensive Millets Promotion’, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
- This initiative aims to demonstrate the improved production and post-harvest technologies, and to demonstrate value addition techniques, in an integrated manner, with cluster approach.
- Poor, small, marginal and tribal farmers have larger stake in this scheme.
- An important objective of the scheme is to encourage farmers of commercial crops to shift to millet cultivation by offering them free kits of critical inputs of nutrients and micro irrigation equipment.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)