Important Facts For Prelims
Biomedical Waste Management in India
- 04 Dec 2024
- 5 min read
Why in News?
Amid concerns related to HIV, recent discussions on biomedical waste management (BMW) have gained attention, highlighting the need for effective waste disposal systems to protect public health and the environment.
What is Biomedical Waste?
- Definition: Biomedical waste refers to human and animal anatomical waste, along with treatment apparatus such as needles, syringes, and other materials used in healthcare facilities during treatment and research.
- It is classified as biologically and chemically hazardous waste, containing biological and microbiological contaminants.
- Treatment and Disposal Methods: Options for managing biomedical waste include, incineration, Plasma pyrolysis, Deep burial, Autoclaving, and recycling.
- Current Status of Biomedical Waste Management:
- As of 2020, India generated approximately 774 tons of biomedical waste per day.
- India has 393,242 healthcare facilities, with 67.8% being non-bedded (clinics, laboratories) and 32.2% being hospitals and nursing homes.
- Approximately 79% of these facilities utilize 218 Common Biomedical Waste Treatment Facilities (CBWTF) for waste management.
- Out of operational CBWTFs, 208 have adopted the Centralised Bar Code System for Tracking Biomedical Waste (CBST-BMW) to enhance monitoring.
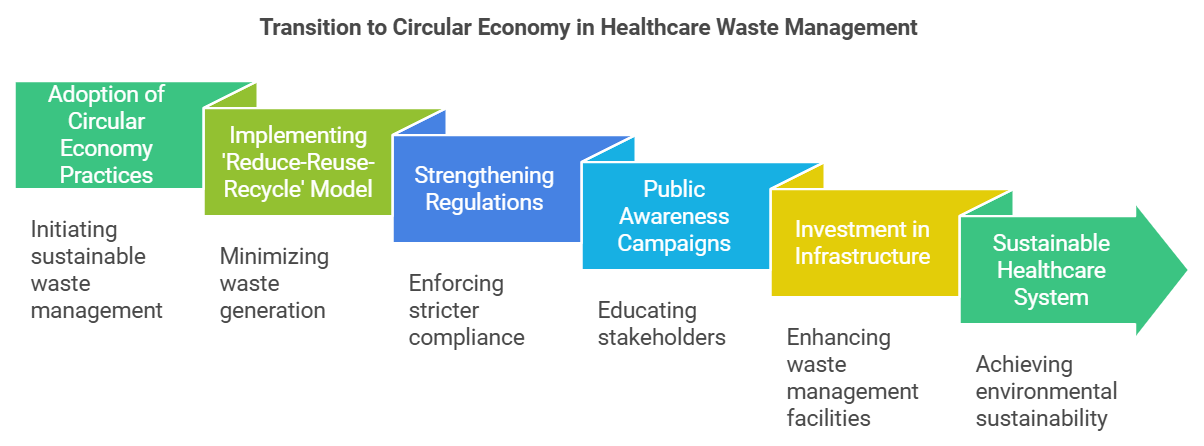
- Strategies for Enhancement:
- Adoption of Circular Economy Practices: Implementing a circular economy model can promote sustainable practices in healthcare waste management.
- IIT Researchers advocate for a 'reduce-reuse-recycle' approach instead of traditional 'take-make-dispose' models.
- Adoption of Circular Economy Practices: Implementing a circular economy model can promote sustainable practices in healthcare waste management.
What are the Provisions for Biomedical Waste Management?
- Biomedical Waste Management Rules, 2016
- The ambit of the rules has been expanded to include vaccination camps, blood donation camps, surgical camps or any other healthcare activity.
- Chlorinated plastic bags, gloves and blood bags has been phased out within two years starting from March 2016.
- Pre-treatment of the laboratory waste, microbiological waste, blood samples and blood bags through disinfection or sterilisation on-site in the manner prescribed by the World Health Organization (WHO) or by the National AIDS Control Organisation (NACO).
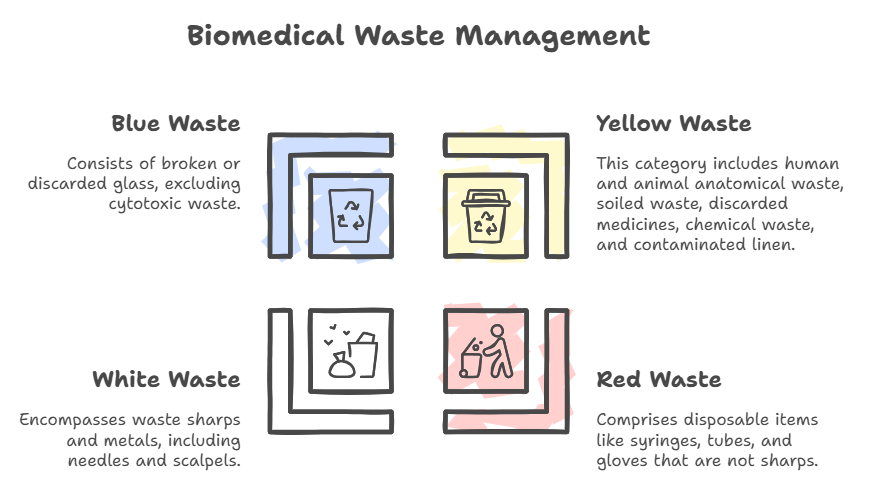
- Bio-medical waste has been classified into 4 categories to improve the segregation of waste at source.
- Hazardous and other wastes (Management and Transboundary Movement) Rules, 2016.
- Basel Convention: The Basel Convention, adopted in 1989, and effective from 1992, is an international treaty aiming to reduce trans-boundary movements of hazardous wastes.
- India is a member of the Basel Convention but has not ratified the Basel ban amendment.
What is the Influence of HIV/AIDS on Policies?
- The late 1980s saw a global crisis with the "Syringe Tide" in the US, leading to stricter regulations like the Medical Waste Tracking Act of 1988.
- In India, significant steps began with the introduction of the Biomedical Waste (Management and Handling) Rules in 1998, recognizing hospital waste as hazardous.
- The Supreme Court's ruling in Dr. B.L. Wadehra vs. Union of India (1996) highlighted pollution concerns, influencing regulatory frameworks.
- SC said that owners and occupiers of premises in Delhi without a latrine or urinal connected to a municipal drain must collect and remove filth to designated depots, following prescribed guidelines.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. As per the Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016 in India, which one of the following statements is correct? (2019)
(a) Waste generator has to segregate waste into five categories.
(b) The Rules are applicable to notified urban local bodies, notified towns and all industrial townships only
(c) The Rules provide for exact and elaborate criteria for the identification of sites for landfills and waste processing facilities.
(d) It is mandatory on the part of the waste generator that the waste generated in one district cannot be moved to another district.
Ans: (c)